进程的切换和系统的一般执行过程
(1)进程调度的时机
1、schedule是一个内核函数,不是一个系统调用,进程的调度只发生在内核中,进程调度函数schedule()只能在内核中被调用,用户进程无法调用, 因此,进程切换需要用到实现用户态到内核态的切换。
2、中断处理过程直接调用schedule(),或者返回用户态时根据need_resched标记调用schedule()。内核线程是一个特殊的进程,只有内核态没有用户态,可以直接调用schedule()进行进程切换,也可以在中断处理过程中进行调度。
(2)进程上下文切换
1、进程切换(或称任务切换、上下文切换):为了控制进程的执行,内核必须有能力挂起正在CPU上执行的进程,并恢复以前挂起的某个进程的执行。
2、挂起正在CPU上执行的进程,与中断时保存现场不同。中断前后是在同一个进程上下文中,只是由用户态转向内核态执行。进程上下文包含了进程执行需要的所有信息:
用户地址空间:包括程序代码,数据,用户堆栈等
控制信息:进程描述符,内核堆栈等
硬件上下文
(3)关键代码分析
schedule()函数选择一个新的进程来运行,并调用context_switch进行上下文的切换,context_switch中的一个关键宏switch_to来进行关键上下文切换。
switch_to 宏中定义了 prev 和 next 两个参数:prev 指向当前进程,next 指向被调度的进程。
1)schedule的代码
asmlinkage__visible void __sched schedule(void)
{
struct task_struct *tsk = current;
sched_submit_work(tsk);
__schedule();
}
static void __sched __schedule(void)
{
struct task_struct *prev, *next;
unsigned long *switch_count;
struct rq *rq;
int cpu;
need_resched:
preempt_disable();
cpu = smp_processor_id();
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
rcu_note_context_switch(cpu);
prev = rq->curr;
schedule_debug(prev);
if (sched_feat(HRTICK))
hrtick_clear(rq);
/*
- Make sure that signal_pending_state()->signal_pending() below
- can't be reordered with __set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE)
- done by the caller to avoid the race with signal_wake_up().
*/
smp_mb__before_spinlock();
raw_spin_lock_irq(&rq->lock);
switch_count = &prev->nivcsw;
if (prev->state && !(preempt_count() & PREEMPT_ACTIVE)) {
if (unlikely(signal_pending_state(prev->state, prev))) {
prev->state = TASK_RUNNING;
} else {
deactivate_task(rq, prev, DEQUEUE_SLEEP);
prev->on_rq = 0;
/*
* If a worker went to sleep, notify and ask workqueue
* whether it wants to wake up a task to maintain
* concurrency.
*/
if (prev->flags & PF_WQ_WORKER) {
struct task_struct *to_wakeup;
to_wakeup = wq_worker_sleeping(prev, cpu);
if (to_wakeup)
try_to_wake_up_local(to_wakeup);
}
}
switch_count = &prev->nvcsw;
}
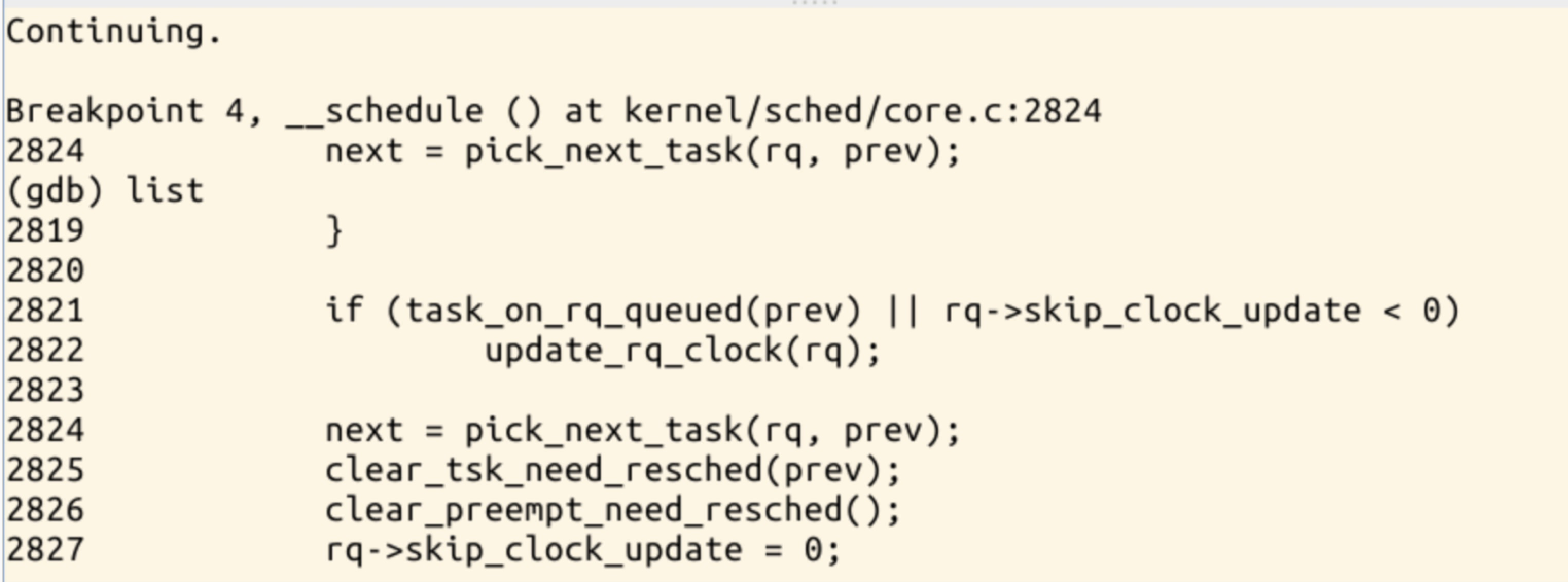
if (task_on_rq_queued(prev) || rq->skip_clock_update < 0)
update_rq_clock(rq);
next = pick_next_task(rq, prev);
clear_tsk_need_resched(prev);
clear_preempt_need_resched();
rq->skip_clock_update = 0;
if (likely(prev != next)) {
rq->nr_switches++;
rq->curr = next;
++*switch_count;
context_switch(rq, prev, next); /* unlocks the rq */
/*
* The context switch have flipped the stack from under us
* and restored the local variables which were saved when
* this task called schedule() in the past. prev == current
* is still correct, but it can be moved to another cpu/rq.
*/
cpu = smp_processor_id();
rq = cpu_rq(cpu);
} else
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&rq->lock);
post_schedule(rq);
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();
if (need_resched())
goto need_resched;
}
next = pick_next_task(rq, prev),封装了进程调度算法,使用某种进程调度策略选择下一个进程。
之后用context_switch(rq, prev, next),实现进程上下文的切换。
然后switch_to(prev,next, prev),切换堆栈和寄存器的状态。
2)stwitch_to的代码
asm volatile("pushfl
" /* save flags /
"pushl %%ebp
" / save EBP /
"movl %%esp,%[prev_sp]
" / save ESP /
"movl %[next_sp],%%esp
" / restore ESP /
"movl $1f,%[prev_ip]
" / save EIP /
"pushl %[next_ip]
" / restore EIP /
"jmp __switch_to
" / regparm call /
"1: "
"popl %%ebp
" / restore EBP /
"popfl
" / restore flags /
/ output parameters /
: [prev_sp] "=m" (prev->thread.sp),
/ =m 表示把变量放入内存,即把 [prev_sp] 存储的变量放入内存,最后再写入prev->thread.sp /
[prev_ip] "=m" (prev->thread.ip),
"=a" (last),
/=a 表示把变量 last 放入 ax, eax = last /
/ clobbered output registers: /
"=b" (ebx), "=c" (ecx), "=d" (edx),
/ b 表示放入ebx, c 表示放入 ecx,d 表示放入 edx, S表示放入 si, D 表示放入 edi /
"=S" (esi), "=D" (edi)
/ input parameters: /
: [next_sp] "m" (next->thread.sp),
/ next->thread.sp 放入内存中的 [next_sp] /
[next_ip] "m" (next->thread.ip),
/ regparm parameters for __switch_to (): /
[prev] "a" (prev),
/eax = prev edx = next/
[next] "d" (next)
: / reloaded segment registers */
"memory");
(3)Linux系统的运行过程

几种特殊情况:
①通过中断处理过程中的调度时机,用户态进程与内核线程之间互相切换和内核线程之间互相切换,与最一般的情况非常类似,只是内核线程运行过程中发生中断没有进程用户态和内核态的转换;
②内核线程主动调用schedule(),只有进程上下文的切换,没有发生中断上下文的切换,比最一般的情况略简略;
③创建子进程的系统调用在子进程中的执行起点及返回用户态,如fork一个子进程时;
④加载一个新的可执行程序后返回到用户态的情况,如execve系统调用加载新的可执行程序;
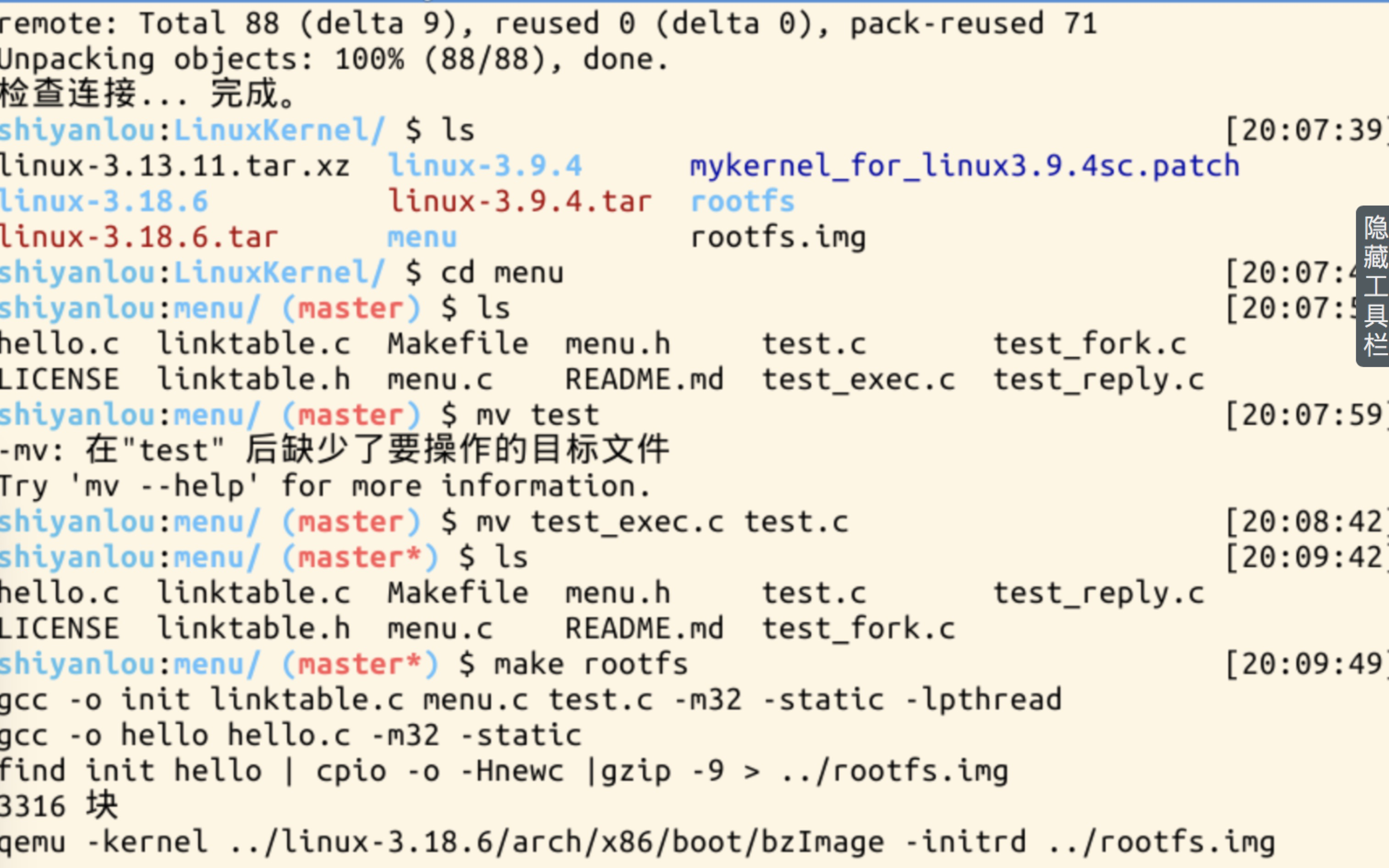
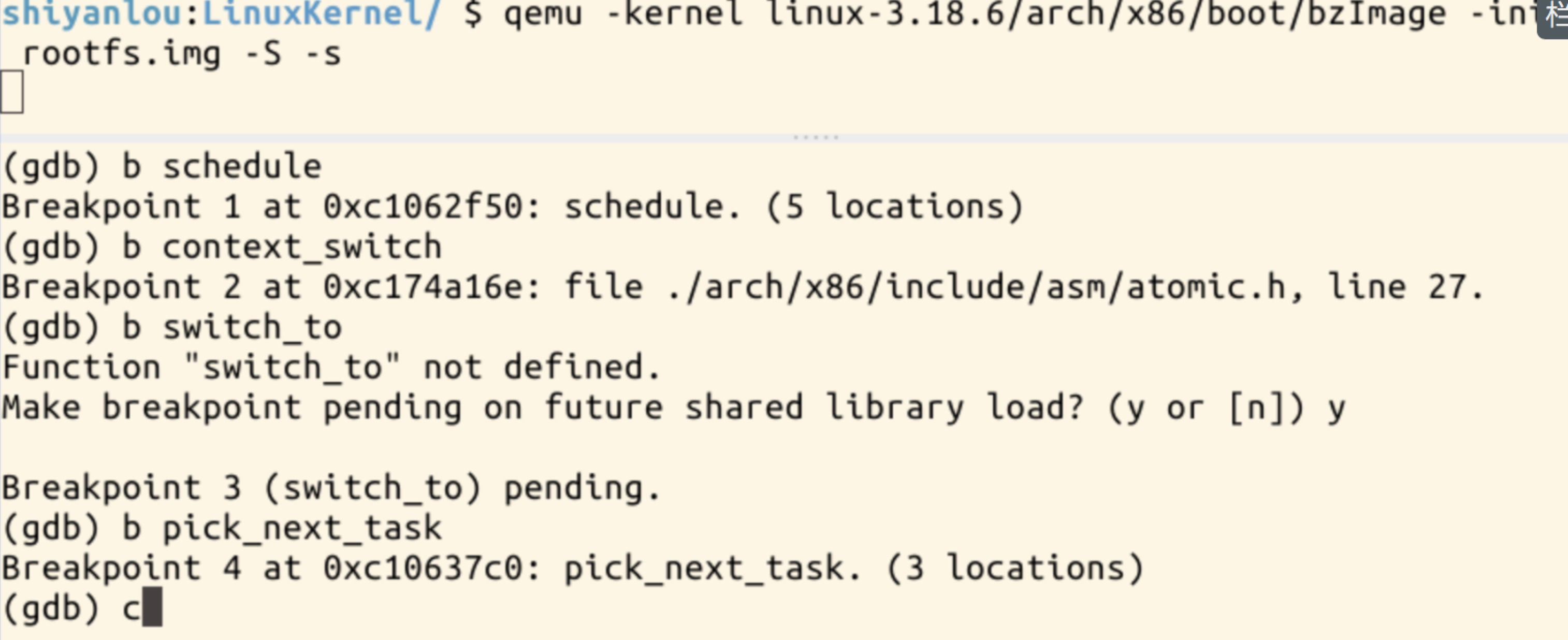
二、实验调试