一 render() redirect() HttpResponse() 响应 是个什么东西
def login(request): if request.method=='POST': username=request.POST.get('username') password=request.POST.get('password') userlist=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username,password=password) if userlist: obj1=redirect('/index/') print(obj1,type(obj1)) return obj1 obj=render(request,'login.html') print(obj,type(obj)) return obj
输出:
这是redirect() status_code: 302(临时移动) 服务器目前正从不同位置的网页响应请求,但请求者应继续使用原有位置来进行以后的请求。会自动将请求者转到不同的位置。但由于搜索引擎会继续抓取原有位置并将其编入索引,因此您不应使用此代码来告诉搜索引擎页面或网站已被移动。
<HttpResponseRedirect status_code=302, "text/html; charset=utf-8", url="/index/"> <class 'django.http.response.HttpResponseRedirect'>
这是render() status_code:200(成功) 服务器已成功处理了请求。通常,这表示服务器提供了请求的网页。
<HttpResponse status_code=200, "text/html; charset=utf-8"> <class 'django.http.response.HttpResponse'>
这是HttpResponse()
<HttpResponse status_code=200, "text/html; charset=utf-8"> <class 'django.http.response.HttpResponse'>
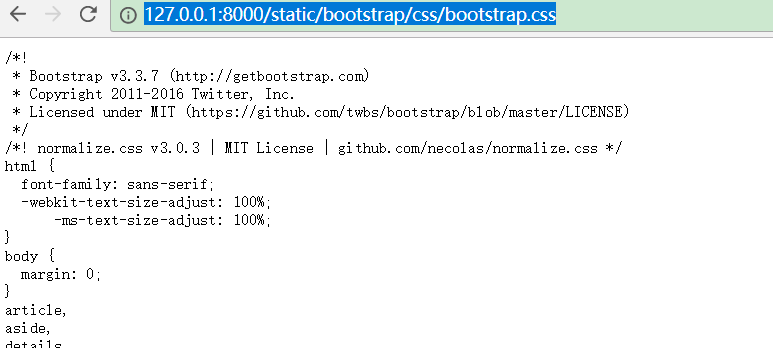
二 自己电脑上模拟CDN的效果
当用Django启动一个项目后,在自己的浏览器输入地址:http://127.0.0.1:8000/static/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.css,就可以依照路径取到相对应的文件,厉害了。