如何初始化父类成员?
父类构造函数和子类构造函数有什么关系?
子类中可以定义构造函数
子类构造函数
-必须对继承而来的成员进行初始化
直接通过初始化列表或者赋值的方式进行初始化
调用父类构造函数进行初始化
父类构造函数在子类中的调用方式
-默认调用
适用于无参构造函数和使用默认参数的构造函数
-显示调用
通过初始化列表进行调用
适用于所有父类构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
public:
Parent(string s)
{
cout << "Parent(string s)" << endl;
}
};
class Child: public Parent
{
public:
Child() //如果没有指定调用父类的哪个构造函数,它将采用默认的方式调用,即调用父类的无参构造函数或者使用默认参数的构造函数。很不幸
//因为在父类中已经定义了带有参数的构造函数,那么编译器就不会提供默认的构造函数了,因此在这个地方没有可用的构造函数可以调用,因此出错。
{
cout << "Child()" << endl;
}
Child(string s) //如果没有指定调用父类的哪个构造函数,它将采用默认的方式调用,即调用父类的无参构造函数或者使用默认参数的构造函数。很不幸
{ // //因为在父类中已经定义了带有参数的构造函数,那么编译器就不会提供默认的构造函数了,因此在这个地方没有可用的构造函数可以调用,因此出错。
cout << "Child(String s)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Child c; //出错,没有可用的父类的构造函数可以调用
Child cc("he");//出错,没有可用的父类构造函数可以调用。
return 0;
}
这个程序说明,如果不显示的调用父类的构造函数,它采用默认调用方式,即调用无参构造函数和使用默认参数的构造函数
可以在父类中添加无参构造函数
class Parent
{
public:
Parent()
{
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
}
Parent(string s)
{
cout << "Parent(string s)" << endl;
}
};
这个地方就是隐式的调用,分析:
Child c-------->调用Parent() --------> Child()
Child cc("he") ------>调用Parent() ------>Child(string s)
显示调用,代码示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
public:
Parent()
{
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
}
Parent(string s)
{
cout << "Parent(string s)" << endl;
}
};
class Child: public Parent
{
public:
Child()
{
cout << "Child()" << endl;
}
Child(string s):Parent(s)
{
cout << "Child(String s)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Child cc("he");
return 0;
}
Child cc("he")-------------->Parent(string s)--------->Child (string s)
上述程序说明:
子对象的构造规则:
-子类对象在创建时首先调用父类的构造函数
-先执行父类构造函数再执行子类构造函数
-父类构造函数可以被隐式调用或者显示调用
对于面向对象的程序,常出现的两种关系:组合和继承
对象创建时构造函数的调用顺序
1.调用父类的构造函数
2. 调用成员变量的构造函数
3. 调用类自身的构造函数
口诀心法:
先父母,后客人,再自己
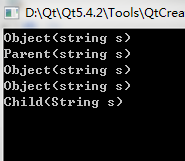
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
public:
Object(string s)
{
cout << "Object(string s) " <<endl;
}
};
class Parent : public Object
{
public:
Parent(): Object("default")
{
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
}
Parent(string s):Object(s)
{
cout << "Parent(string s)" << endl;
}
};
class Child: public Parent
{
private:
Object mO1;
Object mO2;
public:
Child():mO1("mo1"),mO2("mo2")
{
cout << "Child()" << endl;
}
Child(string s):Parent(s),mO1(s),mO2(s)
{
cout << "Child(String s)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Child cc("he");
return 0;
}
子类对象的析构
析构函数的调用顺序与构造函数相反
1.执行自身的析构函数
2.执行成员变量的析构函数
3.执行父类的析构函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Object
{
private:
string ms;
public:
Object(string s)
{
cout << "Object(string s) " <<endl;
ms = s;
}
~Object()
{
cout << "~Object(ms)" << ms << endl;
}
};
class Parent : public Object
{
private:
string ms;
public:
Parent(): Object("default")
{
cout << "Parent()" << endl;
ms = "defalut";
}
Parent(string s):Object(s)
{
cout << "Parent(string s)" << endl;
ms = s;
}
~Parent()
{
cout << "~Parent(ms)" << endl;
}
};
class Child: public Parent
{
private:
Object mO1;
Object mO2;
string ms;
public:
Child():mO1("mo1"),mO2("mo2")
{
cout << "Child()" << endl;
ms = "default";
}
Child(string s):Parent(s),mO1(s),mO2(s)
{
cout << "Child(String s)" << endl;
ms = s;
}
~Child()
{
cout << "~Child(ms)" << ms << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Child cc("he");
return 0;
}
子类对象在创建时需要调用父类构造函数进行初始化
先执行父类构造函数然后执行成员的构造函数
父类构造函数显示调用需要在初始化列表中进行
子类对象在销毁时需要调用父类析构函数进行清理
析构顺序与构造顺序对称相反