数据库学习之多表操作
目录
外键
——什么是外键
——增加与删除外键
INNODB支持的ON语句
多表查询之连接查询
——内连接:inner join
——外连接:left join与rihgt join
——全连接:full join
多表查询之复合条件连接查询
多表查询之子查询
以下内容为扩展和演示:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/6357507.html
外键
什么是外键
外键是用来关联两张表的。 切记:作为外键一定要和关联主键的数据类型保持一致。 关联外键的格式:[ADD CONSTRAINT charger_fk_stu]FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
--外键约束对子表的含义: 如果在父表中找不到候选键,则不允许在子表上进行insert/update
--外键约束对父表的含义: 在父表上进行update/delete以更新或删除在子表中有一条或多条对
-- 应匹配行的候选键时,父表的行为取决于:在定义子表的外键时指定的
-- on update/on delete子句
每一个班主任会对应多个学生 , 而每个学生只能对应一个班主任 先准备两张表:
父表:
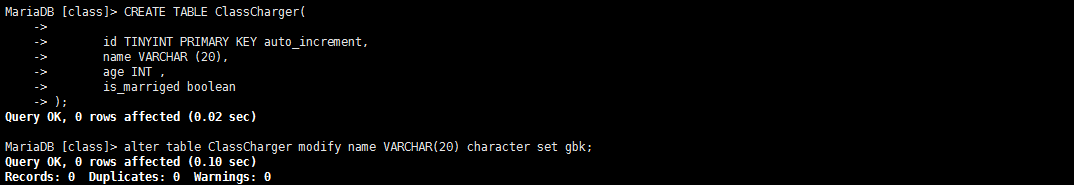
CREATE TABLE ClassCharger(
id TINYINT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR (20),
age INT ,
is_marriged boolean
);
INSERT INTO ClassCharger (name,age,is_marriged) VALUES ("冰冰",29,0),
("丹丹",30,0),
("歪歪",27,0),
("姗姗",20,0),
("小雨",21,0);
子表:
CREATE TABLE Student(
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name VARCHAR (20),
charger_id TINYINT, --切记:作为外键一定要和关联主键的数据类型保持一致
FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
) ENGINE=INNODB;
INSERT INTO Student(name,charger_id) VALUES ("alvin1",2),
("alvin2",4),
("alvin3",1),
("alvin4",3),
("alvin5",1),
("alvin6",3),
("alvin7",2);
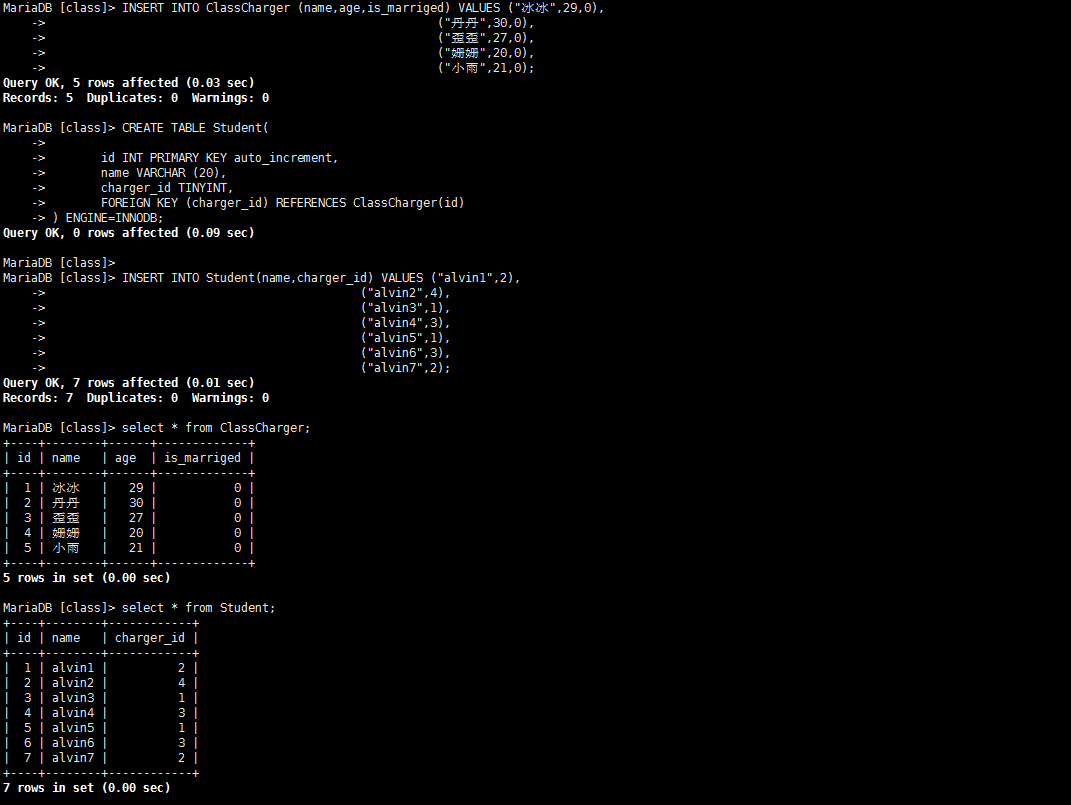
现在我们有5位老师,7位同学。
如果我们现在对老师的表进行操作,比如删除某位老师,按道理来说,如果这位老师有管理的学生,就不能直接删除,除非将他的学生删除或者划到其他老师管理下。
如果你没有关联的话,就没有约束的对老师表做任何操作。
但是现在我们把老师表的id和学生表的charger_id关联起来,你的操作就会受到限制。

增加外键和删除外键
ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT abc
FOREIGN KEY(charger_id)
REFERENCES classcharger(id);
ALTER TABLE student DROP FOREIGN KEY abc;
INNODB支持的ON语句
-----------------innodb支持的四种方式---------------------------------------
-----cascade方式 在父表上update/delete记录时,同步update/delete掉子表的匹配记录
-----外键的级联删除:如果父表中的记录被删除,则子表中对应的记录自动被删除--------
FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
------set null方式 在父表上update/delete记录时,将子表上匹配记录的列设为null
-- 要注意子表的外键列不能为not null
FOREIGN KEY (charger_id) REFERENCES ClassCharger(id)
ON DELETE SET NULL
------Restrict方式 :拒绝对父表进行删除更新操作(了解)
------No action方式 在mysql中同Restrict,如果子表中有匹配的记录,则不允许对父表对应候选键
-- 进行update/delete操作(了解)
多表查询之连接查询
-- 准备两张表
-- company.employee
-- company.department
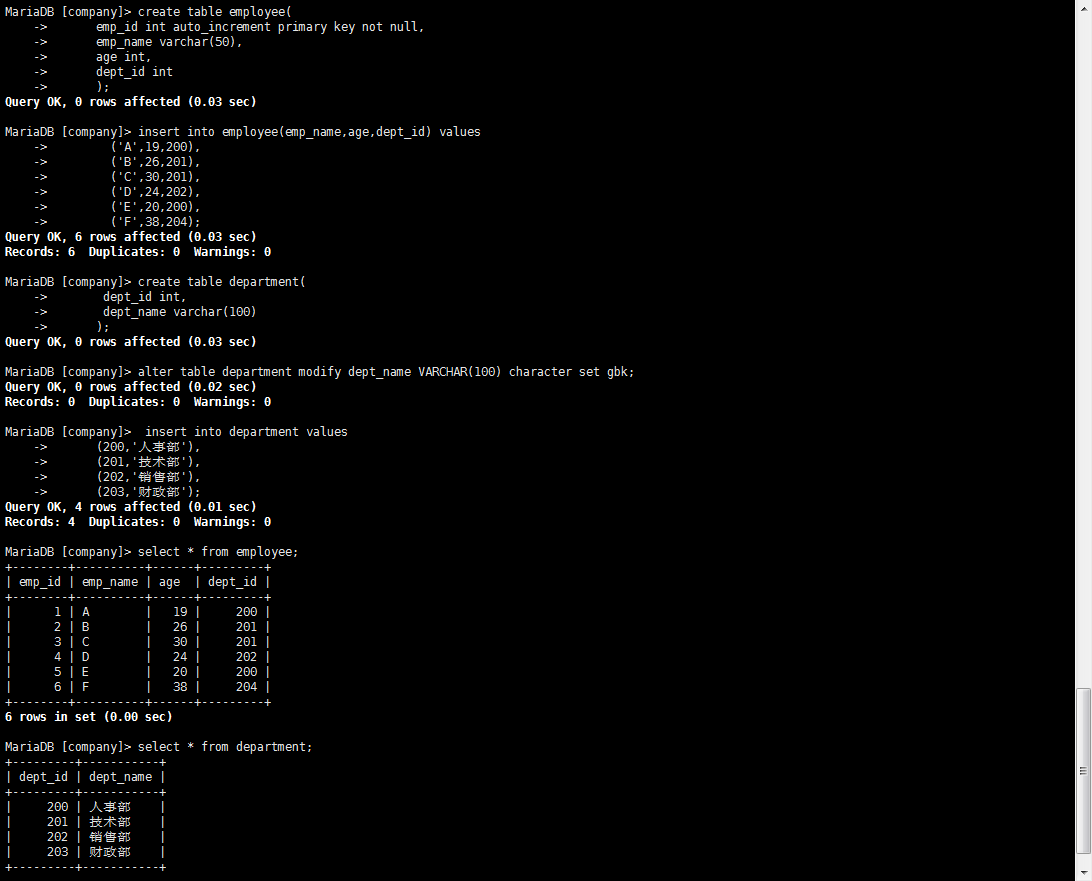
create table employee(
emp_id int auto_increment primary key not null,
emp_name varchar(50),
age int,
dept_id int
);
insert into employee(emp_name,age,dept_id) values
('A',19,200),
('B',26,201),
('C',30,201),
('D',24,202),
('E',20,200),
('F',38,204);
create table department(
dept_id int,
dept_name varchar(100)
);
insert into department values
(200,'人事部'),
(201,'技术部'),
(202,'销售部'),
(203,'财政部');
内连接:inner join
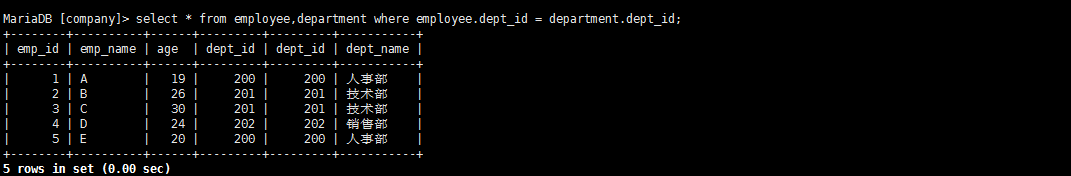
查询两张表中都有的关联数据,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果。
外连接:left join与rihgt join
(1)左外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的结果
select * from employee left join department on employee.dept_id = department.dept_id;
(2)右外连接:在内连接的基础上增加右边有左边没有的结果
select * from employee RIGHT JOIN department on employee.dept_id = department.dept_id;
(3)全外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的和右边有左边没有的结果
-- mysql不支持全外连接 full JOIN
-- mysql可以使用此种方式间接实现全外连接
select * from employee RIGHT JOIN department on employee.dept_id = department.dept_id
UNION
select * from employee LEFT JOIN department on employee.dept_id = department.dept_id;
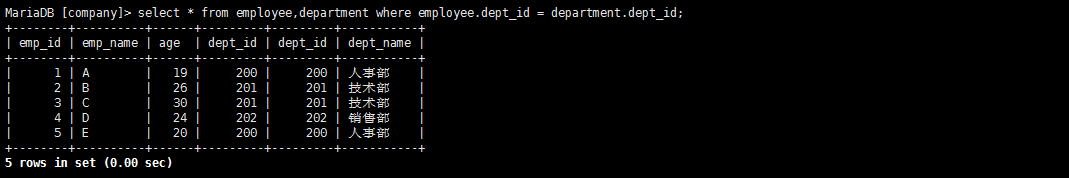
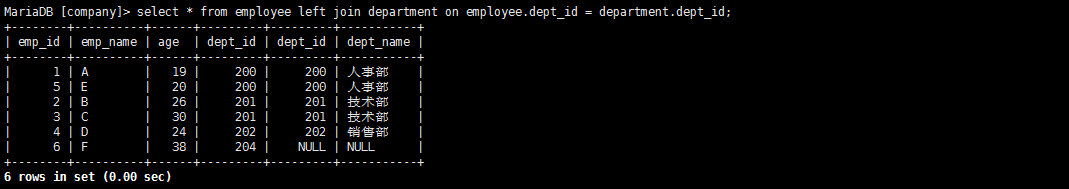
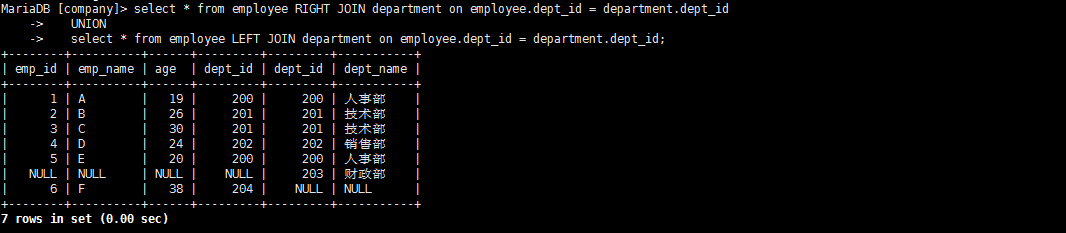
全连接:full join(笛卡尔积查询)

多表查询之复合条件连接查询
查询员工年龄大于等于25岁的部门
SELECT DISTINCT department.dept_name
FROM employee,department
WHERE employee.dept_id = department.dept_id
AND age>25;
以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示
select employee.emp_id,employee.emp_name,employee.age,department.dept_name
from employee,department
where employee.dept_id = department.dept_id
order by age asc;
多表查询之子查询
子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。 内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。 子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字 还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
1. 带IN关键字的子查询
查询employee表,但dept_id必须在department表中出现过
select * from employee
where dept_id IN
(select dept_id from department);
2. 带比较运算符的子查询
=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<>
查询员工年龄大于等于25岁的部门
select dept_id,dept_name from department
where dept_id IN
(select DISTINCT dept_id from employee where age>=25);
3. 带EXISTS关键字的子查询
EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。
而是返回一个真假值。Ture或False
当返回Ture时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询
select * from employee
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT dept_name from department where dept_id=203);
department表中存在dept_id=203,Ture
select * from employee
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT dept_name from department where dept_id=205);
-- Empty set (0.00 sec)
ps: create table t1(select * from t2);