数字图像处理——图像的几何变换
几何变换不改变像素值,而是改变像素所在的位置。
它包括两个独立的算法:
- 空间变换算法
- 插值算法
分类
- 从图像类型上
- 二维图像
- 三维图像
- 从三维到二维平面投影变换
- 从变换的性质
- 基本变换:平移,比例缩放,旋转,镜像,错切
- 复合变换
图像的平移
在同一坐标系下,设(P_0(x_0,y_0)) ,经过水平偏移量( riangle x) ,垂直偏移量( riangle y),得到平移之后的坐标:
用矩阵变换表示为:
求逆?不妨将偏移量直接取负。
我们把变换矩阵求逆之后可以观察一下:
其实也就是
图像的镜像
- 水平镜像
- 垂直镜像
设图像宽度为(Width),高度为(Height)
那么水平镜像的坐标变化为
变换矩阵:
求逆:
void translateTransformSize(Mat const &src, Mat & dst, int dx, int dy){
int rows = src.rows + dx;
int cols = src.cols + dy;
dst.create(rows, cols, src.type());
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
int x0 = i - dx;
int y0 = j - dy;
if (x0 >= 0 && y0 >= 0 && x0 < src.cols && y0 < src.rows)
dst.at<Vec3b>(i, j) = src.at<Vec3b>(x0, y0);
}
}
}
图像的缩放
将给定图像在 (x) 轴方向按比例缩放(f_x) 倍,在(y) 轴方向按比例缩放(f_y)倍,从而获得一副新的图像。
- 若 (f_x = f_y) ,则这样的比例缩放为图像的全比例缩放。
- 若(f_x != f_y) , 则产生几何畸变
坐标的缩放变化:
其反变换:
void zoom(Mat& src, Mat &dst, double sx, double sy){
// 缩放之后的大小
int rows = (src.rows * sx + 0.5);
int cols = (src.cols * sy + 0.5);
dst.create(rows, cols, src.type());
Vec3b * p;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++){
int row = (i / sx + 0.5);
if (row >= src.rows)
row--;
Vec3b *origin = src.ptr<Vec3b>(row);
p = dst.ptr<Vec3b>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
int col = (j / sy + 0.5);
if (col >= src.cols)
col--;
p[j] = origin[col];
}
}
}
图像的旋转
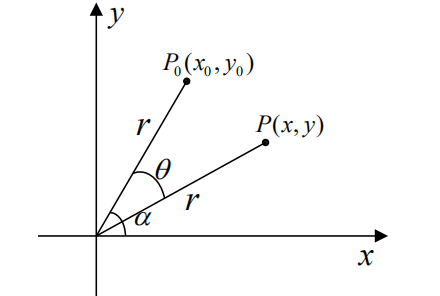
设顺时针旋转( heta) 角后对应点为(P(x,y))
矩阵变换:
其逆运算矩阵为
以上是以旋转中心为原点的坐标系下,坐标的变换,在实际图像中,我们一般是以某个点作为旋转中心来进行旋转的,而原图的坐标系是以左上角为坐标原点的,所以我们要通过转换坐标系来将坐标调整到以旋转中心为原点的坐标系中
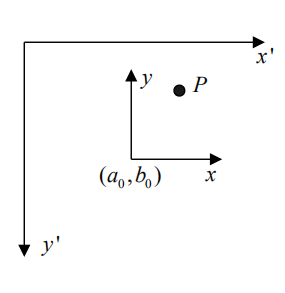
假设在原坐标系下坐标为((x',y')) ,在旋转坐标系下坐标为((x,y)),旋转中心在原坐标系下为((a_0,b_0))
矩阵变换:
其逆变换:
现在求P在原坐标系旋转前坐标((x_0,y_0))和旋转后坐标((x,y))的关系。其中((c,d))为旋转后的坐标中心,((a,b))为在原坐标系中的旋转中心
接下来的问题是,如何确定旋转之后的坐标中心?
很容易想到,图像旋转之后,图像的大小会变(如果要显示完整图像),而旋转中心是始终在中心的,所以我们可以通过计算四个角旋转后的坐标,确定旋转之后的图片大小,进而确定旋转之后的坐标中心(左上角)
已知旋转前的旋转中心坐标:
通过上面的旋转坐标计算,我们很容易的可以求出来四个角旋转之后的坐标,分别是:((x1',y1'),(x2',y2'),(x3',y3'),(x4',y4'))。则旋转后图像宽度和高度为:
请读者想一下这里为什么这么计算宽度和高度?
进而可以得知旋转之后的坐标中心
//该函数是将point顺时针旋转 angle
Point2d coordinates(Point2d point, double angle){
const double cosAng = cos(angle);
const double sinAng = sin(angle);
int x = point.x;
int y = point.y;
int x1 = x * cosAng + y * sinAng;
int y1 = -x * sinAng + y * cosAng;
Point2d res = Point2d(x1, y1);
return res;
}
//旋转主体函数
void rotate(Mat& src, Mat& dst, Point2d center, double angle){
const double cosAng = cos(angle);
const double sinAng = sin(angle);
//请留意这里的坐标运算
Point2d leftTop(-center.x, center.y); //(0,0)
Point2d rightTop(src.cols - center.x, center.y); // (width,0)
Point2d leftBottom(-center.x, -src.rows + center.y); //(0,height)
Point2d rightBottom(src.cols - center.x, -src.rows + center.y); // (width,height)
//以center为中心旋转后四个角的坐标
Point2d transLeftTop, transRightTop, transLeftBottom, transRightBottom;
transLeftTop = coordinates(leftTop, angle);
transRightTop = coordinates(rightTop, angle);
transLeftBottom = coordinates(leftBottom, angle);
transRightBottom = coordinates(rightBottom, angle);
double left = min({ transLeftTop.x, transRightTop.x, transLeftBottom.x, transRightBottom.x });
double right = max({ transLeftTop.x, transRightTop.x, transLeftBottom.x, transRightBottom.x });
double top = max({ transLeftTop.y, transRightTop.y, transLeftBottom.y, transRightBottom.y });
double down = min({ transLeftTop.y, transRightTop.y, transLeftBottom.y, transRightBottom.y });
//得到新图像的宽度和高度
int width = (fabs(left - right) + 0.5);
int height = (fabs(top - down) + 0.5);
dst.create(width, height, src.type());
//num1与num2是为了方便矩阵运算(因为每次计算都有这两个值)
const double num1 = -abs(left) * cosAng - abs(top) * sinAng + center.x;
const double num2 = abs(left) * sinAng - abs(top) * cosAng + center.y;
Vec3b *p;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
p = dst.ptr<Vec3b>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
int x = static_cast<int>(j * cosAng + i * sinAng + num1 + 0.5);
int y = static_cast<int>(-j * sinAng + i * cosAng + num2 + 0.5);
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < src.cols && y < src.rows)
p[j] = src.ptr<Vec3b>(y)[x];
}
}
}
图像的错切

错切之后
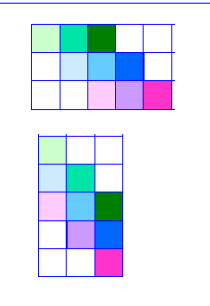
x方向的错切
y方向的错切
初次总结,还有很多的不足,请各位看客多多包涵,小生会更加努力学习!