Each employee of the "Blake Techologies" company uses a special messaging app "Blake Messenger". All the stuff likes this app and uses it constantly. However, some important futures are missing. For example, many users want to be able to search through the message history. It was already announced that the new feature will appear in the nearest update, when developers faced some troubles that only you may help them to solve.
All the messages are represented as a strings consisting of only lowercase English letters. In order to reduce the network load strings are represented in the special compressed form. Compression algorithm works as follows: string is represented as a concatenation of n blocks, each block containing only equal characters. One block may be described as a pair (li, ci), where li is the length of the i-th block and ci is the corresponding letter. Thus, the string s may be written as the sequence of pairs  .
.
Your task is to write the program, that given two compressed string t and s finds all occurrences of s in t. Developers know that there may be many such occurrences, so they only ask you to find the number of them. Note that p is the starting position of some occurrence of s int if and only if tptp + 1...tp + |s| - 1 = s, where ti is the i-th character of string t.
Note that the way to represent the string in compressed form may not be unique. For example string "aaaa" may be given as 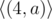 ,
,  ,
, 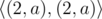 ...
...
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of blocks in the strings t and s, respectively.
The second line contains the descriptions of n parts of string t in the format "li-ci" (1 ≤ li ≤ 1 000 000) — the length of the i-th part and the corresponding lowercase English letter.
The second line contains the descriptions of m parts of string s in the format "li-ci" (1 ≤ li ≤ 1 000 000) — the length of the i-th part and the corresponding lowercase English letter.
Print a single integer — the number of occurrences of s in t.
5 3
3-a 2-b 4-c 3-a 2-c
2-a 2-b 1-c
1
6 1
3-a 6-b 7-a 4-c 8-e 2-a
3-a
6
5 5
1-h 1-e 1-l 1-l 1-o
1-w 1-o 1-r 1-l 1-d
0
In the first sample, t = "aaabbccccaaacc", and string s = "aabbc". The only occurrence of string s in string t starts at position p = 2.
In the second sample, t = "aaabbbbbbaaaaaaacccceeeeeeeeaa", and s = "aaa". The occurrences of s in t start at positions p = 1,p = 10, p = 11, p = 12, p = 13 and p = 14.

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++) #define MS0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) #define RI(x) scanf("%d",&x) #define RII(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y) #define RIII(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z) #define RS(s) scanf("%s",s) #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 #define lowbit(x) x&-x #define key_val ch[ch[rt][1]][0] using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn=1000100; const int INF=1e9+10; const double EPS=1e-10; const double Pi=acos(-1.0); int n,m; ll a[maxn];char s[maxn]; ll b[maxn];char t[maxn]; char ss[20],tt[20]; int f[maxn]; void getNext() { f[2]=2;f[3]=2; REP(i,3,m-1){ int j=f[i]; while(j!=2&&(b[i]!=b[j]||t[i]!=t[j])) j=f[j]; f[i+1]=(b[i]==b[j]&&t[i]==t[j])?j+1:2; } //REP(i,2,m-1) cout<<f[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; } void kmp() { getNext(); int j=2; ll res=0; REP(i,2,n-1){ while(j!=2&&(a[i]!=b[j]||s[i]!=t[j])) j=f[j]; if(s[i]==t[j]&&a[i]==b[j]) j++; if(j==m){ int r=i+1,l=r-m+1; if(1<=l&&r<=n&&s[l]==t[1]&&s[r]==t[m]){ if(a[l]>=b[1]&&a[r]>=b[m]) res++; } j=f[j]; } } cout<<res<<endl; } void solve1() { ll res=0; REP(i,1,n){ if(s[i]==t[1]&&a[i]>=b[1]){ res+=a[i]+1-b[1]; } } cout<<res<<endl; } void solve2() { ll res=0; REP(i,1,n){ int tag=1; REP(j,1,m){ if(s[i+j-1]!=t[j]||a[i+j-1]<b[j]) tag=0; } if(tag) res++; } cout<<res<<endl; } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); #endif while(~RII(n,m)){ REP(i,1,n) scanf("%I64d-%s",&a[i],ss),s[i]=ss[0]; REP(i,1,m) scanf("%I64d-%s",&b[i],tt),t[i]=tt[0]; int sn=1,tn=1; REP(i,2,n){ if(s[i]==s[i-1]) a[sn]+=a[i]; else a[++sn]=a[i],s[sn]=s[i]; } REP(i,2,m){ if(t[i]==t[i-1]) b[tn]+=b[i]; else b[++tn]=b[i],t[tn]=t[i]; } n=sn;m=tn; if(m>=3) kmp(); else if(m==1) solve1(); else solve2(); } return 0; }
