第十周课上测试补做
课程知识点总结
- 排序
- 有类的源代码,针对某一成员变量排序,让类实现
Comparable接口,调用Collection.sort(List)。
- 没有类的源代码,或者多种排序,新建一个类,实现
Comparator接口 调用Collection.sort(List, Compatator)。
- 泛型类声明:
class 名称<泛型列表>
- 创建链表
LinkedList<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>();
- 向链表增加节点
list.add(E obj);
- 从链表中删除节点
list.remove(index)
- 升序排序
public static sort(List<E>list)
- 折半查找list是否含有和参数key一样的元素
int binarySearch(List<T>,Tkey,compareTo<T>c)
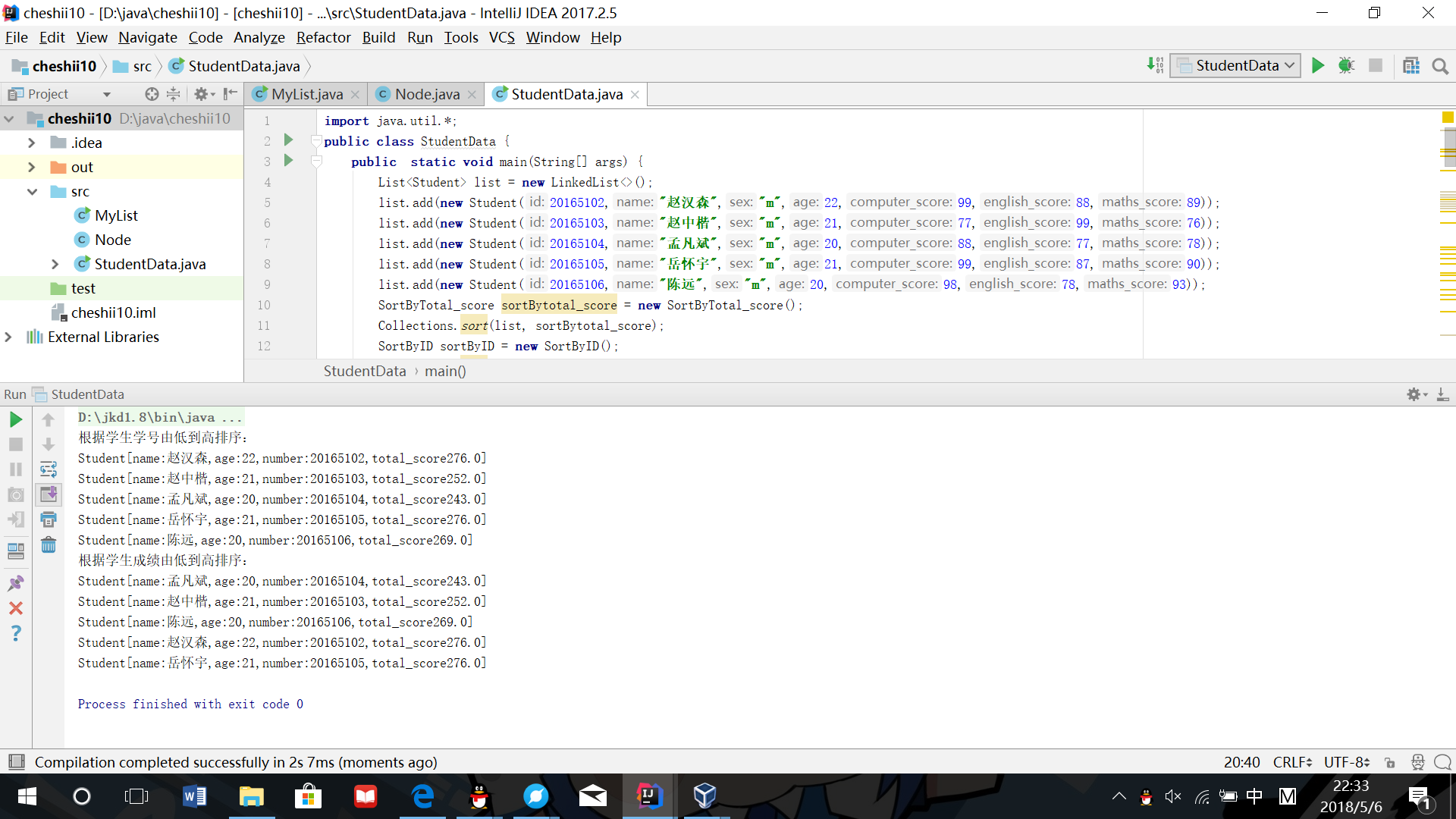
习题补做
排序
import java.util.*;
public class StudentData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new Student(20165102,"赵汉森","m",22,99,88,89));
list.add(new Student(20165103,"赵中楷","m",21,77,99,76));
list.add(new Student(20165104,"孟凡斌","m",20,88,77,78));
list.add(new Student(20165105,"岳怀宇","m",21,99,87,90));
list.add(new Student(20165106,"陈远","m",20,98,78,93));
SortByTotal_score sortBytotal_score = new SortByTotal_score();
Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score);
SortByID sortByID = new SortByID();
Collections.sort(list, sortByID);
System.out.println("根据学生学号由低到高排序:");
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
Collections.sort(list, sortBytotal_score);
System.out.println("根据学生成绩由低到高排序:");
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
class Student {
private int id;//表示学号
private String name;//表示姓名
private int age;//表示年龄
private String sex;//表示性别
private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩
private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩
private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩
private double total_score;// 表示总成绩
private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student[name:"+name+",age:"+age+",number:"+id+",total_score"+total_score+"]";
}
public Student(int id, String name, String sex, int age, double computer_score, double english_score, double maths_score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.computer_score = computer_score;
this.english_score = english_score;
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}//获得当前对象的学号,
public double getComputer_score() {
return computer_score;
}//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩,
public double getMaths_score() {
return maths_score;
}//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩,
public double getEnglish_score() {
return english_score;
}//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩,
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}// 设置当前对象的id值,
public void setComputer_score(double computer_score) {
this.computer_score = computer_score;
}//设置当前对象的Computer_score值,
public void setEnglish_score(double english_score) {
this.english_score = english_score;
}//设置当前对象的English_score值,
public void setMaths_score(double maths_score) {
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}//设置当前对象的Maths_score值,
public double getTotalScore() {
total_score=computer_score + maths_score + english_score;
return total_score;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。
public double getAveScore() {
return getTotalScore() / 3;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。
}
class SortByID implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getId() - o2.getId();
}
}
class SortByTotal_score implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return (int)( o1.getTotalScore() - o2.getTotalScore());
}
}
- 实验结果截图
单链表
import java.util.Iterator;
public class MyList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//选用合适的构造方法,用你学号前后各两名同学的学号创建四个结点
Node<Integer> S1 = new Node<Integer>(20165102, null);
Node<Integer> S2 = new Node<Integer>(20165103, null);
Node<Integer> S3 = new Node<Integer>(20165105, null);
Node<Integer> S4 = new Node<Integer>(20165106, null);
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表
S1.next = S2;
S2.next = S3;
S3.next = S4;
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
Node<Integer> s = S1;
while (s != null) {
System.out.println(s.data);
s = s.next;
}
System.out.println();
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)
Node<Integer> M = new Node<Integer>(20165104, null);
s = S1;
while (s != null) {
if (s.data < 20165104 && s.next.data > 20165104) {
M.next = s.next;
s.next = M;
break;
}
else {
s = s.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
s = S1;
while (s != null) {
System.out.println(s.data);
s = s.next;
}
System.out.println();
//从链表中删除自己
s = S1;
while (s != null) {
if (s.next.data == 20165104) {
s.next = s.next.next;
break;
}
else {
s = s.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
s = S1;
while (s != null) {
System.out.println(s.data);
s = s.next;
}
}
}
- 实验结果截图

第十五章课后编程题
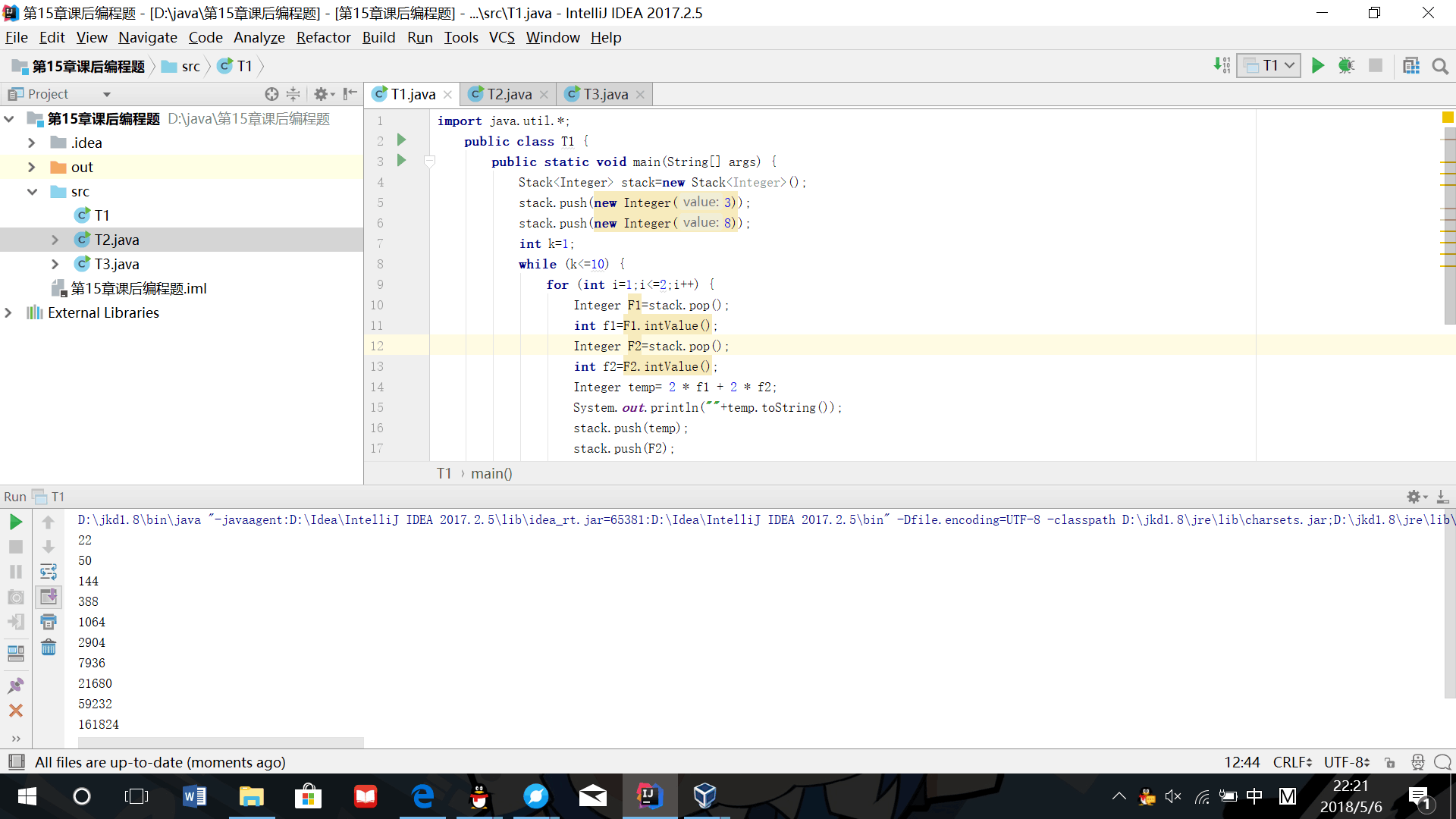
(1)使用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1+2an-2,a1=3,a2=8
import java.util.*;
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(new Integer(3));
stack.push(new Integer(8));
int k=1;
while (k<=10) {
for (int i=1;i<=2;i++) {
Integer F1=stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2=stack.pop();
int f2=F2.intValue();
Integer temp= 2 * f1 + 2 * f2;
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(F2);
k++;
}
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图:
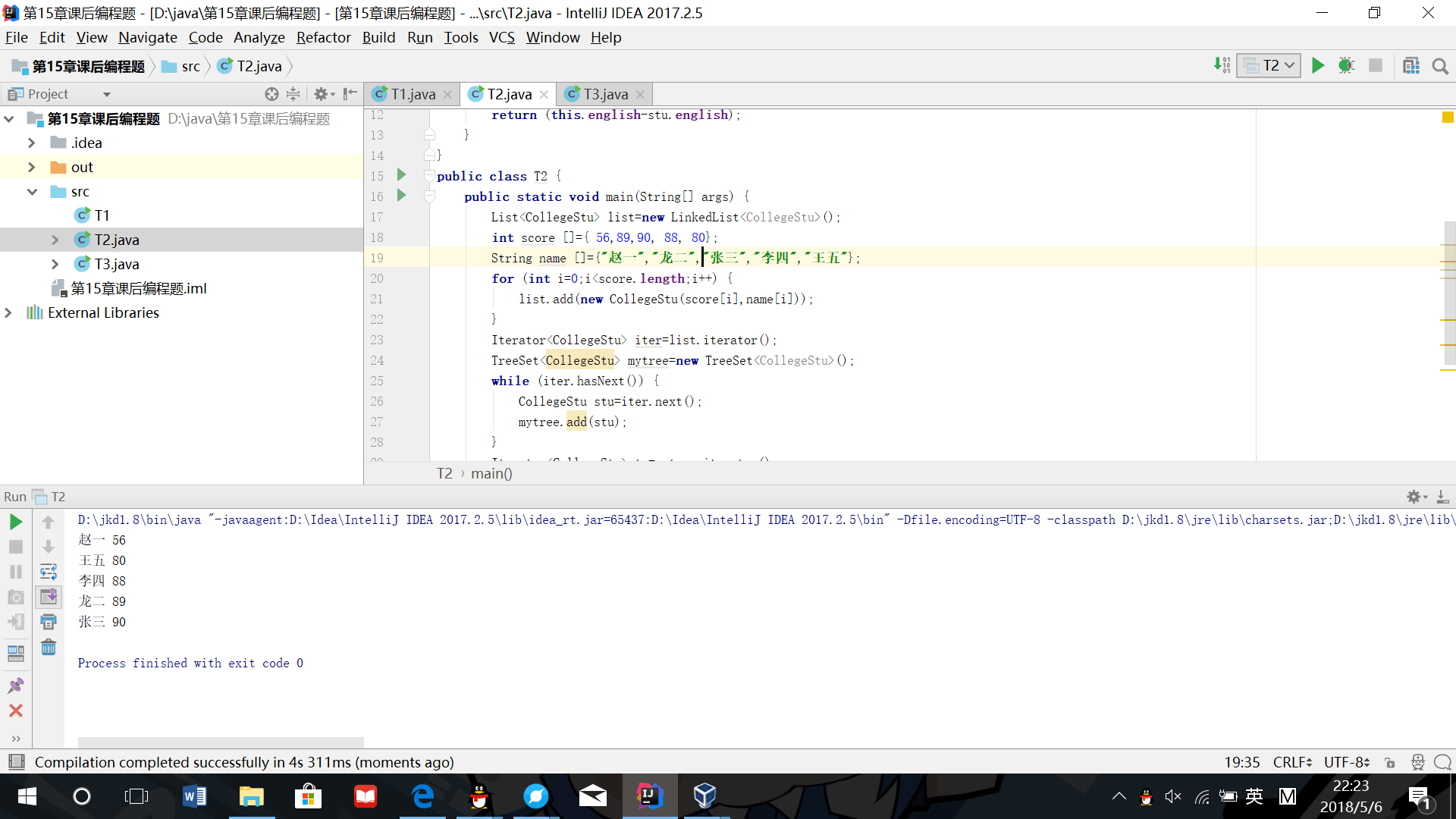
(2)将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果
import java.util.*;
class CollegeStu implements Comparable {
int english=0;
String name;
CollegeStu(int english,String name) {
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
CollegeStu stu=(CollegeStu)b;
return (this.english-stu.english);
}
}
public class T2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<CollegeStu> list=new LinkedList<CollegeStu>();
int score []={ 90, 88, 80};
String name []={"张三","李四","王五"};
for (int i=0;i<score.length;i++) {
list.add(new CollegeStu(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<CollegeStu> mytree=new TreeSet<CollegeStu>();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> te=mytree.iterator();
while (te.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图:
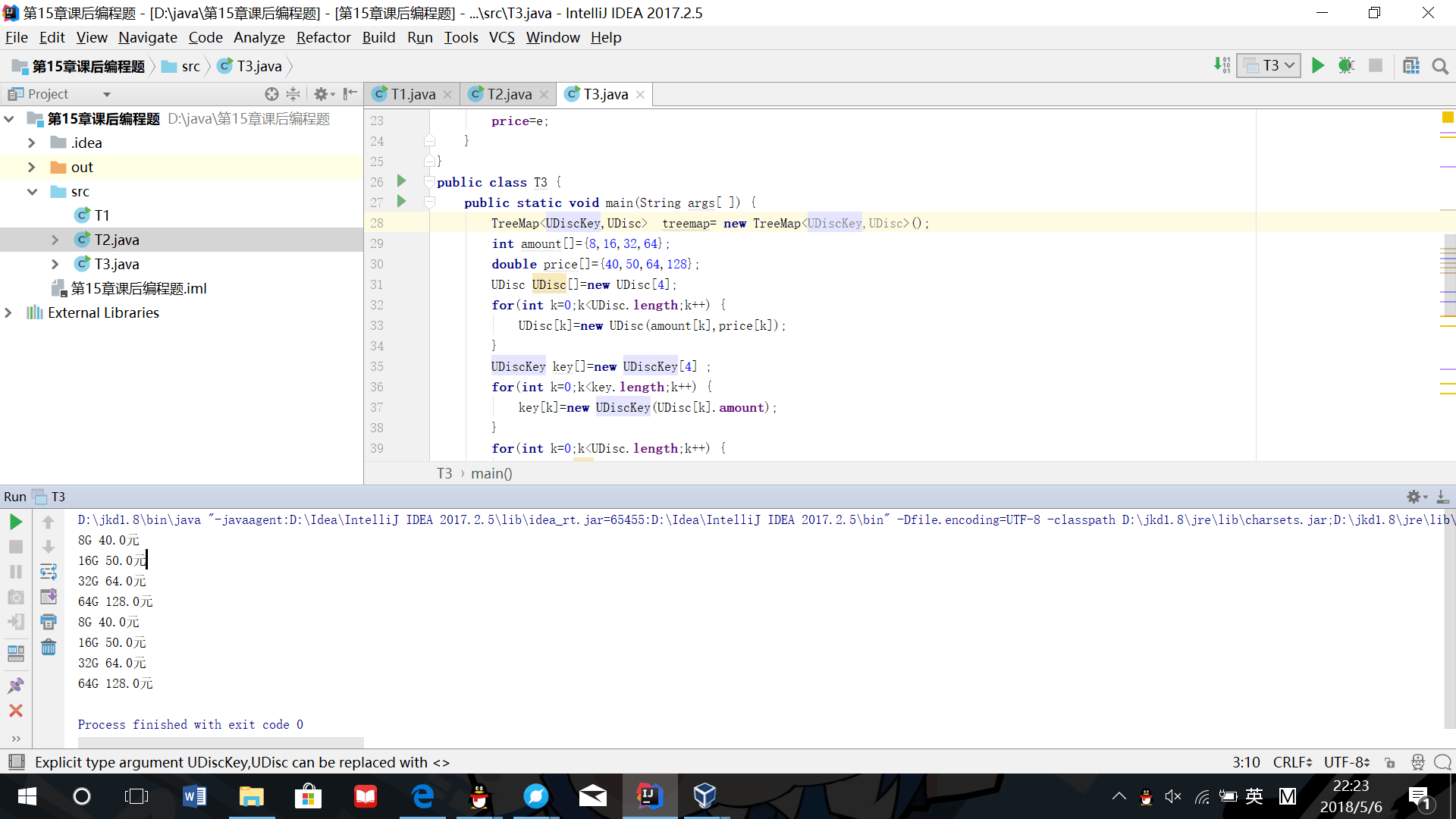
(3)有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量,编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序输出10个U盘的详细信息。
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key=0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
key=d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey disc=(UDiscKey)b;
if((this.key-disc.key)==0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return (int) ((this.key - disc.key) * 1000);
}
}
}
class UDisc{
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int m,double e) {
amount=m;
price=e;
}
}
public class T3 {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap= new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();
int amount[]={8,16,32,64};
double price[]={40,50,64,128};
UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4] ;
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount);
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
int number=treemap.size();
Collection<UDisc> collection=treemap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
treemap.clear();
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price);
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
number=treemap.size();
collection=treemap.values();
iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图: