最近有项目对于性能要求非常高,虽然系统大部分都是IO密集型,但也不排除有计算密集型的操作,比如将来在项目中采用了Mongdb,那么将会有非常多的机会对大的泛型集合进行查询,计算(比如sum操作)等,多少能起到一定的性能提升作用,多核心CPU如果不充分利用起来实在有些可惜。
文中的部分代码均参考Parallel Programming with Microsoft .NET,这篇文章是以第五章后面的习题来分享。题目给了一个思路,对于一个过程是否可以采取并行运算,最好事先画一张流程图,看看哪些部分是可以并行的,即之间没有任何的依赖关系,图中能放在一个水平线上的即表示可以并行的部分。
说明:
1:本文的代码不考虑IO,即全部代码都是在CPU中执行,对于有IO的情况,会在后面的文章中做充分的尝试。
2:测试环境是:Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU T9550 @2.66GHZ
题目:将下面代码并行起来。
var b = F1(a); var d = F2(c); var e = F3(b,d); var f = F4(e); var g = F5(e); var h = F6(f,g);
首先我们来看下这6个函数的执行流程图,图中箭头代表依赖方向,线上的字母分别代表输入输出参数。
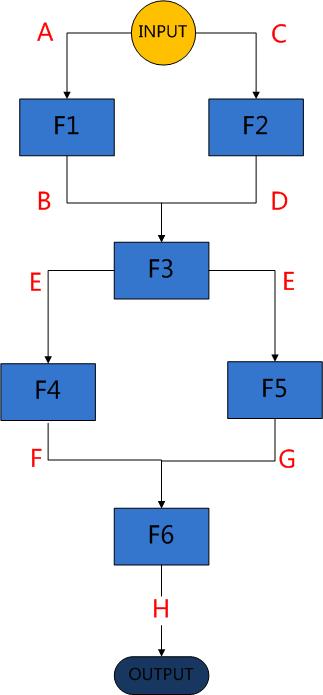
分析:从图中可以看出,F1,F2在同一水平线了,同样,F4,F5也在同一水平线上,这说明这两部分是可以并行的。
测试的核心函数是一个数字累加的过程:
 View Code
View Code
/// Simulates a CPU-intensive operation on a single core. The operation will use approximately 100% of a
/// single CPU for a specified duration.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="seconds">The approximate duration of the operation in seconds</param>
/// <returns>true if operation completed normally; false if the user canceled the operation</returns>
public static bool DoCpuIntensiveOperation(double seconds)
{
return DoCpuIntensiveOperation(seconds, CancellationToken.None, false);
}
/// <summary>
/// Simulates a CPU-intensive operation on a single core. The operation will use approximately 100% of a
/// single CPU for a specified duration.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="seconds">The approximate duration of the operation in seconds</param>
/// <param name="token">A token that may signal a request to cancel the operation.</param>
/// <param name="throwOnCancel">true if an execption should be thrown in response to a cancellation request.</param>
/// <returns>true if operation completed normally; false if the user canceled the operation</returns>
public static bool DoCpuIntensiveOperation(double seconds, CancellationToken token, bool throwOnCancel = false)
{
if (token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (throwOnCancel)
token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
return false;
}
long ms = (long)(seconds * 1000);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
long checkInterval = Math.Min(20000000, (long)(20000000 * seconds));
// loop to simulate a computationally intensive operation
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
i += 1;
// periodically check to see if the user has requested cancellation
// or if the time limit has passed
if (seconds == 0.0d || i % checkInterval == 0)
{
if (token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (throwOnCancel) token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
return false;
}
if (sw.ElapsedMilliseconds > ms)
return true;
}
}
}
6个函数内容如下,基本就是些加减法:
 View Code
View Code
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F1(int value)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(2.0);
return value * value;
}
/// <summary>
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F2(int value)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(1.0);
return value - 2;
}
/// <summary>
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F3(int value1, int value2)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(0.1);
return value1 + value2;
}
/// <summary>
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F4(int value)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(1.0);
return value + 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F5(int value)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(1.0);
return value + 5;
}
/// <summary>
/// A computationally intensive function
/// </summary>
static int F6(int value1, int value2)
{
SampleUtilities.DoCpuIntensiveOperation(1);
return value1 + value2;
}
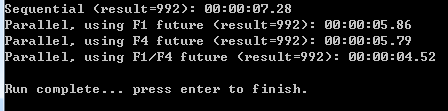
为了做对比,我分别做了以下几部分测试:
1:传统的顺序计算;
2:只将F1并行起来;
3:只将F4并行起来;
4:将F1,F4都并行起来。
/// Sequential example
/// </summary>
public static int Example1()
{
var a = 22;
var c = 11;
var b = F1(a);
var d = F2(c);
var e = F3(b,d);
var f = F4(e);
var g = F5(e);
var h = F6(f, g);
return h;
}
/// <summary>
/// A parallel example that uses the futures pattern for F1
/// </summary>
public static int Example2()
{
var a = 22;
var bf = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F1(a));
var c = F2(11);
var d = F3(bf.Result,c);
var f = F4(d);
var g = F5(d);
var h = F6(f , g);
return h;
}
/// <summary>
/// A parallel example that uses the futures pattern for F4
/// </summary>
public static int Example3()
{
var a = 22;
var b = F1(a);
var c = F2(11);
var d = F3(b, c);
var f = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F4(d));
var g = F5(d);
var h = F6(f.Result, g);
return h;
}
/// <summary>
/// A parallel example that uses the futures pattern for F1/F4
/// </summary>
public static int Example4()
{
var a = 22;
var bf = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F1(a));
var c = F2(11);
var d = F3(bf.Result, c);
var f = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F4(d));
var g = F5(d);
var h = F6(f.Result, g);
return h;
}
测试结果:从下图可以非常清晰的看出,在使用并行后,性能得到了明显的提升,如果在release下应该效果会更好。
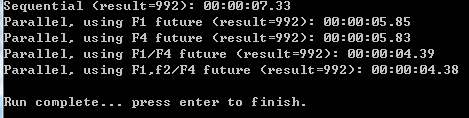
下面的一个测试,只是写法上的不同,从理论上来讲,和Example4对比没有实质的性能提升。如果两个任务可以并行,我们将其中一个task用并行模式即可。
/// 些种写法只是做一个对比,理论上没有性能提升
/// </summary>
public static int Example5()
{
var a = 22;
var bf = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F1(a));
var c = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F2(11));
var d = F3(bf.Result, c.Result);
var f = Task<int>.Factory.StartNew(() => F4(d));
var g = F5(d);
var h = F6(f.Result, g);
return h;
}
执行的测试结果图如下:
总结:并行运算是个好东西,主要是需要搞清楚它的适用场景,它主要针对计算型的运算,如果都是些数据库操作之类的IO访问,作用并不是特别大,如果处理的数据量不大,性能也不会有提升,反而也许会有影响,创建线程也是需要开销的,核心的就是确认好适用场景,然后是确认可以并行的部分。对于IO操作,下面的内容我会根据实际情况做些测试,本文有什么不对的地方,希望大家批评指正。
