<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>定位</title>
<style media="screen">
.box1{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(184, 208, 162);
}
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
}
.box3{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(188, 211, 213);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
</div>
<div class="box2"
</div>
<div class="box3">
</div>
</body>
</html>
输出:
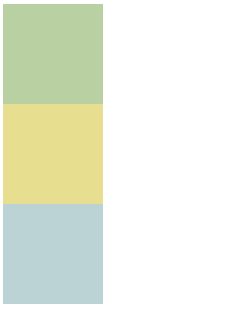
定位:将指定的元素摆放到页面的任意位置
可以通过position属性来设置元素的定位
输入static:
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
position: static;
}
输出:元素没有移动,static为默认值
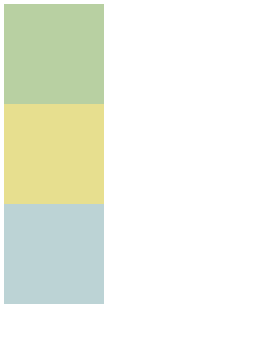
relative:相对定位
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
position: relative;
}
输出:当开启了元素的相对定位以后,而不设置偏移量时,元素不会发生任何变化
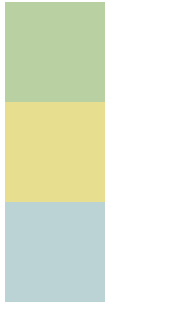
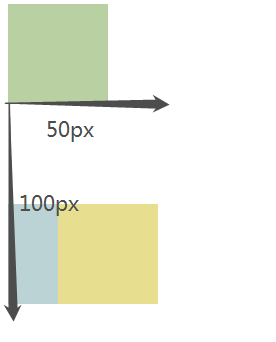
输入偏移量(left,right,top,bottom,一般选择水平方向的一个偏移量和垂直方向的一个偏移量进行定位就可以):
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 100px;
}
输出:1、相对定位 relative 是相对于元素在文档流中原来的位置进行定位
2、相对定位会使元素上升一个层级
3、相对定位的元素不会脱离文档流
插入一个内联元素:
span{
background-color: rgb(209, 198, 209);
position: relative;
}
<span>span元素</span>
输出:相对定位不会改变元素的性质,块元素还是块元素,内联元素还是内联元素
