扩展方法使你能够向现有类型“添加”方法,而无需创建新的派生类型、重新编译或以其他方式修改原始类型。 扩展方法是一种特殊的静态方法,但可以像扩展类型上的实例方法一样进行调用。这是msdn的描述。上面几句我看好多博客都是这样开头的。所以我也这样开头。
原本想着上一篇博客回顾了下泛型,将具体的模糊化,这个应该讲反射,将模糊的具体化,不过呢看了下反射东西不少,一晚上我也总结不完,还要留点时间打飞机呢。于是想了想就总结下扩展吧。
一、为什么要有扩展方法?
开头也说了,无需创建新的派生类型、重新编译或其他方式修改原始类型给现有类或接口添加方法。比如在没有扩展之前,会经常有一些helper工具类,例如处理字符串、时间的。有了扩展我们可以直接扩展字符串类或时间类就可以了,这样不用在实例化helper类就能直接处理。
二、扩展方法有什么特征?
扩展方法是静态方法,是类的一部分,但是实际上没有放在类的源代码中。
扩展方法所在的类也必须被声明为static
C#只支持扩展方法,不支持扩展属性、扩展事件等。
扩展方法的第一个参数是要扩展的类型,放在this关键字的后面,this后面的参数不属于方法的参数
在扩展方法中,可以访问扩展类型的所有公共方法和属性。
扩展方法扩展自哪个类型,就必须是此类型的变量来使用,其他类型无法使用
如果扩展方法和实例方法具有相同的签名,则优先调用实例方法
扩展自父类上的方法,可以被子类的对象直接使用
扩展自接口上的方法,可以被实现类的对象直接使用
扩展方法最终还是被编译器编译成:静态类.静态方法()
三、demo
上面几句基本总结把扩展总结完了,下面做一个demo来说明一下。
1.定义IAnimal接口 声明void Eat();方法
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExtensionMethod { public interface IAnimal { void Eat(); } }
2.定义Person类实现接口IAnimal实现void Eat();方法
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExtensionMethod { public class Person:IAnimal { public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("Person Eat"); } } }
3.定义扩展方法ExtensionMethod
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExtensionMethod { public static class ExtensionMethod { public static void Eat(this IAnimal iAnimal) { Console.WriteLine("IAnimalExtension Eat"); } public static void Sleep(this IAnimal iAnimal) { Console.WriteLine("IAnimalExtension Sleep"); } public static void Eat(this Person person) { Console.WriteLine("PersonExtension Eat"); } public static void Sleep(this Person person) { Console.WriteLine("PersonExtension Sleep"); } } }
上面在ExtensionMethod类中定义了4个扩展方法,两个是对接口IAnimal的扩展,两个是对Person类的扩展。
4.实例化测试
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExtensionMethod { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IAnimal p = new Person(); p.Eat(); p.Sleep(); Console.WriteLine("----------------这是底线------------------------"); Person p1 = new Person(); p1.Eat(); p1.Sleep(); Console.WriteLine("----------------这是底线------------------------"); ExtensionMethod.Eat(p); ExtensionMethod.Sleep(p); Console.WriteLine("----------------这是底线------------------------"); ExtensionMethod.Eat(p1); ExtensionMethod.Sleep(p1); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
上面Mian方法中,首先实例化了一个Person对象,赋值给IAnimal类型的变量,调用Eat()和Sleep()方法。然后又实例化了一个Person对象,这次赋值给Person类型的变量。
下面来看下运行结果是不是出乎意料:
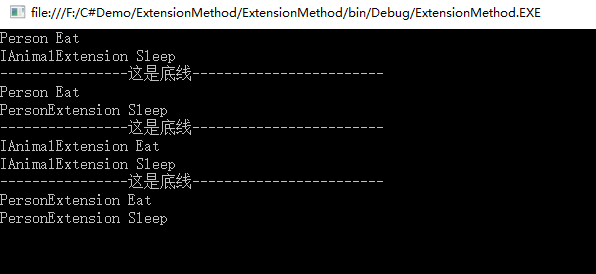
p和p1我们可以对比着来分析,对于Eat()方法都是输出"Person Eat",如果扩展方法和实例方法具有相同的签名,则优先调用实例方法,这句话正好能解释为什么。但是对于Sleep()方法,我们可以看到使用IAnimal类型的变量调用的是接口的扩展方法,使用Person类型的变量调用的是Person类型的扩展方法。扩展方法扩展自哪个类型,就必须是此类型的变量来使用,其他类型无法使用,与这句虽然有点出入,但也是蛮符合的。我是这样理解的:对于同名方法,实例方法优先扩展方法,自身扩展方法优先父类方法。 也可能是因为子类覆盖了父类的扩展方法。
我们可以把Person对的扩展方法注释,然后看下运行结果。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ExtensionMethod { public static class ExtensionMethod { public static void Eat(this IAnimal iAnimal) { Console.WriteLine("IAnimalExtension Eat"); } public static void Sleep(this IAnimal iAnimal) { Console.WriteLine("IAnimalExtension Sleep"); } //public static void Eat(this Person person) //{ // Console.WriteLine("PersonExtension Eat"); //} //public static void Sleep(this Person person) //{ // Console.WriteLine("PersonExtension Sleep"); //} } }

从上面的结果可以看到,扩展自接口上的方法,可以被实现类的对象直接使用,其实扩展自父类上的方法,可以被子类的对象直接使用和接口类似