谈到TreeSet的特点,估计大家脑海里想到的都是:有序,不可重复,红黑树,基于Treemap实现,自定义排序等特点。这篇博客帮助大家从源码梳理下TreeSet的知识点。
1.构造函数
TreeSet提供了四种构造器
- TreeSet()
- TreeSet(Collection< ? extends E> c)
- TreeSet(Comparator< ? super E> comparator)
- TreeSet(SortedSet< E > s)
四种构造器在底层都调用了同一个方法。以无参构造函数为例。[1]处的this方法最终调用的是[2]的方法,其中四个构造器的传参都被TreeMap封装了一层。
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); //[1]
}
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {//[2]
this.m = m;
}
2.增
TreeSet在添加元素时,会把元素放入TreeMap中的key上来确保元素的唯一性,并让其value指向一个空对象。TreeSet#add()方法会调用TreeMap#put()方法添加元素,添加元素时,从树的根节点开始遍历直到找到新增元素的parent节点,添加进去。通过TreeMap的源码可以看出维护的是一个红黑树数据结构。
PS:由于TreeSet的实例化时都会调用TreeMap的无参构造函数,此时
TreeMap#comparator=null;
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// Use linear-time version if applicable
if (m.size()==0 && c.size() > 0 &&
c instanceof SortedSet && //是否是SortedSet类或其子类
m instanceof TreeMap) {
SortedSet<? extends E> set = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
TreeMap<E,Object> map = (TreeMap<E, Object>) m;
Comparator<?> cc = set.comparator();
Comparator<? super E> mc = map.comparator();
if (cc==mc || (cc != null && cc.equals(mc))) {//[3]
map.addAllForTreeSet(set, PRESENT);
return true;
}
}
return super.addAll(c); // 不是SortedSet子类,就是Collection子类
}
3.删
TreeSet中提供了两个和删除相关的方法。
TreeSet#clear()复用了TreeMap#clear()方法,把root节点置为null,size置为0;
通过TreeSet#remove()移除特定元素时,TreeSet首先先遍历出该元素,然后将红黑树中的元素置为null,重新平衡红黑树。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
/**
* Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.
*/
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
4.比较器
TreeSet中有两种排序,一个是自然排序,一个是重写compareTo()方法自定义排序。
自然排序可以参考Integer,String等类中的实现。其顺序也是我们常见的“1,2,3,4”,“a,b,c,d”。假如我们想让Student对象中String类型的字段倒序输出呢
@Data
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
String name;
/**
* 这里的参数o,其实是TreeMap中维护的根节点
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
System.out.println("name:"+name+",参数:"+o.getName());
int i = this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
return i==0?0:-i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> set = new TreeSet<>();
Student a = new Student();
a.setName("a");
Student b = new Student();
b.setName("b");
Student c = new Student();
c.setName("c");
Student d = new Student();
d.setName("d");
Student e = new Student();
e.setName("e");
Student f = new Student();
f.setName("f");
set.add(a);
set.add(c);
set.add(e);
set.add(b);
set.add(d);
set.add(f);
for (Student str: set) {
System.out.print(str.getName());
}
}
其结果如下:
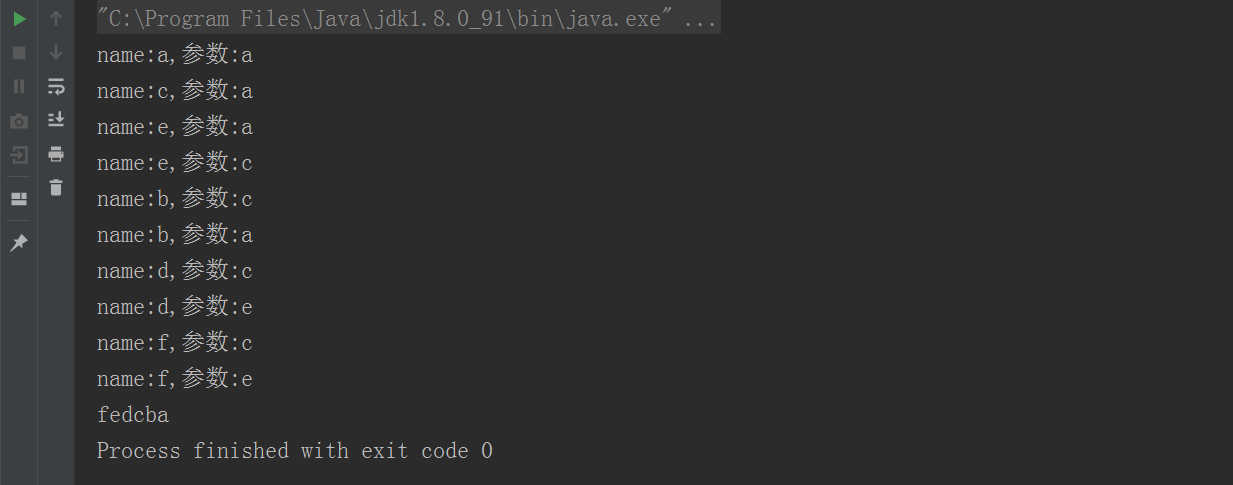
从打印的日志可以看出,每次插入新的元素,都会从根节点开始遍历比较。当然TreeSet中也提供了我们倒序输出的方法。有兴趣可以自己试验下。
- descendingSet()
- descendingIterator()
总结
TreeSet是通过TreeMap实现的一个有序的、不可重复的集合,底层维护的是红黑树结构。当TreeSet的泛型对象不是java的基本类型的包装类时,对象需要重写Comparable#compareTo()方法