1、this关键字
构造方法之间的调用用this关键字
构造方法调用格式:this(参数列表);
构造方法调用举例:
创建一个Person类,写一个空参构造方法,让这个空参构造方法调用有参构造方法,然后测试
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
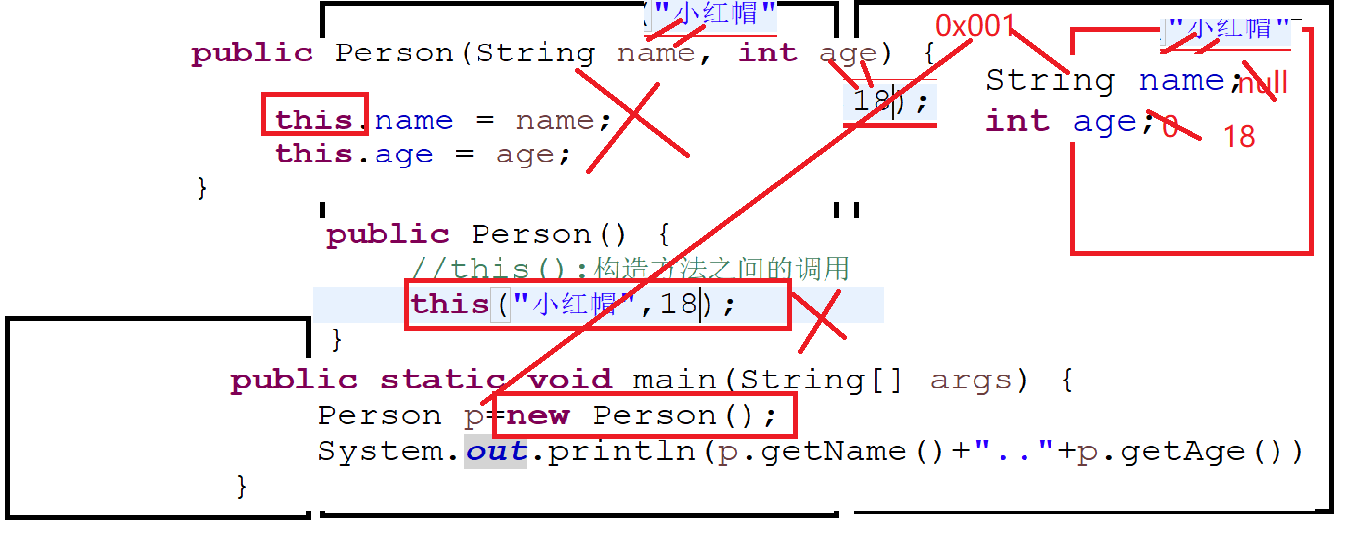
public Person() {
this("小红帽",18);
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean get(Person p){
return p.age==this.age;
}
}
上述代码中空参构造Person()调用了有参构造Person(String name,int age);最后一个get方法是用于比较两个人的年龄是否相等,返回值是布尔值
创建一个测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person();
System.out.println(p.getName()+"..."+p.getAge());
Person p1=new Person();
p1.setAge(18);
p1.setName("小红");
System.out.println(p.get(p1));
}
运行结果为:
小红帽...18
true
图解:
2、super关键字
super,调用父类的构造方法
创建一个Student类继承这个person类
public class Student extends Person{
public Student(){
super("狗子",18);
}
}
创建一个测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student s=new Student();
System.out.println(s.getName()+"..."+s.getAge());
}
运行结果
狗子...18
注意事项:
this关键字,用于区分成员变量和局部变量之间的重名问题,this代表的是对象,谁调用我,this就代表哪个对象,调用时,必须出现在在构造方法的第一行,原因是初始化内容要先执行
super关键字,super 用于调用父类中的构造方法,类中默认的构造方法都有一个默认的super,如果隐式的super,在父类中没有对用的空参构造,则必须通过this或者super显示调用构造方法
如果子类构造方法中第一行出现了this调用本类构造方法,则该构造方法的隐式super调用父类构造方法的语句就没有了,因为this要在第一行,初始化内容要先执行
父类构造方法中也是有隐式定义的super。只要是构造方法每个构造方法的第一行都是有一个隐式的super
应用举例
创建一个Person类
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
创建一个student类继承这个person类
public class Student extends Person {
public Student(String name,int age){
super(name,age);
}
}
创建一个woker类继承person类
public class Woker extends Person{
public Woker() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Woker(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
创建一个测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student a=new Student("张三",18);
Woker w=new Woker("李四",20);
System.out.println(a.getName()+"..."+a.getAge());
System.out.println(w.getName()+"..."+w.getAge());
}