来源于:https://www.wangdaye.net/archives/n-e-t-t-y-zhi-f-a-s-t-t-h-r-e-a-d-l-o-c-a-l
前言
netty的concurrent包下有一些非常优秀的并发操作类,FastThreadLocal就是其中之一。
| 类 | 简称 |
|---|---|
| FastThreadLocalThread | ftlt |
| FastThreadLocal | ftl |
谈谈JDK的ThreadLocal
简介
ThreadLocal 是 Java 里一种特殊变量,它是一个线程级别变量,每个线程都有一个 ThreadLocal 就是每个线程都拥有了自己独立的一个变量,竞态条件被彻底消除了,在并发模式下是绝对安全的变量。
可以通过 ThreadLocal
会自动在每一个线程上创建一个 T 的副本,副本之间彼此独立,互不影响,可以用 ThreadLocal 存储一些参数,以便在线程中多个方法中使用,用以代替方法传参的做法。这是一种空间换时间的思想。
使用
既然jdk已经有ThreadLocal,为何netty还要自己造个FastThreadLocal?FastThreadLocal快在哪里?
这需要从jdk ThreadLocal的本身说起。如下图:
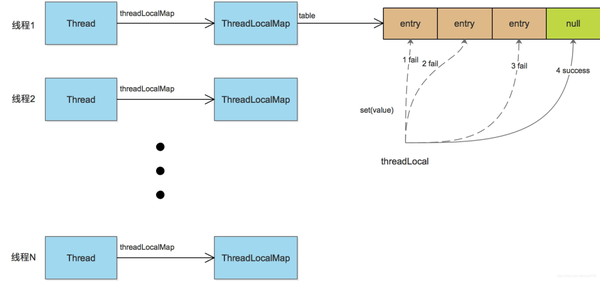 在java线程中,每个线程都有一个ThreadLocalMap实例变量(如果不使用ThreadLocal,不会创建这个Map,一个线程第一次访问某个ThreadLocal变量时,才会创建)。
在java线程中,每个线程都有一个ThreadLocalMap实例变量(如果不使用ThreadLocal,不会创建这个Map,一个线程第一次访问某个ThreadLocal变量时,才会创建)。
该Map是使用线性探测的方式解决hash冲突的问题,如果没有找到空闲的slot,就不断往后尝试,直到找到一个空闲的位置,插入entry,这种方式在经常遇到hash冲突时,影响效率。
FastThreadLocal(下文简称ftl)直接使用数组避免了hash冲突的发生,具体做法是:每一个FastThreadLocal实例创建时,分配一个下标index;分配index使用AtomicInteger实现,每个FastThreadLocal都能获取到一个不重复的下标。
当调用ftl.get()方法获取值时,直接从数组获取返回,如return array[index],如下图:

源码分析
根据上文图示可知,ftl的实现,涉及到InternalThreadLocalMap、FastThreadLocalThread和FastThreadLocal几个类,自底向上,我们先从InternalThreadLocalMap开始分析。
InternalThreadLocalMap类的继承关系图如下:
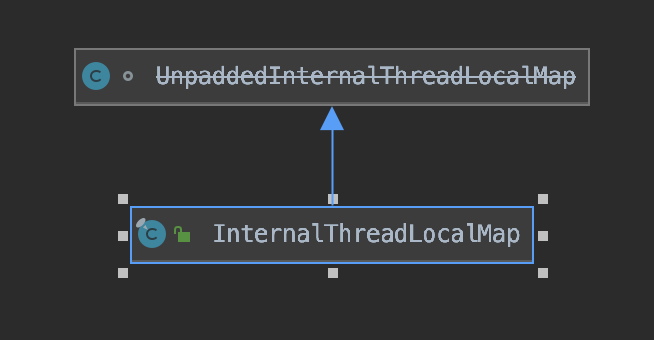
InternalThreadLocalMap介绍
InternalThreadLocalMap是Netty用来代替JDK中的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类的,InternalThreadLocalMap使用数组来代替Hash表,每个FastThreadLocal被创建时,会拥有一个全局唯一且递增的索引index,该index就代表FastThreadLocal对应数组的下标,Value会被直接放到该下标处,访问也是一样,根据index快速定位元素,非常的快速,压根就不存在哈希冲突,时间复杂度始终是O(1),缺点就是会浪费点内存空间,不过在内存越来越廉价的今天,这是值得的。 先看几个和FastThreadLocal相关的属性,后面会用到:
static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
Object[] indexedVariables;
数组indexedVariables就是用来存储ftl的value的,使用下标的方式直接访问。nextIndex在ftl实例创建时用来给每个ftl实例分配一个下标,slowThreadLocalMap在线程不是ftlt时使用到。
属性分析
InternalThreadLocalMap的主要属性:
// 用于标识数组的槽位还未使用
public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
/**
* 用于标识ftl变量是否注册了cleaner
* BitSet简要原理:
* BitSet默认底层数据结构是一个long[]数组,开始时长度为1,即只有long[0],而一个long有64bit。
* 当BitSet.set(1)的时候,表示将long[0]的第二位设置为true,即0000 0000 ... 0010(64bit),则long[0]==2
* 当BitSet.get(1)的时候,第二位为1,则表示true;如果是0,则表示false
* 当BitSet.set(64)的时候,表示设置第65位,此时long[0]已经不够用了,扩容处long[1]来,进行存储
*
* 存储类似 {index:boolean} 键值对,用于防止一个FastThreadLocal多次启动清理线程
* 将index位置的bit设为true,表示该InternalThreadLocalMap中对该FastThreadLocal已经启动了清理线程
*/
private BitSet cleanerFlags;
private InternalThreadLocalMap() {
super(newIndexedVariableTable());
}
private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {
Object[] array = new Object[32];
Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);
return array;
}
比较简单,newIndexedVariableTable()方法创建长度为32的数组,然后初始化为UNSET,然后传给父类。之后ftl的值就保存到这个数组里面。
❝注意,这里保存的直接是变量值,不是entry,这是和jdk ThreadLocal不同的。InternalThreadLocalMap就先分析到这,其他方法在后面分析ftl再具体说。
❞
FastThreadLocal介绍
ftlt的实现分析
要发挥ftl的性能优势,必须和ftlt结合使用,否则就会退化到jdk的ThreadLocal。ftlt比较简单,关键代码如下:
public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {
// This will be set to true if we have a chance to wrap the Runnable.
private final boolean cleanupFastThreadLocals;
private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;
public final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap() {
return threadLocalMap;
}
public final void setThreadLocalMap(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
this.threadLocalMap = threadLocalMap;
}
}
ftlt的诀窍就在threadLocalMap属性,它继承java Thread,然后聚合了自己的InternalThreadLocalMap。后面访问ftl变量,对于ftlt线程,都直接从InternalThreadLocalMap获取变量值。
ftl的属性和实例化
private final int index;
public FastThreadLocal() {
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
非常简单,就是给属性index赋值,赋值的静态方法在InternalThreadLocalMap:
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException(“too many thread-local indexed variables”);
}
return index;
}
可见,每个ftl实例以步长为1的递增序列,获取index值,这保证了InternalThreadLocalMap中数组的长度不会突增。
ftl的 get()方法实现分析
public final V get() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); // 1
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index); // 2
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
V value = initialize(threadLocalMap); // 3
registerCleaner(threadLocalMap); // 4
return value;
}
「1. 先来看看InternalThreadLocalMap.get()方法如何获取threadLocalMap:」
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
因为结合FastThreadLocalThread使用才能发挥FastThreadLocal的性能优势,所以主要看fastGet方法。该方法直接从ftlt线程获取threadLocalMap,还没有则创建一个InternalThreadLocalMap实例并设置进去,然后返回
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
slowGet方法是通过slowThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal对象包装的)去获取InternalThreadLocalMap,相当于使用原生的 ThreadLocal了
「2. threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index)就简单了,直接从数组获取值,然后返回:」
public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
}
「3. 如果获取到的值不是UNSET,那么是个有效的值,直接返回。如果是UNSET,则初始化。」
private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
V v = null;
try {
v = initialValue();
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
// 获取ftl的初始值,然后保存到ftl里的数组,如果数组长度不够则扩充数组长度,然后保存,不展开。
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, v);
//addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this)的实现,是将ftl实例保存在threadLocalMap内部数组第0个元素的Set集合中。
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
return v;
}

「4. registerCleaner(threadLocalMap)的实现」
private void registerCleaner(final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (FastThreadLocalThread.willCleanupFastThreadLocals(current) || threadLocalMap.isCleanerFlagSet(index)) {
return;
}
threadLocalMap.setCleanerFlag(index);
// TODO: We need to find a better way to handle this.
/*
// We will need to ensure we will trigger remove(InternalThreadLocalMap) so everything will be released
// and FastThreadLocal.onRemoval(...) will be called.
ObjectCleaner.register(current, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
remove(threadLocalMap);
// It's fine to not call InternalThreadLocalMap.remove() here as this will only be triggered once
// the Thread is collected by GC. In this case the ThreadLocal will be gone away already.
}
});
*/
ftl的资源回收机制
在netty中对于ftl提供了三种回收机制:
自动: 使用ftlt执行一个被FastThreadLocalRunnable wrap的Runnable任务,在任务执行完毕后会自动进行ftl的清理。
手动: ftl和InternalThreadLocalMap都提供了remove方法,在合适的时候用户可以(有的时候也是必须,例如普通线程的线程池使用ftl)手动进行调用,进行显示删除。
自动: 为当前线程的每一个ftl注册一个Cleaner,当线程对象不强可达的时候,该Cleaner线程会将当前线程的当前ftl进行回收。(netty推荐如果可以用其他两种方式,就不要再用这种方式,因为需要另起线程,耗费资源,而且多线程就会造成一些资源竞争,在netty-4.1.34版本中,已经注释掉了调用ObjectCleaner的代码。)
ftl在netty中的使用
ftl在netty中最重要的使用,就是分配ByteBuf。基本做法是:每个线程都分配一块内存(PoolArena),当需要分配ByteBuf时,线程先从自己持有的PoolArena分配,如果自己无法分配,再采用全局分配。
但是由于内存资源有限,所以还是会有多个线程持有同一块PoolArena的情况。不过这种方式已经最大限度地减轻了多线程的资源竞争,提高程序效率。
具体的代码在PoolByteBufAllocator的内部类PoolThreadLocalCache中:
final class PoolThreadLocalCache extends FastThreadLocal<PoolThreadCache> {
@Override
protected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() {
final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas);
final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = leastUsedArena(directArenas);
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (useCacheForAllThreads || current instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
// PoolThreadCache即为各个线程持有的内存块的封装
return new PoolThreadCache(
heapArena, directArena, tinyCacheSize, smallCacheSize, normalCacheSize,
DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL);
}
// No caching so just use 0 as sizes.
return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
结束
❝识别下方二维码!回复: 「
❞入群」 ,扫码加入我们交流群!

