position中常用的4种属性:
1、position-static
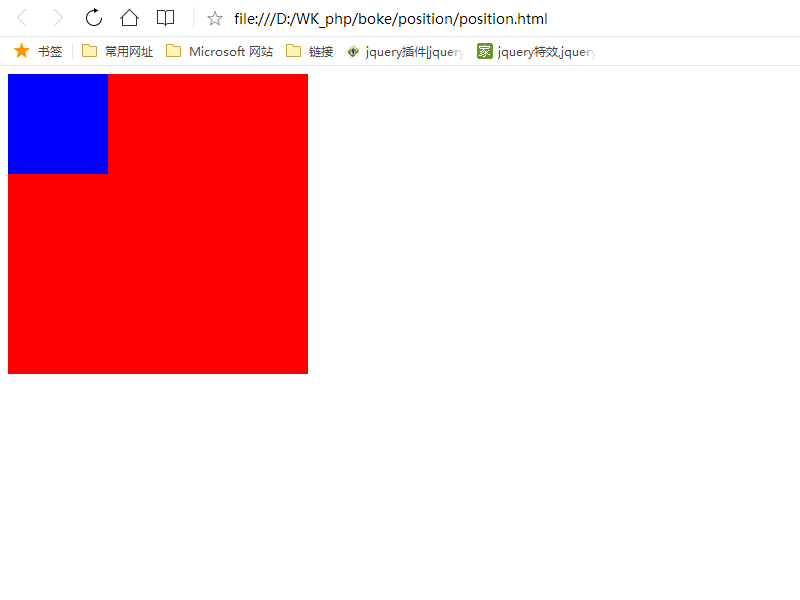
static元素默认属性,即没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中,不会受top,bottom,left,right影响
html: <div class="head"> <div class="content"></div> </div>
css: .head{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background: red; } .content{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; position: static; }
页面显示:
2、position-fixed
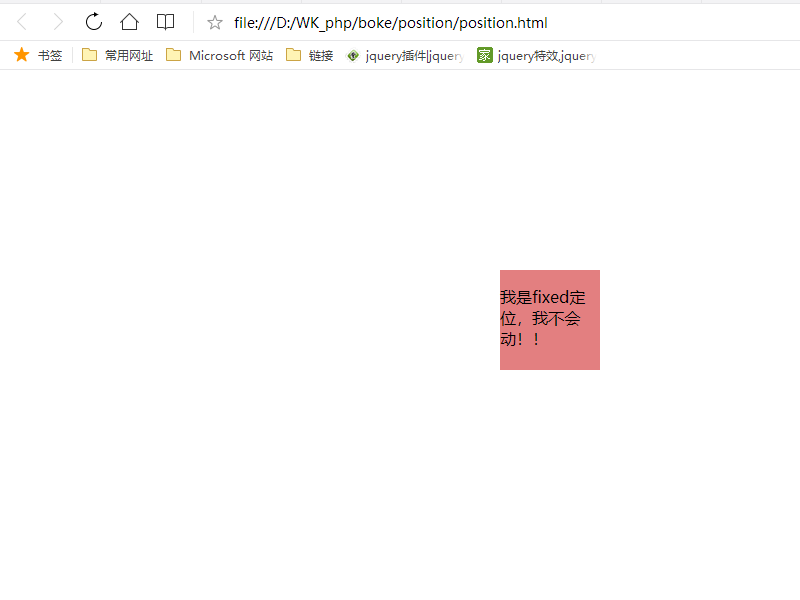
fixed定位是指元素相对于浏览器窗口的固定位置,不会随窗口滑动而改变位置;fixed定位的元素位置与文档流无关,就不会占用空间,会和其他元素重叠
html: <div class="f_content"> <p>我是fixed定位,我不会动!!</p> </div>
css: .f_content{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: rgba(227,127,128,1.00); position: fixed; top: 200px; left: 500px; }
网页显示:
3、position- relative
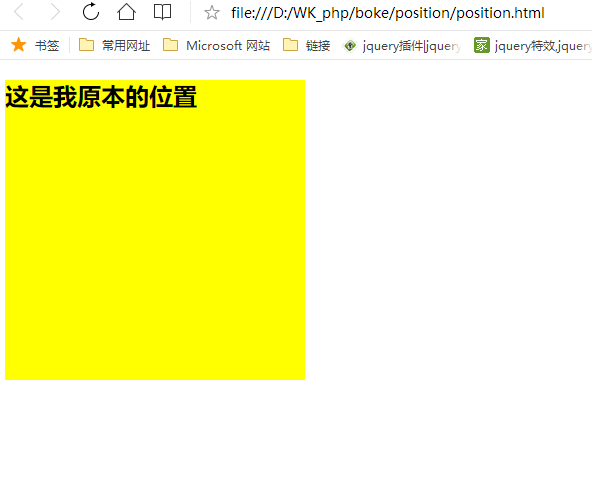
relative相对定位,是指相对于元素本身而发生的定位(位置改变)
<div style=" 300px; height: 300px;background: yellow; "> <h2>这是我原本的位置</h2> </div>
网页显示:
相对定位之后:
<div style=" 300px; height: 300px;background: yellow; "> <h2 style="position: relative; top: 100px;">这是我定位的位置 </h2> </div>

<div style=" 200px; height: 200px;background: yellow;"> <h2>我没有定位</h2> <h2 style="position: relative;top: -40px;">我是定位了的</h2> </div>
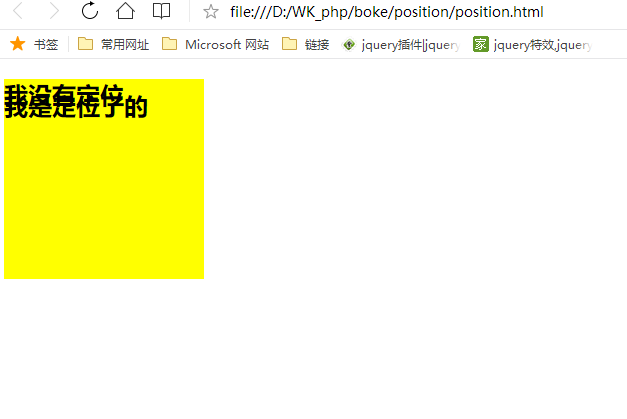
以上说明relative定位的元素发生移动时,不会对其他元素造成影响
4、position-absolute
absolute绝对定位,它是相对于已经定位了的最近的父元素发生的定位,如果没有定位的父元素,那它就相对于<html>来定位
元素没有定位的父元素:
div style=" 400px;height: 400px;background: green;"> <div style=" 300px;height: 300px;background: blue;"> <span style="position: absolute; right: 40px; background: yellow;">我在哪</span> </div> </div>

有定位的父元素:
<div style=" 400px;height: 400px;background: green;"> <div style=" 300px;height: 300px;background: blue; position:absolute;"> <span style="position: absolute; right: 40px; background: yellow;">我在哪</span> </div> </div>
显示:

相对于父父标签:
<div style=" 400px;height: 400px;background: green; position: absolute;"> <div style=" 300px;height: 300px;background: blue;"> <span style="position: absolute; right: 40px; background: yellow;">我在哪</span> </div> </div>
显示:

当给第一个div标签添加了position-fixed属性时,显示的跟第3张相同;
当给第一个div标签添加position-static属性时,显示的跟第1张相同;
这就说某个元素有absolute定位时,如果其父元素有position:fixed/relative/absolute时,其定位会相对于父元素来改变位置;父元素没有position:fixed/relative/absolute时,其定位会相对于<html>来改变位置