题目描述
在 W 星球上有 n 个国家。为了各自国家的经济发展,他们决定在各个国家 之间建设双向道路使得国家之间连通。但是每个国家的国王都很吝啬,他们只愿 意修建恰好 n – 1 条双向道路。 每条道路的修建都要付出一定的费用,这个费用等于道路长度乘以道路两端 的国家个数之差的绝对值。例如,在下图中,虚线所示道路两端分别有 2 个、4 个国家,如果该道路长度为 1,则费用为 1×|2 – 4|=2。图中圆圈里的数字表示国 家的编号。 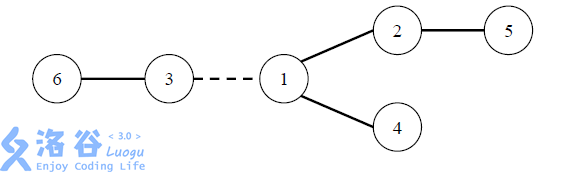
由于国家的数量十分庞大,道路的建造方案有很多种,同时每种方案的修建 费用难以用人工计算,国王们决定找人设计一个软件,对于给定的建造方案,计 算出所需要的费用。请你帮助国王们设计一个这样的软件。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
输入的第一行包含一个整数 n,表示 W 星球上的国家的数量,国家从 1 到 n 编号。 接下来 n – 1 行描述道路建设情况,其中第 i 行包含三个整数 ai、bi和 ci,表 示第 i 条双向道路修建在 ai与 bi两个国家之间,长度为 ci。
输出格式:
输出一个整数,表示修建所有道路所需要的总费用。
哇, noi , 好怕怕,哎?好像有点水...
首先这是一棵树, size[i]表示以i为节点的子树的大小, 设一个点为i, 它的父亲节点为fa, 则显然两个点的相差的国家为(n - 2 * size[i]), 这样可以用bfs或dfs预处理出每个点子树的大小, 然后枚举每条边即可, 洛谷dfs就可以过, 本校oj需要bfs。。。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int MAXN = 1e6 + 100; //const int MAXM = 3e3 + 10; template < typename T > inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; T ff = 1, ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) { if(ch == '-') ff = -1; ch = getchar(); } while(isdigit(ch)) { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar(); } x *= ff; } template < typename T > inline void write(T x) { if(x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x; if(x > 9) write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 + '0'); } struct edge { int y, v, next; }e[MAXN << 1]; int n, size[MAXN], fa[MAXN]; int tot = 1, lin[MAXN]; int id[MAXN], ti = 0; ll ans; inline void add(int xx, int yy, int vv) { e[++tot].y = yy; e[tot].v = vv; e[tot].next = lin[xx]; lin[xx] = tot; } /*void DFS(int x) { size[x] = 1; for(int i = lin[x], y; i; i = e[i].next) { if(size[y = e[i].y]) continue; DFS(y); ans += (ll)abs(n - 2 * size[y]) * e[i].v; size[x] += size[y]; } }*/ void BFS() { queue < int > q; q.push(1); while(!q.empty()) { int x = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = lin[x], y; i; i = e[i].next) { if((y = e[i].y) != fa[x]) { fa[y] = x; q.push(y); id[++ti] = y; } } } } int main() { // freopen("1.in", "r", stdin); read(n); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { int x, y, v; read(x); read(y); read(v); add(x, y, v); add(y, x, v); } for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) size[i] = 1; BFS(); for(int i = ti; i >= 1; --i) size[fa[id[i]]] += size[id[i]]; for(int i = 2; i <= tot; i += 2) { int x = e[i].y, y = e[i ^ 1].y; int mi = min(size[x], size[y]); ans += (ll)abs(n - 2 * mi) * e[i].v; } // DFS(1); write(ans); return 0; }