首先需要先知道一个概念: 二叉搜索树 —— 左孩子比父亲小,右孩子大于等于父亲
一、Splay的旋转
旋转是Splay的精髓也是至关重要的操作
旋转也分为左旋、右旋
这里是直接概括了所有旋转的规律:
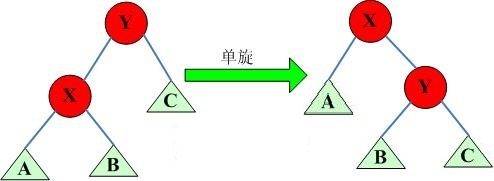
我们定义一个结点与他父亲的关系是 x ,那么在旋转时,他的父亲成为了他的 !x 儿子,并且那个上文中所说的“多余结点”,同时也是当前节点的 !x 儿子,但在旋转之后需要成为当前节点的“前”父节点的 x 儿子。
我们可以先看看这部分的代码
inline bool get_which(int x) { return sons[f[x]][1] == x; } inline void update(int x) { if (x) { sub_siz[x] = cnt[x]; if (sons[x][0]) sub_siz[x] += sub_siz[sons[x][0]]; if (sons[x][1]) sub_siz[x] += sub_siz[sons[x][1]]; } } inline void rotate(int x) { int father = f[x],grand_father = f[father],which_son = get_which(x); sons[father][which_son] = sons[x][which_son^1]; // 修改"前父亲"的孩子 f[sons[father][which_son]] = father; // 修改孩子的父亲 sons[x][which_son^1] = father; // 修改 x 的孩子 f[father] = x; // 修改"前父亲"的父亲 f[x] = grand_father; // 修改当前 x 的父亲 if (grand_father) sons[grand_father][sons[grand_father][1] == father] = x; update(father); update(x); }
Spaly操作:
只需要记住一句话:我们在链很长的时候,每次执行先旋父节点再旋当前节点的操作,一次总操作之后,这条链的深度会减半。
inline void splay(int x) { for (int fa;fa=f[x];rotate(x)) if (f[fa]) rotate((get_which(x)==get_which(fa))?fa:x); root=x; }
我们在进行与点有关的操作的时候都需要进行Splay,借此来维护树的随机性
模版:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <string.h> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <stack> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <math.h> #include <cstdio> #include <iomanip> #include <time.h> #include <bitset> #include <cmath> #include <sstream> #define LL long long #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define ls nod<<1 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 const double eps = 1e-10; const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;; const LL mod = 1e9 + 7; int sgn(double a){return a < -eps ? -1 : a < eps ? 0 : 1;} using namespace std; int f[maxn],cnt[maxn],val[maxn],sons[maxn][2],sub_siz[maxn]; int whole_siz,root; inline void S_clear(int x) { sons[x][0] = sons[x][1] = sub_siz[x] = cnt[x] = val[x] = 0; } inline bool get_which(int x) { return sons[f[x]][1] == x; } inline void update(int x) { if (x) { sub_siz[x] = cnt[x]; if (sons[x][0]) sub_siz[x] += sub_siz[sons[x][0]]; if (sons[x][1]) sub_siz[x] += sub_siz[sons[x][1]]; } } inline void rotate(int x) { int father = f[x],grand_father = f[father],which_son = get_which(x); sons[father][which_son] = sons[x][which_son^1]; f[sons[father][which_son]] = father; sons[x][which_son^1] = father; f[father] = x; f[x] = grand_father; if (grand_father) sons[grand_father][sons[grand_father][1] == father] = x; update(father); update(x); } inline void splay(int x) { for (int fa;fa=f[x];rotate(x)) if (f[fa]) rotate((get_which(x)==get_which(fa))?fa:x); root=x; } inline void ins(int x) { if (!root) { whole_siz++; sons[whole_siz][0] = sons[whole_siz][1] = f[whole_siz] = 0; root = whole_siz; sub_siz[whole_siz] = cnt[whole_siz] = 1; val[whole_siz] = x; return ; } int now = root,fa = 0; while (1) { if (x == val[now]) { cnt[now]++; update(now); update(fa); splay(now); break; } fa = now; now = sons[now][val[now]<x]; if (!now) { whole_siz++; sons[whole_siz][0] = sons[whole_siz][1] = 0; f[whole_siz] = fa; sub_siz[whole_siz] = cnt[whole_siz] = 1; sons[fa][val[fa]<x] = whole_siz; val[whole_siz] = x; update(fa); splay(whole_siz); break; } } } inline int find_num(int x) { int now = root; while (1) { if (sons[now][0] && x <= sub_siz[sons[now][0]]) now = sons[now][0]; else { int tmp = (sons[now][0]?sub_siz[sons[now][0]]:0)+cnt[now]; if (x <= tmp) return val[now]; x -= tmp; now = sons[now][1]; } } } inline int find_rank(int x) { int now = root,ans = 0; while (1) { if (x < val[now]) now = sons[now][0]; else { ans += (sons[now][0]?sub_siz[sons[now][0]]:0); if (x == val[now]) { splay(now); return ans+1; } ans += cnt[now]; now = sons[now][1]; } } } inline int find_pre() { int now = sons[root][0]; while (sons[now][1]) now = sons[now][1]; return now; } inline int find_suffix() { int now = sons[root][1]; while (sons[now][0]) now = sons[now][0]; return now; } inline void my_delete(int x) { int hhh = find_rank(x); if (cnt[root] > 1) { cnt[root]--; update(root); return ; } if (!sons[root][0] && !sons[root][1]) { S_clear(root); root = 0; whole_siz = 0; return ; } if (!sons[root][0]) { int old_root = root; root = sons[root][1]; f[root] = 0; S_clear(old_root); return ; } else if (!sons[root][1]) { int old_root = root; root = sons[root][0]; f[root] = 0; S_clear(old_root); return ; } int left_max = find_pre(),old_root = root; splay(left_max); sons[root][1] = sons[old_root][1]; f[sons[old_root][1]] = root; S_clear(old_root); update(root); } int main(){ int m,num,be_dealt; cin >> m; for(int i = 1;i <= m;i++){ cin >> num; cin >> be_dealt; switch(num) { case 1:ins(be_dealt);break; case 2:my_delete(be_dealt);break; case 3:printf("%d ",find_rank(be_dealt));break; case 4:printf("%d ",find_num(be_dealt));break; case 5:ins(be_dealt);printf("%d ",val[find_pre()]);my_delete(be_dealt);break; case 6:ins(be_dealt);printf("%d ",val[find_suffix()]);my_delete(be_dealt);break; } } return 0; }
参考博客:https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/pks-LOVING/more-senior-data-structure-te-bie-qian-di-qian-tan-splay