1.为什么使用面向对象?
现实世界是由什么组成的,世界由对象组成
面向对象的思想符合人类思维习惯,面向对象的思想描述面向对象的世界
2.软件出现的目的
n用计算机的语言描述现实世界
n用计算机解决现实世界的问题
3.面向对象设计和开发程序的好处
n交流更加流畅
n提高设计和开发效率
4.一个现实世界的问题
宠物——现实世界的对象
如何在计算机中描述它们?
从现实中抽象出类分三步:1. 找出它的种类2. 找出它的属性3. 找出它的行为
第一步:发现类(根据“对象”抽象出“类”)
class Dog {
}
第二步:发现类的属性(只放和业务相关的属性)
class Dog {
String name = "旺财"; // 昵称
int health = 100; // 健康值
int love = 0; // 亲密度
String strain = "拉布拉多犬"; // 品种
}
第三步:发现类的方法
class Dog {
String name = "旺财"; // 昵称
int health = 100; // 健康值
int love = 0; // 亲密度
String strain = "拉布拉多犬"; // 品种
/* 输出狗的信息 */
public void print() {
// 输出狗信息的代码
}
5.类图
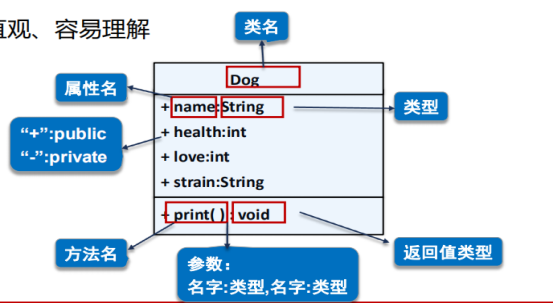
举例:实现宠物领养
public class Dog {
// 狗狗实体类
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String strain;
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ strain);
}
}
public class Penguin {
// 企鹅实体类
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String gender;
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ gender);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Adopt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = null;
Dog dog = null;
Penguin penguin = null;
int choice = 0;
String answer = "y";
while (answer.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("请输入领养宠物的名字");
name = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入您要领养宠物的类型;1-狗;2-企鹅");
choice = input.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
// 领养狗
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入狗狗的种类,1-拉布拉多;2-哈士奇");
choice = input.nextInt();
dog = new Dog(); // 创建新的空间
dog.name = name;
if (choice == 1) {
dog.strain = "拉布拉多";
} else if (choice == 2) {
dog.strain = "哈士奇";
}
dog.love = 60;
dog.health = 60;*/
break;
case 2:
// 领养企鹅
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入企鹅的性别;1-Q仔;2-Q妹");
choice = input.nextInt();
penguin = new Penguin();
penguin.name = name;
if (choice == 1) {
penguin.gender = "Q" + "仔";
} else if (choice == 2) {
penguin.gender = "Q" + "妹";
}
penguin.love = 60;
penguin.health = 60;
break;
default:
System.out.println("对不起,输入有误,请重新输入");
break;
}
System.out.println("还要继续领养吗? y-继续;n-退出");
answer = input.next();
}
// 输出
if (dog != null) {
dog.print();
}
if (penguin != null) {
penguin.print();
}
}
}
心得:根据现实世界的信息,用程序的角度去描述出来
因为Dog dog = null;为空,只做了一个房间,并没有赋值;所以使用dog.什么的时候需要new一个对象(不能给房间直接赋值)
如何查看领养了那个宠物,查看那个房间没有空着。则代表领养到了...
如果想重复领养,目前达不到,存放企鹅和狗狗的只有一个房间。多次领养无意义...
列表可以帮助实现
6.整理代码快捷键
Ctrl+shift+f
7.如何修改快捷键
Windows--->preference-->查找输入keys--->进行修改
8.封装-----构造方法
上述对宠物的初始化不方便,如果狗狗有100个属性则需要写100次dog.xx;且每次初始化dog,每次都需要重复写那么多。比较繁琐,应符合写少做多。
对象初始化
Penguin pgn=new Penguin();
pgn.name = "qq";
pgn.sex = "Q仔";
能否在创建对象的同时就完成赋值?构造方法(new完直接赋值)
构造方法是提前把属性写好
举例:无参构造方法
public class Dog {
// dog
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String strain;
//构造方法
//构造方法没有返回值
public Dog(){
name="旺仔";
health=60;
love=90;
strain="中华田园犬";
}
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ strain);
}
}
public class Penguin {
// 企鹅
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String gender;
//构造方法
//构造方法没有返回值
public Penguin(){
name="QQ";
health=60;
love=60;
gender="Q仔";
}
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ gender);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Adopt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = null;
Dog dog = null;
Penguin penguin = null;
int choice = 0;
String answer = "y";
while (answer.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("请输入领养宠物的名字");
name = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入您要领养宠物的类型;1-狗;2-企鹅");
choice = input.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
// 领养狗
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入狗狗的种类,1-拉布拉多;2-哈士奇");
choice = input.nextInt();
dog = new Dog(); // 创建新的空间
break;
case 2:
// 领养企鹅
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入企鹅的性别;1-Q仔;2-Q妹");
choice = input.nextInt();
penguin = new Penguin();
break;
default:
System.out.println("对不起,输入有误,请重新输入");
break;
}
System.out.println("还要继续领养吗? y-继续;n-退出");
answer = input.next();
}
// 输出
if (dog != null) {
dog.print();
}
if (penguin != null) {
penguin.print();
}
}
}
9.无参类型构造方法
系统提供默认无参构造方法
语法:
访问修饰符 构造方法名 ( ) {
//初始化代码
}
示例:
public Penguin() {
}
10. 带参数的构造方法
所谓没有参数的构造方法就是指,需要自己做一个对象,不是按照意愿造出来的,而是系统提供什么就必须安要求来...
举例:
public class Dog {
// dog
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String strain;
// 带参数构造方法
// this-当前对象
public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){
this.name=name;
this.health=health;
this.love=love;
this.strain=strain;
}
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ strain);
}
}
public class DogTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 带参数构造方法
Dog dog=new Dog("阿福",100,20,"沙皮");
dog.print();
}
}
心得:
带参数的构造方法可以按照自己的心意去做,所以需要输入一些东西,有什么属性输什么属性
需要把参数的信息挨个赋值给类的属性,利用this
This.name指的是public String name,然后把传过来的参数 给类的成员变量this.name=name
当没有无参数的方法时main不能添加Dog dog=new Dog();
11.带参数构造方法常见错误
举例:
public class Dog {
// dog
// field
public String name;
public int health;
public int love;
public String strain;
// 带参数构造方法
// this-当前对象
public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){
this.name=name;
this.health=health;
this.love=love;
this.strain=strain;
}
// methods
public void print() {
System.out.println("姓名" + name + "健康值" + health + "可爱值" + love + "种类"
+ strain);
}
}
public class DogTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog=new Dog();
dog.print();
}
}
错在哪里?
1.前面一个类,后面一个测试类
测试类里面调用的是不带参数的构造方法,但本类里并没有提供不带参数的构造方法,故出错
2.当无参方法和有参数方法同时出现时,调用无参方法也会成功
12.不带参数的构造方法有俩个特点
1.系统默认提供无参构造方法
2.当系统还有带参数的构造方法时,系统不在提供默认的无参构造方法
补充:构造方法和一般方法区别
1)到目前为止,学习两种方法,分别为构造方法和一般方法,那么他们之间有什么异同呢?
构造方法在对象创建时就执行了,而且只执行一次。(类名与构造方法名相同、无返回值)
一般方法是在对象创建后,需要使用时才被对象调用,并可以被多次调用。(类名与方法相同或不同都可以、返回值为空或有返回值)
2)有了构造方法之后可以对对象的属性进行初始化,那么还需要对应的set和get方法吗?
需要相应的set和get方法,因为对象在创建之后需要修改和访问相应的属性值时,在这时只能通过set或者get方法来操作。
13.构造方法重载
变量不能同名、类不能同名、为什么方法可以同名?因为方法的重载
举例:
public class Demo {
/*方法的重载 overload
* 1-两个方法 方法名相同
* 2-参数不同
* 3-与返回值 访问控制符无关
* */
public void print(){
System.out.println("打印");
}
public String print(int d){
System.out.println("打印");
return null;
}
}
14.构造方法重载的调用
pgn = new Penguin();
pgn.print();
pgn = new Penguin("美美", 80, 20, "Q仔");
pgn.print();
public Penguin () {
name = "qq";
love = 20;
sex = "Q仔";
}
public Penguin (String name,int health,int love,String sex ) {
this.name = name;
this.health = health;
this.love = love;
this.sex = sex;
}
15.static关键字
可以修饰成员变量、方法
修饰成员变量,通过类名直接访问成员变量
可以绕过new,直接拿类来访问不用拿对象来访问它。
无论修饰成员变量,还是成员方法static都写在类型的前面;在使用的时候不需要new对象
1-修饰成员变量 类名.fileldName
2-修饰成员方法 类名.methodName
3-修饰静态代码块
举例:变量
package demo1;
public class Penguin {
// static
//属性
public static String MALE="Q仔";
public static String FEMALE="Q妹";
}
package demo1;
public class PenguinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//属性
System.out.println(Penguin .MALE);
System.out.println(Penguin.FEMALE);
}
}
心得:一般用static修饰的都大写
不用new和对象直接把属性使用
举例:方法
package demo1;
public class Penguin {
/*//方法
public static void test(){
System.out.println("test static method");
}
}
package demo1;
public class PenguinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法
Penguin.test();
}
}
举例:静态代码块
package demo1;
public class Penguin {
//无参数
public Penguin(){
System.out.println("无参...");
}
//静态代码块
//优先于构造方法去执行
static{
System.out.println("代码块");
System.out.println("静态代码块");
System.out.println("************");
}
}
package demo1;
public class PenguinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Penguin a=new Penguin();
}
}
16.为什么要使用封装
属性随意访问,不合理的赋值;如何解决,使用封装
举例:
package demo4;
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int love;
private int health;
private String strain;
/*
*
* set和get方法
*
* */
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getLove() {
return love;
}
public void setLove(int love) {
if(love<0||love>100) {
System.out.println("亲密度只能在0-100之间");
this.love=60;
}else{
this.love = love;
}
}
public int getHealth() {
return health;
}
public void setHealth(int health) {
if(health<0||health>100) {
System.out.println("健康值只能在0-100之间");
this.health=60;
}else{
this.health = health;
}
}
public String getStrain() {
return strain;
}
public void setStrain(String strain) {
this.strain = strain;
}
/*
*
* 带参数的构造方法
*
* */
public Dog(String name, int love, int health, String strain) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.love = love;
this.health = health;
this.strain = strain;
}
/*
*
* 不带参数的构造方法
*
*
* */
public Dog() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/*
*
* toString() 自动生成
*
* */
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [name=" + name + ", love=" + love + ", health=" + health
+ ", strain=" + strain + "]";
}
}
package demo4;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Adopt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = null;
Dog dog = null;
Penguin penguin = null;
int choice = 0;
String answer = "y";
while (answer.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("请输入领养宠物的名字");
name = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入您要领养宠物的类型;1-狗;2-企鹅");
choice = input.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
// 领养狗
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入狗狗的种类,1-拉布拉多;2-哈士奇");
dog = new Dog(); // 创建新的空间
choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) {
dog.setStrain("拉布拉多"); 调用set方法
} else if (choice == 2) {
dog.setStrain("哈士奇");
}
dog.setName(name);
System.out.println("请输入狗狗的健康值");
dog.setHealth(input.nextInt());
System.out.println("请输入狗狗的可爱值");
dog.setLove(input.nextInt());
break;
case 2:
// 领养企鹅
answer = "n";
System.out.println("请输入企鹅的性别;1-Q仔;2-Q妹");
choice = input.nextInt();
penguin = new Penguin();
if (choice == 1) {
penguin.setGender(Penguin.MALE);
} else if (choice == 2) {
penguin.setGender(Penguin.FEMALE);
}
penguin.setName(name);
System.out.println("请输入企鹅的健康值");
penguin.setHealth(input.nextInt());
System.out.println("请输入企鹅的可爱值");
penguin.setLove(input.nextInt());
break;
default:
System.out.println("对不起,输入有误,请重新输入");
break;
}
System.out.println("还要继续领养吗? y-继续;n-退出");
answer = input.next();
}
// 输出
if (dog != null) {
System.out.println(dog.toString());
} else if (penguin != null) {
System.out.println(penguin.toString());
}
}
}
心得:健康值属性不能被赋值-100,不能修改。想要实现不被修改,在测试类里随意添加这样是不合理的。不允许修改,故需要封装
封装分二步:1-将属性的访问符改为private
2-set 设置 修改
3-get 读 获取
做限制可以在set方法里做限制
Penguin.MALE 值被固定,不被修改
17.快捷键
Alt+shift+s
Get 、set、无参方法、带参方法可以帮助生成
但是自定义的方法和属性需要自己写
18.什么是封装
封装:将类的某些信息隐藏在类内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问
19. 如何使用封装
修改属性的可见性
1在getter/setter方法中加入属性控制语句(设为private)
2创建公有的getter/setter方法(用于属性的读写)
2在getter/setter方法中加入属性控制语句(对属性值的合法性进行判断)
20. this的用法
关键字this用来指向当前实例对象(内存里正在运行的哪个实例对象),它的另一作用是用来区分对象的成员变量与方法的形参。
调用属性
this.health = 100;
this.name = "大黄";
调用方法
this.print();
调用构造方法
this();
this("小黑",100,100,"雄");
this();如果使用,必须是构造方法中的第一条语句
举例:

不能在普通方法里调用this();
只能在构造方法中调用this();

不能在无参中调用带参,只能在带参中调用无参数方法
this关键字主要有三个应用:
(1)this调用本类中的属性,也就是类中的成员变量;
(2)this调用本类中的其他方法;
(3)this调用本类中的其他构造方法,调用时要放在构造方法的首行。
Public Class Student {
String name; //定义一个成员变量name
private void SetName(String name) { //定义一个参数(局部变量)name
this.name=name; //将局部变量的值传递给成员变量
}
}
应用一:引用成员变量
如上面这段代码中,有一个成员变量name,同时在方法中有一个形式参数,名字也是name,然后在方法中将形式参数name的值传递给成员变量name,虽然我们可以看明白这个代码的含义,但是作为Java编译器它是怎么判断的呢?到底是将形式参数name的值传递给成员变量name,还是反过来将成员变量name的值传递给形式参数name呢?也就是说,两个变量名字如果相同的话,那么Java如何判断使用哪个变量?此时this这个关键字就起到作用了。this这个关键字其代表的就是对象中的成员变量或者方法。也就是说,如果在某个变量前面加上一个this关键字,其指的就是这个对象的成员变量或者方法,而不是指成员方法的形式参数或者局部变量。为此在上面这个代码中,this.name代表的就是对象中的成员变量,又叫做对象的属性,而后面的name则是方法的形式参数,代码this.name=name就是将形式参数的值传递给成员变量。这就是上面这个代码的具体含义。
21. 总结
抽象:用程序的语言描述现实世界
1-找到类
2-属性
3-方法
构造方法
作用:初始化对象属性
1-无参数
Public 类名(){
}
2-带参数
Public 类名(String name){
This.name=name;
}
A系统默认提供无参数的构造方法
B当系统提供了带参数的构造方法时,不在提供无参数方法
封装
1-将属性public变为private
2-增加get/set方法,读取/写入
3-重新修改set方法
Static
1-属性
2-方法
Person p=new Person();
p.field ;
p.method;
--------------------------------------------
Person.filed;
Person.method();
3-静态代码块
优先于构造方法去执行
Static{
}
方法的重载
1-同一个类中
2-俩个或多个同名方法
3-参数不同
4-与访问修饰符和返回值无关