【前言】
面向资源的 Restful 风格的 api 接口本着简洁,资源,便于扩展,便于理解等等各项优势,在如今的系统服务中越来越受欢迎。
.net平台有WebAPi项目是专门用来实现Restful api的,其良好的系统封装,简洁优雅的代码实现,深受.net平台开发人员所青睐,在后台服务api接口中,已经逐步取代了辉煌一时MVC Controller,更准确地说,合适的项目使用更加合适的工具,开发效率将会更加高效。
python平台有tornado框架,也是原生支持了Restful api,在使用上有了很大的便利。
Java平台的SpringMVC主键在Web开发中取代了Struts2而占据了更加有力的地位,我们今天着重讲解如何在Java SpringMVC项目中实现Restful api。
【实现思路】
Restful api的实现脱离不了路由,这里我们的Restful api路由由spring mvc 的 controller来实现。
【开发及部署环境】
开发环境:Windows 7 ×64 英文版
Intellij IDEA 2017.2
部署环境:JDK 1.8.0
Tomcat 8.5.5
测试环境:chrome
fiddler
【实现过程】
1、搭建spring mvc maven项目
这里的搭建步骤不再赘述,如有需要参考,请导航至博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/qixiaoyizhan/p/5819392.html
2、新建控制器 StudentController
为了体现Restful api 我们采用注解,RequestMapping("/api/Student")
具体的代码如下:
1 package Controllers; 2 3 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; 4 5 @RestController 6 @RequestMapping("/api/Student") 7 public class StudentController { 8 9 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) 10 public String Get() { 11 return "{"id":"1","name":"1111111111"}"; 12 } 13 14 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) 15 public String Post() { 16 return "{"id":"2","name":"2222222222"}"; 17 } 18 19 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT) 20 public String Put() { 21 return "{"id":"3","name":"3333333333"}"; 22 } 23 24 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE) 25 public String DELETE() { 26 return "{"id":"4","name":"4444444444"}"; 27 } 28 29 @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) 30 public String Get(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { 31 return "{"id":""+id+"","name":"get path variable id"}"; 32 } 33 }
这里有Get,Post,Put,Delete分别对应 查询,添加,修改,删除四种对资源的操作,即通常所说的CRUD。
spring mvc可实现restful的方式有@Controller和@RestController两种方式,两种方式的区别如下:
@Controller的方式实现如果要返回json,xml等文本,方法体上需要额外添加@ResponseBody注解,例如:
1 @ResponseBody //用于返回json数据或者text格式文本 2 @RequestMapping(value = "/TestJson", method = RequestMethod.GET) 3 public String TestJson() { 4 return "{"id":"1001","name":"zhangsan"}"; 5 }
@RestController方式不需要写@ResponseBody,但是不能返回模型绑定数据和jsp视图,只能返回json,xml文本,仅仅是为了更加方便返回json资源而已。
上述的Rest方法中多写了个Get方法:
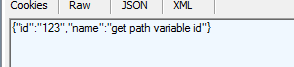
1 @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) 2 public String Get(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { 3 return "{"id":""+id+"","name":"get path variable id"}"; 4 }
该方法可以直接在url拼接一个参数,更加方便对资源的定向访问,例如查一个student list 可以默认空参数,而查询对应的某一个student详情信息,可以id=studentId 定向查询单条,使得我们对资源的访问更加快捷方便。
还有一种更加简洁的写法,Spring4.3中引进了{@GetMapping、@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping}几种写法,让接口的声明更加地简洁。下面代码展示了用这种注解方式进行Rest接口的定义:
1 package Controllers; 2 3 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; 4 5 @RestController 6 @RequestMapping("/api/Student") 7 public class StudentController { 8 9 @GetMapping() 10 public String Get() { 11 return "{"id":"1","name":"1111111111"}"; 12 } 13 14 @PostMapping() 15 public String Post() { 16 return "{"id":"2","name":"2222222222"}"; 17 } 18 19 @PutMapping() 20 public String Put() { 21 return "{"id":"3","name":"3333333333"}"; 22 } 23 24 @DeleteMapping() 25 public String DELETE() { 26 return "{"id":"4","name":"4444444444"}"; 27 } 28 29 @GetMapping(value = "/{id}") 30 public String Get(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { 31 return "{"id":"" + id + "","name":"get path variable id"}"; 32 } 33 }
【系统测试】
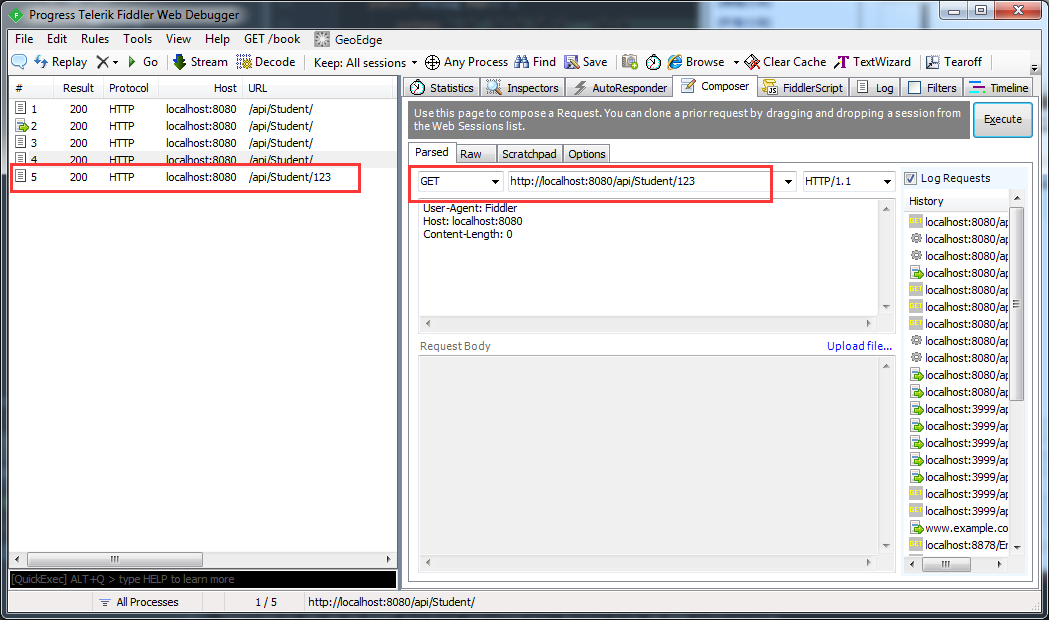
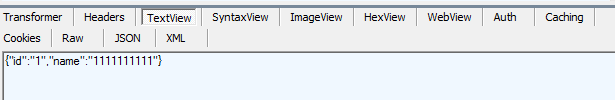
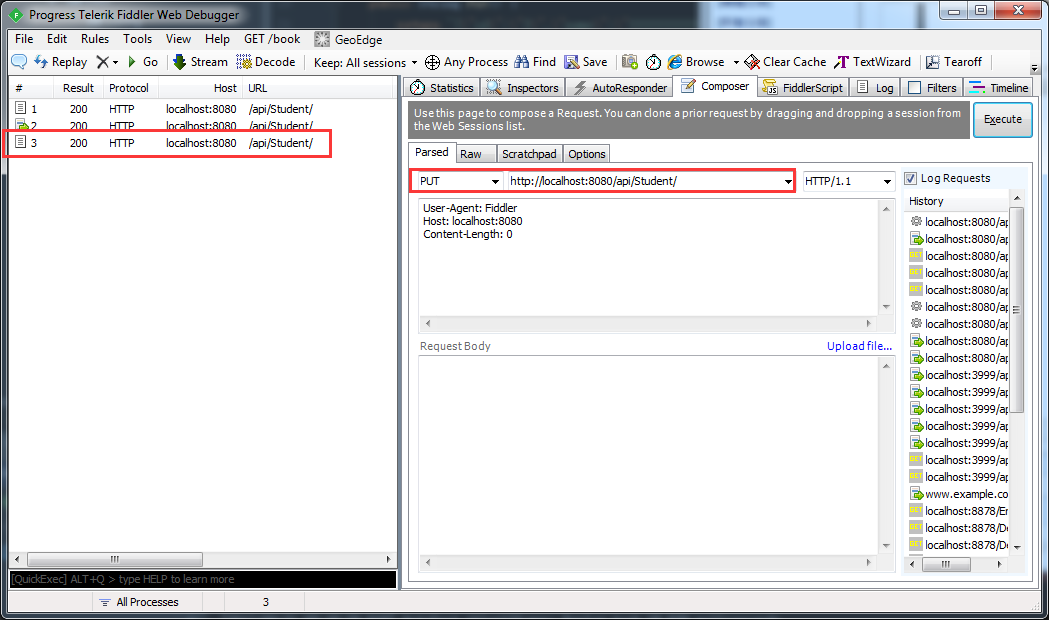
运行系统,使用fiddler调用restful api接口:
1.Get方式

2.Post方式


3.Put方式
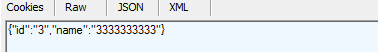
4.Delete方式
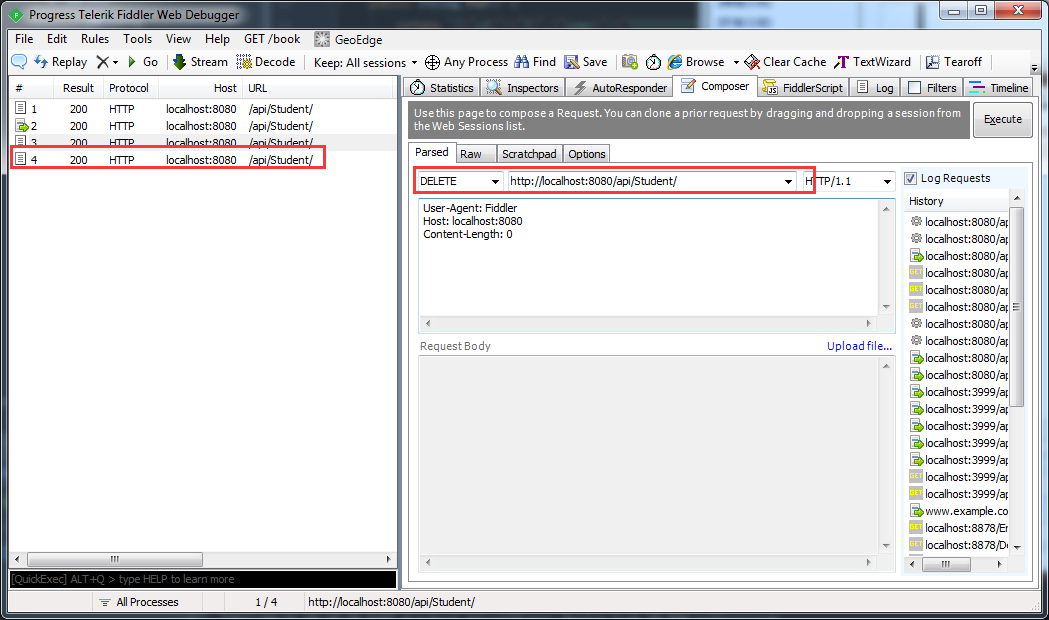
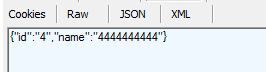
5.Get/id方式