ServletContext对象中封装的真个web项目中的信息,一个web项目中只有一个ServletContext对象,但可以有多个servlet对象
ServletContext对象的生命周期 创建: 服务器启动或 发布web应用(前提,服务器启动状态) 销毁:web应用被卸载(服务器关闭,移除该web应用)
怎样获得ServletContext对象
之前是在servlet类中的init方法中通过config.getServletContext();得到一个对象
但是通过查阅API他们的继承关系 直接getServletContext()返回一个ServletContext对象。
作用
(1)获得web应用中任何资源的绝对路径
代码展示
public class Servlet03 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().write("hello dandan...");
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context=getServletContext();
//获取服务器上资源的绝对路径
String pathA=context.getRealPath("a.txt");
String pathB=context.getRealPath("WEB-INF/b.txt");
String pathC=context.getRealPath("WEB-INF/classes/com/oracle/web/c.txt");
System.out.println(pathA);
System.out.println(pathB);
System.out.println(pathC);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
当发出请求


(2)ServletContext是一个域对象
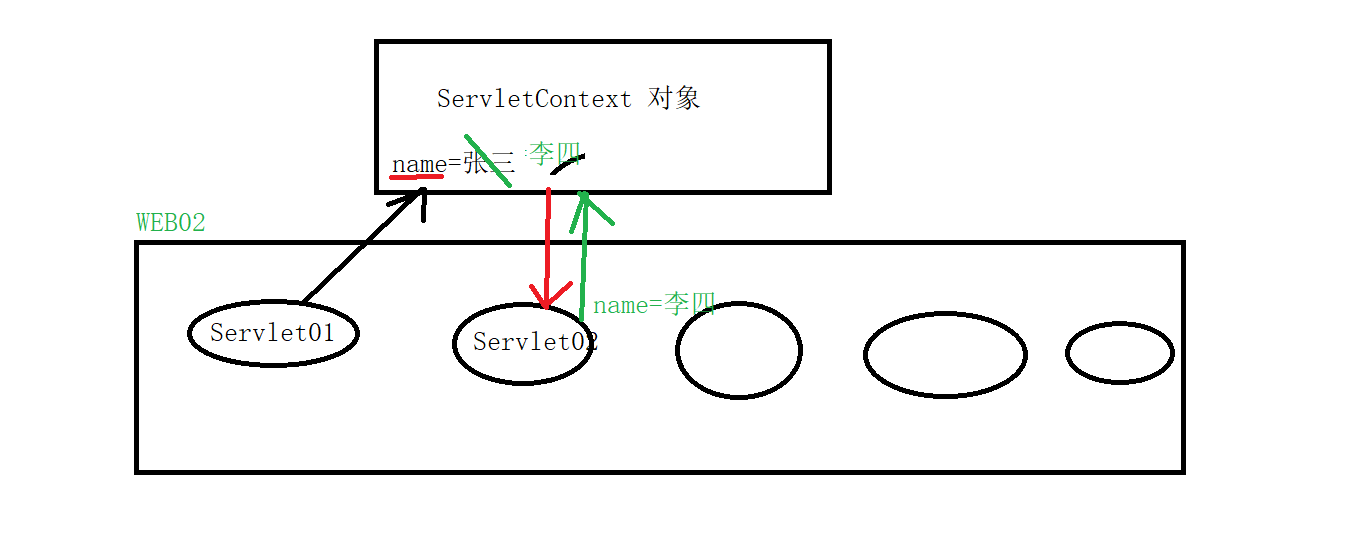
ServletContext域对象的作用范围:整个web应用(所有的web资源都可以随意向 servletcontext域中存取数据,数据可以共享)
可以存取数据,可以实现从Servlet01中写入数据,从Servlet02中读取数据
数据存储的方式还是以键值对的方式存储,同时同一个键值对的key值相同就value值就会被覆盖掉
图解
域对象的通用的方法(所有域对象通用方法)
setAtrribute(String name,Object obj);
getAttribute(String name)
removeAttribute(String name);
代码展示 从Servlet01中写入数据,从Servlet02中读取数据
public class MyServlet01 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().write("hello dandan...");
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context=getServletContext();
//域对象存值
context.setAttribute("name", "张三");
context.setAttribute("password", "123123");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
public class MyServlet02 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context=getServletContext();
//域对象取值
System.out.println(context.getAttribute("name"));
System.out.println(context.getAttribute("password"));
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}