刚开始的解决方案是(参考网络上别人写的):
自定义一个 CompressionHttpHandler,实现 System.Web.IHttpHandler 接口,在 ProcessRequest 添加以下代码:
这样传输的内容就是经过GZip压缩的,到客户端时浏览器会自动将其解压。
但是这样做的效率不高,每次都需要在服务器端进行压缩,浪费了资源,所以我在这基础上改了一下,就是在本地将文件先进行压缩,然后设置 Content-encoding,这样便可减少浪费服务器很多资源。
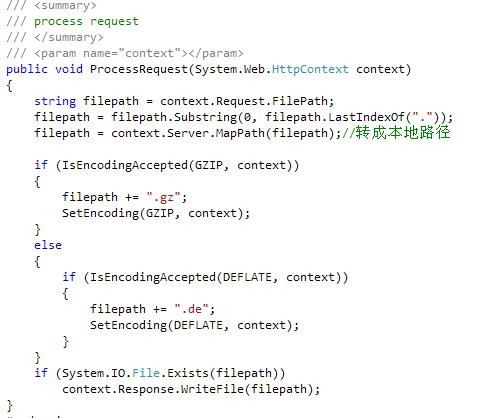

首先取得请求的路径,然后判断浏览器是否支持GZip压缩,如果支持,则设置Content-encoding为gzip,然后设置输出的压缩文件为采用GZip压缩的,最后将文件写入到context.Response中。
注:在这里我将采用GZip压缩的文件命名为 原文件 + .gz,Deflate则为 原文件 + .de,且压缩的文件和原文件必须在同一目录。
Web.Config中添加如下:
以引入一个ExtJS为例说说如何使用:
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://localhost/website1/Scripts/ext-all.js.c"></script>
这里提供一个简单的工具,用来压缩文件(采用GZIP和Deflate)
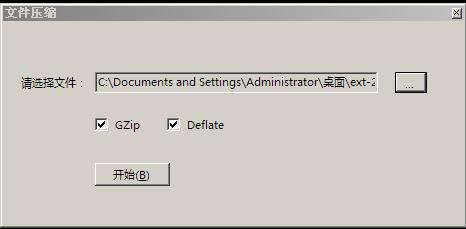
先选择要压缩的原文件,然后点开始即可。
下面我们看看实际效果:
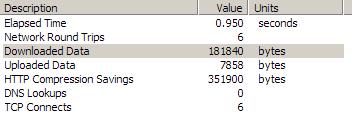
这是采用了浏览器压缩的

这是未压缩的
对比一下可以看出效果还是不错的。
有需要的朋友可以点击此处下载本文代码