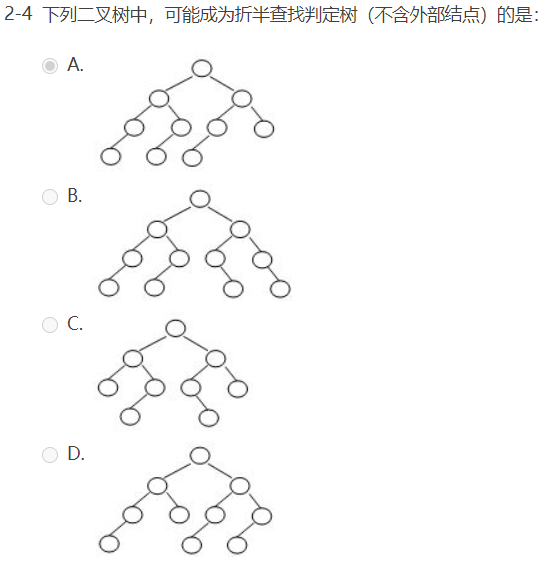
选择题:












函数题:
6-1 二分查找:
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define NotFound 0
typedef int ElementType;
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
List ReadInput(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表。元素从下标1开始存储 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P;
L = ReadInput();
scanf("%d", &X);
P = BinarySearch( L, X );
printf("%d
", P);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:
5
12 31 55 89 101
31
输出样例1:
2
输入样例2:
3
26 78 233
31
输出样例2:
0
代码:

Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X )
{
if(L == NULL)
return NotFound;//不符合条件,空
int low=1, high=L->Last;//设置左右指针
int mid;
while(low<=high)//左右指针相遇跳出循环
{
mid = (low+high)/2;
if(X>L->Data[mid])
low = mid+1;
else if(X<L->Data[mid])
high = mid-1;
else
return mid;
}
return NotFound;//未找到,空
}
6-2 线性探测法的查找函数:
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXTABLESIZE 100000 /* 允许开辟的最大散列表长度 */
typedef int ElementType; /* 关键词类型用整型 */
typedef int Index; /* 散列地址类型 */
typedef Index Position; /* 数据所在位置与散列地址是同一类型 */
/* 散列单元状态类型,分别对应:有合法元素、空单元、有已删除元素 */
typedef enum { Legitimate, Empty, Deleted } EntryType;
typedef struct HashEntry Cell; /* 散列表单元类型 */
struct HashEntry{
ElementType Data; /* 存放元素 */
EntryType Info; /* 单元状态 */
};
typedef struct TblNode *HashTable; /* 散列表类型 */
struct TblNode { /* 散列表结点定义 */
int TableSize; /* 表的最大长度 */
Cell *Cells; /* 存放散列单元数据的数组 */
};
HashTable BuildTable(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表 */
Position Hash( ElementType Key, int TableSize )
{
return (Key % TableSize);
}
#define ERROR -1
Position Find( HashTable H, ElementType Key );
int main()
{
HashTable H;
ElementType Key;
Position P;
H = BuildTable();
scanf("%d", &Key);
P = Find(H, Key);
if (P==ERROR)
printf("ERROR: %d is not found and the table is full.
", Key);
else if (H->Cells[P].Info == Legitimate)
printf("%d is at position %d.
", Key, P);
else
printf("%d is not found. Position %d is returned.
", Key, P);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:(-1表示该位置为空)
11
11 88 21 -1 -1 5 16 7 6 38 10
38
输出样例1:
38 is at position 9.
输入样例2:
11
11 88 21 -1 -1 5 16 7 6 38 10
41
输出样例2:
41 is not found. Position 3 is returned.
输入样例3:
11
11 88 21 3 14 5 16 7 6 38 10
41
输出样例3:
ERROR: 41 is not found and the table is full.
代码:

Position Find( HashTable H, ElementType Key )
{
Position p, p1;
int cts=0;
p = p1 =Hash(Key, H->TableSize);
while(H->Cells[p].Data!=Key&&H->Cells[p].Info!=Empty)
{
cts++;
if(cts == MAXTABLESIZE)
return ERROR;//若没有空单元,则返回ERROR
p = (p1 + cts)%H->TableSize;
}
return p;
}
6-3 分离链接法的删除操作函数:
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define KEYLENGTH 15 /* 关键词字符串的最大长度 */
typedef char ElementType[KEYLENGTH+1]; /* 关键词类型用字符串 */
typedef int Index; /* 散列地址类型 */
typedef enum {false, true} bool;
typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToLNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToLNode Position;
typedef PtrToLNode List;
typedef struct TblNode *HashTable; /* 散列表类型 */
struct TblNode { /* 散列表结点定义 */
int TableSize; /* 表的最大长度 */
List Heads; /* 指向链表头结点的数组 */
};
Index Hash( ElementType Key, int TableSize )
{
return (Key[0]-'a')%TableSize;
}
HashTable BuildTable(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表 */
bool Delete( HashTable H, ElementType Key );
int main()
{
HashTable H;
ElementType Key;
H = BuildTable();
scanf("%s", Key);
if (Delete(H, Key) == false)
printf("ERROR: %s is not found
", Key);
if (Delete(H, Key) == true)
printf("Are you kidding me?
");
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1: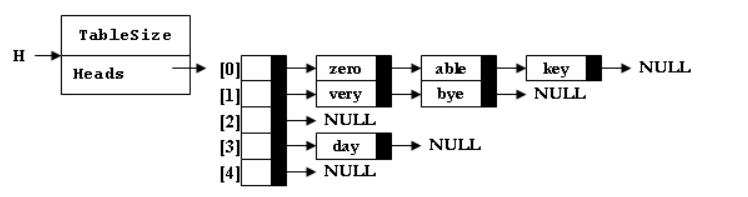
able
输出样例1:
able is deleted from list Heads[0]
输入样例2:(散列表如样例1图)
date
输出样例2:
ERROR: date is not found
代码:

bool Delete( HashTable H, ElementType Key )
{
Position p,q;
Index pos;//关键字地址
pos = Hash(Key, H->TableSize);//初始化散列位置
p = H->Heads[pos].Next;//从该邻接表第一个节点开始
while(p&&strcmp(p->Data, Key))//当未到表尾,并且Key未找到时
{
q = p;
p = p->Next;
}
if(p==NULL)
return false;
else
{
printf("%s is deleted from list Heads[%d]",Key,pos);
q = p->Next;
free(p);//删除p节点,释放p内存
return true;
}
}
编程题:
7-1 两个有序序列的中位数:

输入样例1:
5
1 3 5 7 9
2 3 4 5 6
输出样例1:
4
输入样例2:
6
-100 -10 1 1 1 1
-50 0 2 3 4 5
输出样例2:
1
代码:

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int a[100001]={0},b[100001]={0},c[200002]={0};//a,b分别用于存储两行数,c用于排序的时候按顺序填入
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)//读入两个数组的元素
{
if(i==0)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[j]);
}
if(i==1)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[j]);
}
}
int x=0,y=0;
int i=0;
while(x<n&&y<n)//分别进行比较, 按照升序依次填入c数组中,
{
if(a[x] > b[y])
{
c[i] = b[y];
i++;
y++;
}
else
{
c[i] = a[x];
i++;
x++;
}
}
while(y<n)//
{
c[i++] = a[y++];
}
while(x<n)//
{
c[i++] = b[x++];
}
int mid = (i-1)/2;//寻找中位数,
printf("%d",c[mid]);
return 0;
}
7-2 是否同一棵二叉搜索树:

输入样例:
4 2
3 1 4 2
3 4 1 2
3 2 4 1
2 1
2 1
1 2
0
输出样例:
Yes
No
No
代码:

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Tree
{
int data;
struct Tree *Left;
struct Tree *Right;
}TNode, *BTree;
void BuildT(BTree &T, int a)
{
if(T == NULL)
{
T = new Tree;
T->data = a;
T->Left = T->Right = NULL;
}
else
{
if(a<T->data)
BuildT(T->Left, a);
else
BuildT(T->Right, a);
}
}
int panduan(Tree *t1, Tree *t2)
{
if(!t1&&!t2)
return 1;
if(t1&&t2)
if(t1->data==t2->data )
if(panduan(t1->Left,t2->Left )&&panduan(t1->Right,t2->Right ))
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n, l,a;
int flag=0;
while(cin>>n)
{
Tree *t = NULL;
if(n == 0)
return 0;
cin>>l;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
BuildT(t, a);
}
while(l--)
{
Tree *tt = NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
BuildT(tt, a);
}
flag = panduan(t, tt);
if(flag==0)
cout<<"No"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
7-3 是否完全二叉搜索树:

输入样例1:
9
38 45 42 24 58 30 67 12 51
输出样例1:
38 45 24 58 42 30 12 67 51
YES
输入样例2:
8
38 24 12 45 58 67 42 51
输出样例2:
38 45 24 58 42 12 67 51
NO
代码:

#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int a[105];
int n,m;
void insert(int p, int data)
{
if(a[p] == 0)
{
a[p] = data;
return ;
}
if(data > a[p])
insert(p*2, data);
else
insert(p*2+1, data);
}
int main()
{
//int n,m;
//int a[105];
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(a, 0, sizeof(int));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&m);
insert(1, m);
}
int nn=0;;
int i=0;;
while(nn<n)
{
while(a[i] == 0)
i++;
if(nn)
printf(" %d", a[i]);
else
printf("%d",a[i]);
i++;
nn++;
}
if(i == n+1)
printf("
YES
");
else
printf("
NO
");
}
