第十周课下补做
排序与链表知识点
- Collections类提供的用于排序和查找的类的方法如下:
public static sort(List<E>list)该方法可以将list中的元素按升序排列。
- 声明泛型类:
class 名称<泛型列表>
- 链表的创建:
LinkedList<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>();
- 增加节点:
list.add(E obj);
- 删除节点:
list.remove(index)
- 有类的源代码,针对某一成员变量排序,让类实现Comparable接口,调用
Collection.sort(List)
- 没有类的源代码,或者多种排序,新建一个类,实现Comparator接口 调用
Collection.sort(List, Compatator)
课上内容补做截图
第一题:排序
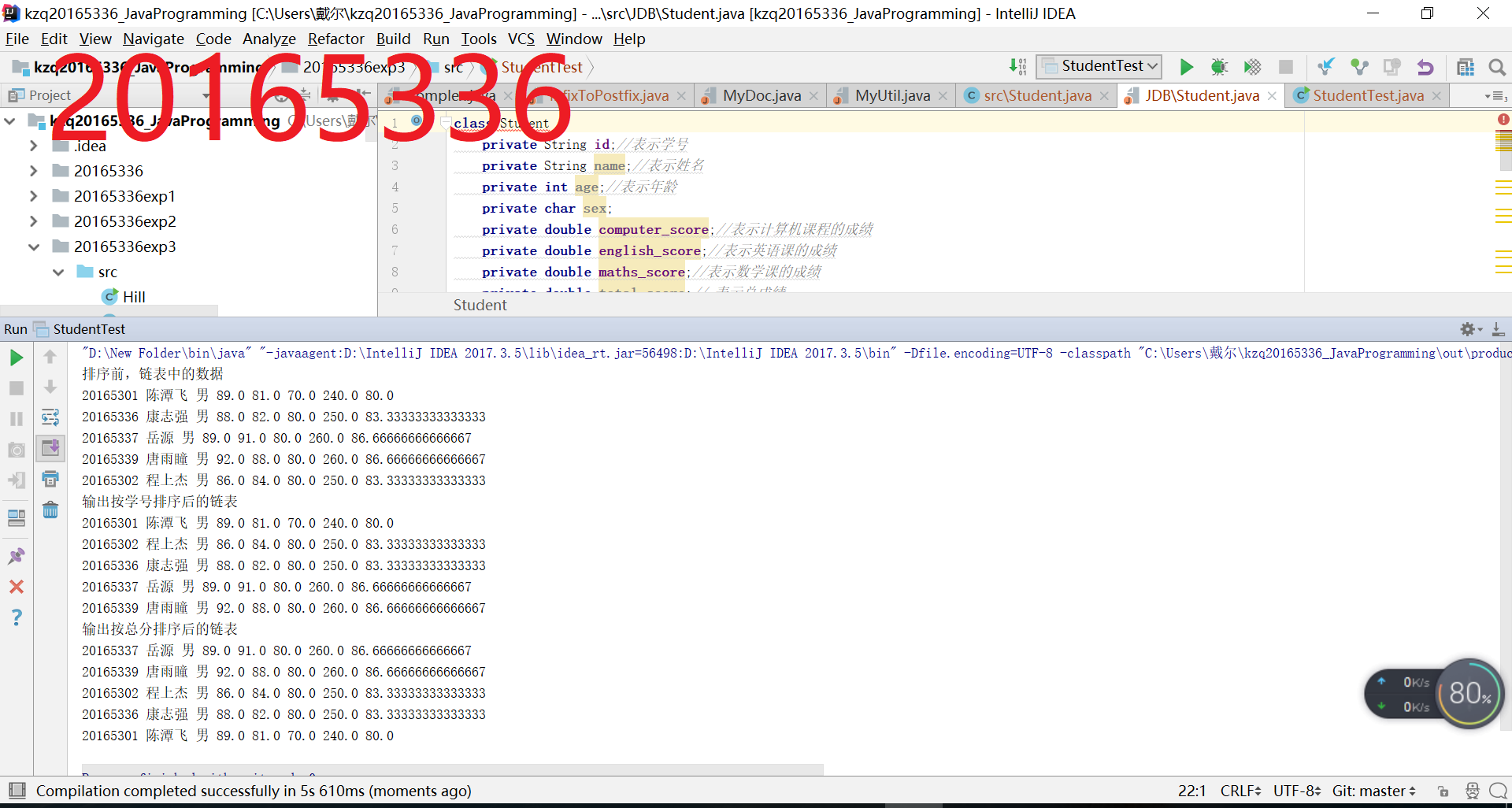
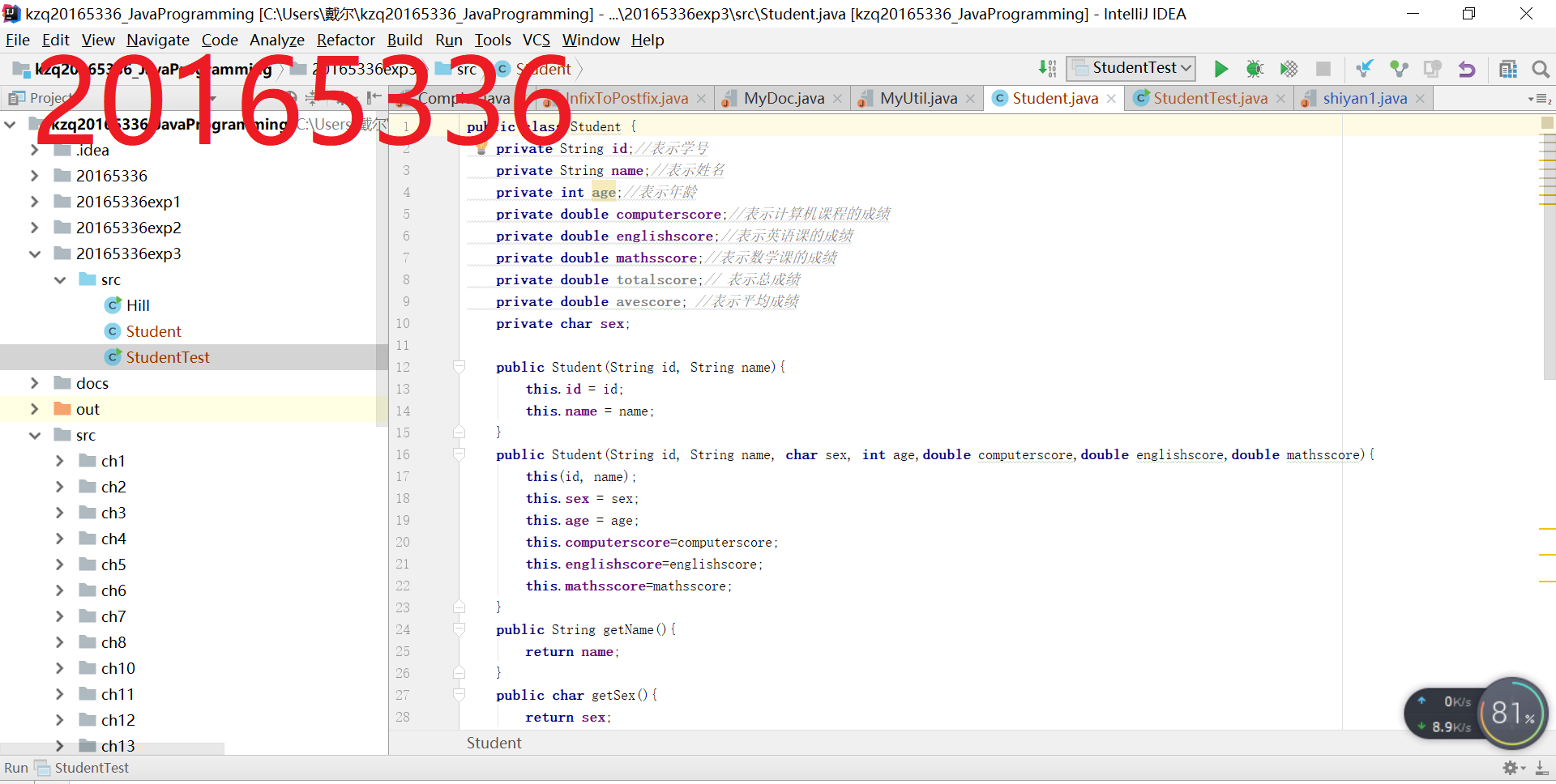
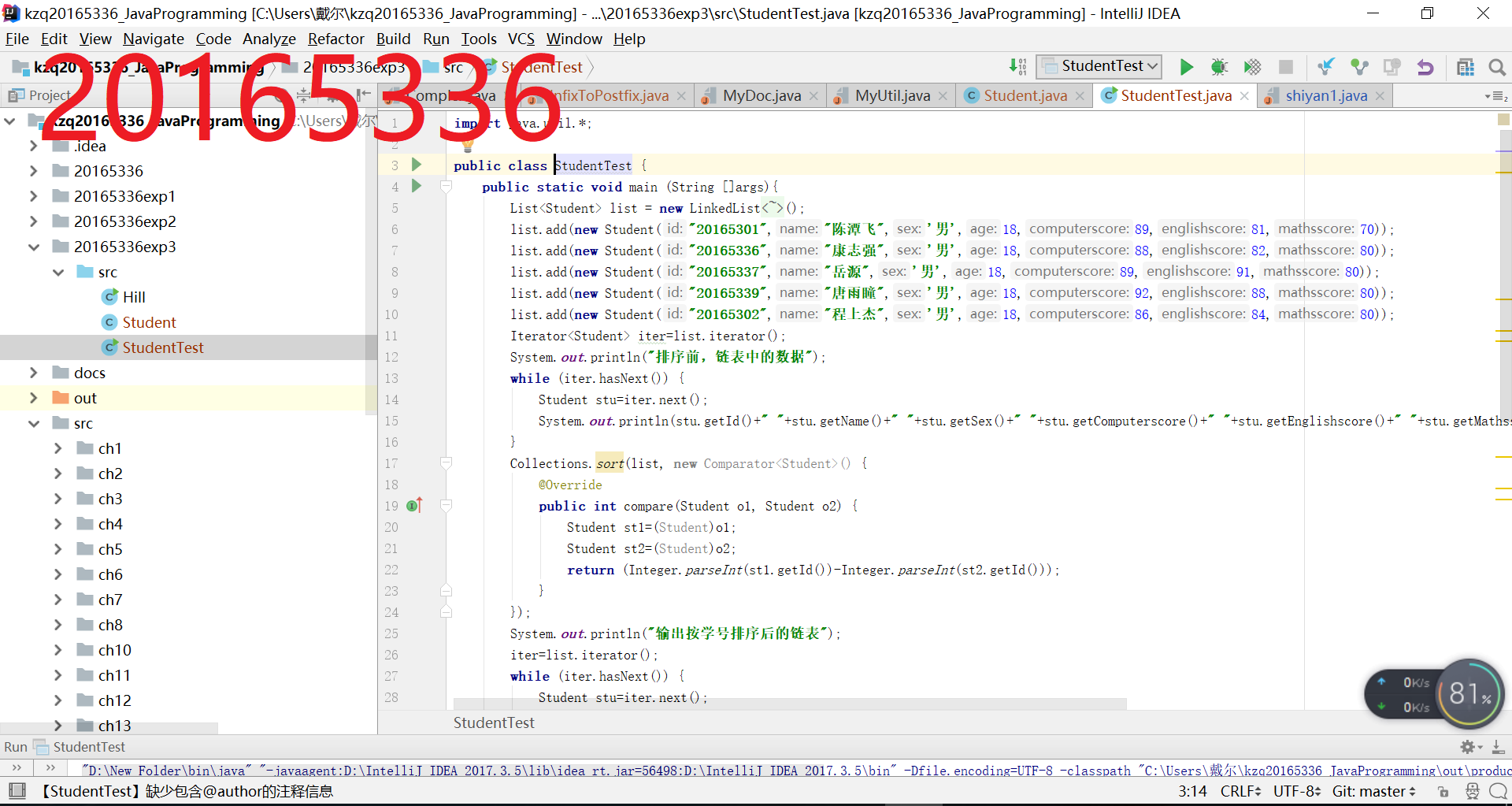
第二题:单链表


教材代码分析
- 例子一:声明了一个泛型类Cone,Cone对象计算体积时,只关心他的底是否能计算面积并不关心底的类型。
- 例子二:比较了迭代器与使用get方法的优缺点。
- 例子三:告诉我们老版本JDK的链表需要把节点中的对象进行强制转换,而泛型类建立时不用转换比较方便。
- 例子四:建立Student类运用Collections调用sort方法将链表中的对象按其height值升序排序。
- 例子五:运用洗牌为背景Collecttions类可以重新随机排列以及旋转链表中的数据。
- 例子六:堆栈的举例演示。
- 例子七:关于散列映射的举例,方便我们区分有无键值储存的区别。
- 例子八:树集举例演示。
- 例子九:运用键值储存数据,树映射与树集的不同是保证节点是按照结点中的关键字升序排序。
- 例子十:自动装箱与拆箱这是JDK新版本可以自动将基本类型实现到相应对象的转换。
课后编程题
第一题

import java.util.*;
public class An {
public static void main(String args[]){
Stack<Integer> stack= new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(new Integer(3));
stack.push(new Integer(8));
int k =1;
while(k<=10){
Integer F1 =stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2 =stack.pop();
int f2 =F2.intValue();
Integer temp = new Integer(2*f1+2*f2);
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(F2);
stack.push(F1);
stack.push(temp);
k++;
}
}
}
第二题
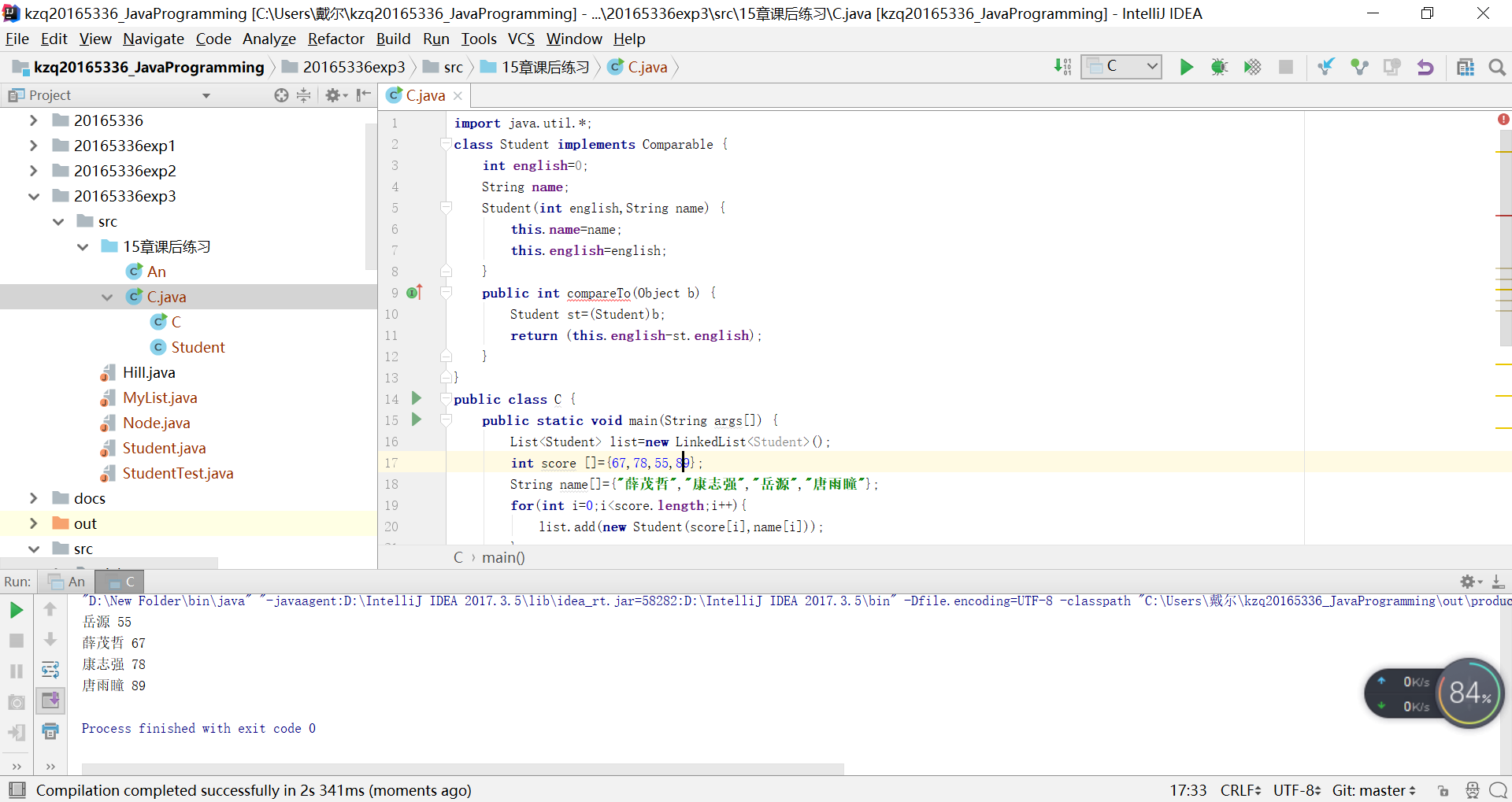
import java.util.*;
class Student implements Comparable {
int english=0;
String name;
Student(int english,String name) {
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
public int compareTo(Object b) {
Student st=(Student)b;
return (this.english-st.english);
}
}
public class C {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List<Student> list=new LinkedList<Student>();
int score []={67,78,55,89};
String name[]={"薛茂哲","康志强","岳源","唐雨瞳"};
for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){
list.add(new Student(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<Student> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<Student> mytree=new TreeSet<Student>();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Student stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<Student> te=mytree.iterator();
while(te.hasNext()) {
Student stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
第三题

import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key=0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
key=d;
}
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey disc=(UDiscKey)b;
if((this.key-disc.key)==0)
return -1;
else
return (int)((this.key-disc.key)*1000);
}
}
class UDisc{
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int m,double e) {
amount=m;
price=e;
}
}
public class K {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap= new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();
int amount[]={1,2,4,8,16};
double price[]={111,266,390,556};
UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4];
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount); }
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]); }
int number=treemap.size();
Collection<UDisc> collection=treemap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元"); }
treemap.clear();
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price); }
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]); }
number=treemap.size();
collection=treemap.values();
iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
}
}







