Description
Venture MFG Company, Inc. has made a game board. This game board has 15 holes and these holes are filled with pegs except one hole. A peg can jump over one or more consecutive peg s to the nearest empty hole along the straight line. As a peg jump over the pegs you remove them from the board. In the following figure, the peg at the hole number 12 or the peg at the hole number 14 can jump to the empty hole number 5. If the peg at the hole number 12 is moved then the peg at the hole number 8 is removed. Instead, if the peg at the hole number 14 is moved then the peg at the hole number 9 is removed.
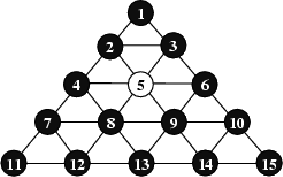
Write a program which find a shortest sequence of moving pegs to leave the last peg in the hole that was initially empty. If such a sequence does not exist the program should write a message ``IMPOSSIBLE".
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case is a single integer which means an empty hole number.
Output
For each test case, the first line of the output file contains an integer which is the number of jumps in a shortest sequence of moving pegs. In the second line of the output file, print a sequence of peg movements. A peg movement consists of a pair o f integers separated by a space. The first integer of the pair denotes the hole number of the peg that is moving, and the second integer denotes a destination (empty) hole number.
If there are multiple solutions, output the lexicographically smallest one.
Sample Input
1 5
Sample Output
10 12 5 3 8 15 12 6 13 7 9 1 7 10 8 7 9 11 14 14 5
题目大意:在如图中的棋盘(固定5行)上,每个棋子的走法类似于象棋中“炮”的走法,只能隔着棋子沿直线走,每走一步造成的效果是该棋子落到第一个空白处,并且沿途经过的棋子全部消失。求使最后一个棋子恰好落在第n个点上的最短、字典序最小的路径。
题目分析:这道题说白了有15个位置,每个位置上可能有棋子也可能没有棋子,棋子的状况总共有2^15种。起点是(2^15)-1,终点是1<<(n-1),BFS即可,状态转移也不难,但比较复杂。
代码如下:
# include<iostream>
# include<cstdio>
# include<queue>
# include<map>
# include<cmath>
# include<string>
# include<cstring>
# include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int tot=(1<<15)-1;
struct node
{
int s,t;
string step;
node(int _s,int _t,string _step):s(_s),t(_t),step(_step){}
bool operator < (const node &a) const {
if(t==a.t)
return step>a.step;
return t>a.t;
}
};
int mark[1<<15];
map<int,char>mp;
int d[6][2]={{-1,-1},{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,1},{1,0},{1,1}};
int get_pos(int x,int y)
{
return x*(x-1)/2+y;
}
void get_XY(int n,int &x,int &y)
{
x=1;
for(int i=1;i<=5&&n-i>0;++i)
++x,n-=i;
y=n;
}
bool ok(int x,int y)
{
if(x>=1&&x<=5&&y>=1&&y<=x)
return true;
return false;
}
void print(string p)
{
for(int i=0;i<p.size();++i)
printf("%d%c",p[i]-'A'+1,(i==p.size()-1)?'
':' ');
}
void bfs(int goal)
{
priority_queue<node>q;
memset(mark,0,sizeof(mark));
mark[tot^goal]=1;
q.push(node(tot^goal,0,""));
while(!q.empty())
{
node u=q.top();
q.pop();
//cout<<u.t<<' '<<u.s<<' '<<u.step<<endl;
if(u.s==goal){
printf("%d
",u.t);
print(u.step);
return ;
}
int x,y;
for(int i=1;i<=15;++i){
if(u.s&(1<<(i-1))){
get_XY(i,x,y);
for(int j=0;j<6;++j){
int nx=x+d[j][0],ny=y+d[j][1];
if(!ok(nx,ny))
continue;
int pos=get_pos(nx,ny);
if(!(u.s&(1<<(pos-1))))
continue;
int s=u.s^(1<<(i-1));
while(u.s&(1<<(pos-1)))
{
s^=(1<<(pos-1));
nx=nx+d[j][0],ny=ny+d[j][1];
if(!ok(nx,ny))
break;
pos=get_pos(nx,ny);
}
s^=(1<<(pos-1));
string step=u.step+mp[i];
step+=mp[get_pos(nx,ny)];
if(ok(nx,ny)&&!mark[s]){
mark[s]=1;
q.push(node(s,u.t+1,step));
}
}
}
}
}
printf("IMPOSSIBLE
");
}
int main()
{
for(int i=1;i<=15;++i)
mp[i]=i+'A'-1;
int T,n;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
bfs(1<<(n-1));
}
return 0;
}