一、配置Nginx隐藏版本号
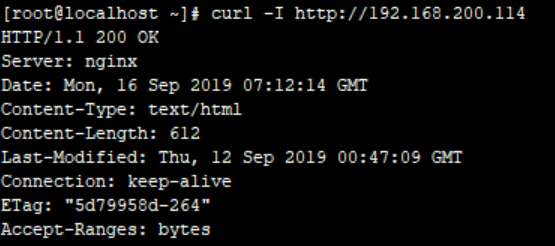
查看头部信息:curl -I http://192.168.200.114
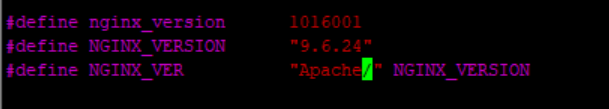
1、修改源码包(在安装之前)
如果装完了nginx先卸掉,步骤如下:
[root@localhost ~]# killall -9 nginx
[root@localhost ~]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.16.1/
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# make clean
rm -rf Makefile objs
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# rm -rf /usr/src/nginx-1.16.1/
正式的步骤:
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.16.1/
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# vim src/core/nginx.h
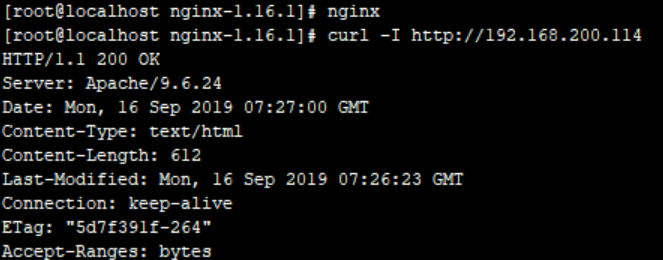
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module && make && make install
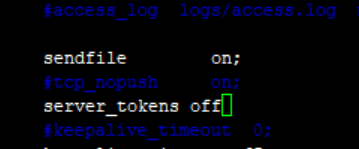
2、修改配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx

补充:LNMP:Linux Nginx Mysql Php
LAMP:Linux Apache Mysql Php
WAMP:Windows Apache Mysql Php
LNMMP:LNMP:Linux Nginx Mysql Memcached Php
LNMT:Linux Nginx Mysql Tomcat
二、修改Nginx 的用户和组
两种方式:在安装时直接--user=nginx/--group=nginx
或安装之后 在配置文件里修改
如果不去修改用户和组的话nginx默认是一个低级权限的用户的身份(nobody)来运行的,它对系统的资源以及文件的管控是有限制的。
1、[root@localhost ~]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module && make && make install
2、[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf

[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx
[root@localhost ~]# ps uax | grep nginx
root 42587 0.0 0.1 48084 1980 ? Ss 15:26 0:00 nginx: master process nginx
nginx 43272 0.0 0.3 51908 3436 ? S 16:26 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 43273 0.0 0.3 51908 3436 ? S 16:26 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 43279 0.0 0.0 112656 972 pts/2 R+ 16:26 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
三、配置Nginx网页缓存时间
当Nginx将网页数据返货给客户端后,可设置资源在客户端的缓存的时间,以方便客户端在日后进行相同内容的请求时直接返回,以避免重复请求,加快了访问的速度,一般针对静态网页进行设置,对动态网页不可设置缓存时间,可在Windows客户端中使用fiddier查看网页缓存时间。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf

测试:现在网上下载一个图片linux.jpg
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
[root@localhost html]# killall -HUP nginx

四、实现Ngnix日志的切割(脚本)
[root@localhost ~]# tail -f /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log 这是Nginx的一个日志
#!/bin/bash
#cut_nginx_log.sh
[root@localhost ~]# vim /opt/cut_nginx_log.sh
添加以下内容:
datetime=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d")
log_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs"
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
[ -d $log_path/backup ] || mkdir -p $log_path/backup
if [ -f $pid_path ]
then
mv $log_path/access.log $log_path/backup/access.log-$datetime
kill -USR1(它会给进程传递一个信号:创建一个新的日志) $(cat $pid_path)
find $log_path/backup -mtime +30 | xargs rm -f(只保留近30天的日志)
else
echo " Error,Nginx is not working!" | tee -a /var/log/massages
fi
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /opt/cut_nginx_log.sh
[root@localhost ~]# /opt/cut_nginx_log.sh
[root@localhost ~]# ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/backup/
access.log-20190915
生成了一个新的日志
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log 里面是空的,因为是新产生的
[root@localhost ~]# tail -f /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log

[root@localhost ~]# killall -9 nginx //把nginx关掉
[root@localhost ~]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid //把pid文件删除
[root@localhost ~]# /opt/cut_nginx_log.sh //在执行一遍就报错了
Error,Nginx is not working!
并且这个信息还会保存到 /var/log/massages下
做一个周期性的计划任务:分时日月周
[root@localhost ~]# crontab -e
五、配置Nginx连接超时
在企业网站中,为了避免同一个客户长时间占用连接,造成服务资源浪费,可以设置相应的连接超时参数,实现控制连接访问时间。
keepalive_timeout 65; //保持的连接时间,默认为65秒
client_header_timeout 60; //设置客户端的等待的请求头的时间
client_body_timeout 60; //等待客户端的主体

[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# nginx
[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx
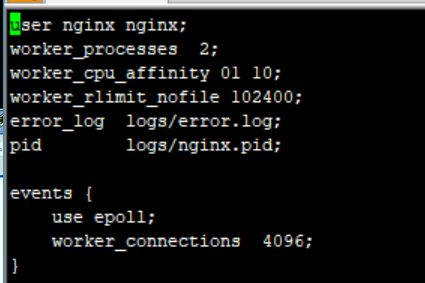
六、更改Nginx运行的进程数量
修改配置文件的worker_processes参数,一般设置为CPU的个数或者倍数
七、配置Nginx实现网页压缩功能
用户访问网站时就是在网站上下载资源
Nginx的ngx_http_gzip_module压缩模块提供了对文件内容压缩的功能,允许nginx服务区将输出内容发送到客户端之间进行压缩,以节约网站贷款,提升用户的访问体验,模块默认以安装。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
添加以下内容:
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain text/javascript application/x-javascript text/css text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss;

[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx
八、配置Nginx实现防盗链功能
再开一个虚拟机192.168.200.115,安装Nginx
115想要盗取114的图片
复制114的图片地址:http://192.168.200.114/linux.jpg
需修改配置文件:[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html


开始防盗:
配置说明:valid referers 设置信任的网站
none 浏览器在访问时有一个referer,告诉浏览器我是从那个页面的链接过来的,服务器基此可获得一些信息用于处理
blocked referer不为空的情况,用户直接访问图片
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
添加以下内容:
location ~* .(wma|wmv|asf|mp3|mmf|zip|rar|jpg|gif|png|swf|flv)$ {
valid_referers none blocked *.source.com source.com;
if ($valid_referers) {
rewrite ^/ http://www.source.com/error.jpg;
}
}
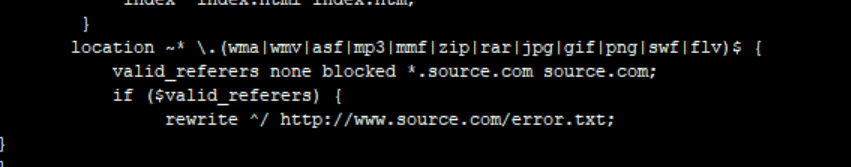
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/error.txt

[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx
去115的网页强制刷新(Ctrl+F5)
九、对FPM模块进行参数优化
Nginx的PHP解析功能实现如果是交由FPM(fastcgi 进程管理器)处理的,为了提高PHP的处理速度。可以对FPM模块进行参数跳转
Ngingx是通过FPM调用的PHP
FPM优化参数:
pm:使用哪种方法启动fpm进程,可以说是static和dynamic。前者将产生固定数量的fpm进程,后者将以动态的方式产生fpm进程。
pm.max_children:static方式下开启的fpm进程数
pm.start_servers:动态方式下初始的fpm进程数量
pm.min_spare_servers:动态方式下最小的fpm空闲进程数
pm.max_spare_servers:动态方式下最大的fpm空闲进程数
注:以上的调整要根据服务器的内存与服务器的负载进行调整
十、Ngingx为目录添加访问控制
1、用户访问控制
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
在配置文件里添加以下内容
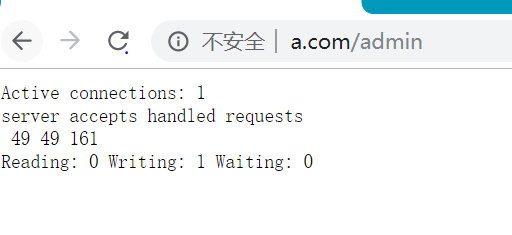
location /admin {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost ~]# killall -HUP nginx
如果谁都可以金的话就不安全,所以要做一些限制
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install httpd-tools
[root@localhost ~]# which htpasswd
/usr/bin/htpasswd
第一次创建需要用-c,之后就不用了,因为如果一直有-c就一直只有一个用户,它会刷新重建
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user lty
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user lty
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user
lty:$apr1$PdqILTOU$MyDqX6OgHAJLilDq4m7oN/
basic:是一种认证方式,其实有两种认证方式:基本(基准)认证,摘要认证
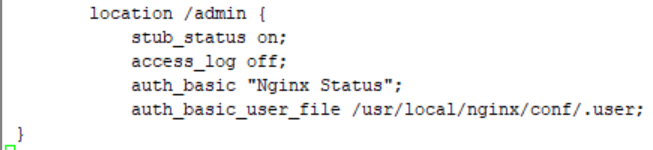
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
添加内容:
auth_basic "Nginx Status";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/.user;

2、客户端地址访问控制
在配置文件中添加 allow 192.168.200.0/24;就是允许200网段的客户端访问
deny 192.168.200.0/24;就是拒绝访问
十一、自定义错误页面
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@localhost html]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@localhost html]# vim 40x.html 在里面写入:
<img src="error.jpg" />
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
error_page 401 403 404 408 /40x.html;
location = /40x.html {
root html;
}
[root@localhost html]# killall -HUP nginx
十二、自动索引
[root@localhost ~]# cd -
/usr/local/nginx/html
[root@localhost html]# mkdir mirrors
[root@localhost html]# cd mirrors
[root@localhost mirrors]# mkdir {3..7}.{1..9}
[root@localhost mirrors]# ls
3.1 3.4 3.7 4.1 4.4 4.7 5.1 5.4 5.7 6.1 6.4 6.7 7.1 7.4 7.7
3.2 3.5 3.8 4.2 4.5 4.8 5.2 5.5 5.8 6.2 6.5 6.8 7.2 7.5 7.8
3.3 3.6 3.9 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.3 5.6 5.9 6.3 6.6 6.9 7.3 7.6 7.9
[root@localhost mirrors]# cd 7.9
[root@localhost 7.9]# ls
[root@localhost 7.9]# touch CentOS7.9.iso
[root@localhost 7.9]# cd
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 添加内容:
location /mirrors {
autoindex on;
}


十三、目录别名功能
十四、通过UA实现手机端和电脑端的分离
实现nginx区分pc和手机访问不同的网站,是物理上完全隔离的两套网站(一套移动端,一套pc端)这样带来的好处是pc端和移动端的内容可以不一样,移动版网站不需要包含特别多的内容,只要包含必要的文字和较小的图片,这样会更节省流量,有好处当然也会增加困难,难题就是你需要维护两套设备,并且需要自动识别出来用户的物理设备并跳转到相应的网站,当判断错误时,用户可以手动切换回正确的网站。
十五、nginx平滑升级版本
1、平滑升级概述
随着网站并发访问量越来越高,nginx web服务器也越来越流行,nginx换代越来越频繁,1.15.2版本的nginx更新了许多的新功能,生产环境中版本升级是必然的,但是线上业务不能停,此时nginx升级就是运维的重要的工作了。
2、nginx平滑升级原理
多进程模式下的请求分配方式
Nginx默认工作在多进程模式下,即主进程(master process)启动后完成配置加线和端口绑定等工作,fork出指定数量的工作进程(worker process),这些子进程会持有监听端口的文件描述符(fd)并通过在该描述上添加监听事件来接受连接(accept)。
信号的接受和处理
Nginx主进程在启动完成后会进入等待的状态,负责相应各类系统消息,如:SIGCHLD、SIGHP、SIGUSR2等。
Nginx信号简介
主进程支持的信号:
TIME INT:立刻退出
QUIT:等待工作进程结束后再退出
KILL:强制终止进程
HUP:重新加载配置文件,使用新的配置启动工作进程,逐步关闭旧的进程
USR1:重新打开日志文件
USR2:启动新的主进程,实现热升级
WINCH:逐步关闭工作进程
首先查看一下执行安装的命令
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: Apache/9.6.24
built by gcc 4.8.3 20140911 (Red Hat 4.8.3-9) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module
为了保证实验顺利,先杀死,再开
[root@localhost ~]# killall -9 nginx
[root@localhost ~]# nginx
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.16.1/
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module && make(不加make install,这样文件生成了就还没有放在指定的位置上)
3、备份二进制文件,用新版本的替换
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx old 把1.15版本的备份改名为old
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ 把1.16版本的拷进去,这样里面新旧版本都有了
4、确保配置文件无报错
[root@localhost nginx-1.16.1]# nginx -t 新的程序加载旧的配置文件看看有没有问题
5、发送USR2信息
[root@localhost ~]# ps ax | grep nginx
[root@localhost ~]# kill USR2 50882
[root@localhost ~]# ps ax | grep nginx
完成!!!
6、发送WINCH信号
[root@localhost ~]# kill WINCH 50882 旧的工作进程逐步退出
注:回滚步骤,发送HUP信号
7、发送QUIT信号
[root@localhost ~]# kill QUIT 50882
结束!!!
十六、查看CPU相关信息
1、查看CPU型号
[root@localhost ~]# grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo | uniq
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'physical id' /proc/cpuinfo
2、查看物理CPU个数
[root@localhost ~]# grep 'physical id' /proc/cpuinfo | uniq | ec -l
3、查看CPU核心数
grep 'core id' /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l
4、查看CPU线程数
grep 'processor' /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l