长沙大佬的博客
Orz高一进队,Orz pku一本,跟我这种人真是云泥之别
今年二月我还不知道在哪个地方玩泥巴的时候人家都已经把插头dp打得炉火纯青了,Orz orz
大佬的博客写得非常好了,我就随便口胡两句
一开始不是很懂这玩意,直到看到另一个大佬说的一句话
“值得注意的一点是,插头不是表示将要去某处的虚拟状态,而是表示已经到达某处的现实状态。
也就是说,如果有一个插头指向某个格子,那么这个格子已经和插头来源联通了,我们接下来要考虑的是从这个插头往哪里走。”
任意条回路的情况,用轮廓线dp这个路径,轮廓线上就是若干向右或向支出来的部分,这种东西就被取名叫插头,用二进制状态表示每单位轮廓线上有没有这种支出来的插头-也就是一条路径经过它并且没成回路下一步要继续沿着支出的方向走。
如图,红色的是一条轮廓线,绿色代表插头,插头并不表示路径的方向,仅表示路径接下来应向那边延伸(浅绿色虚线代表这个期望的延伸)
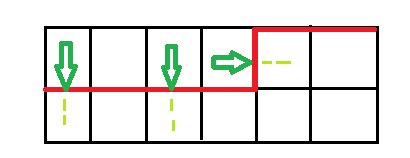
那么对于一个插头的转移看能往那边走就往那边转,如图,紫色代表转移后的轮廓线,粉色代表左右绿色插头的两种转移方式

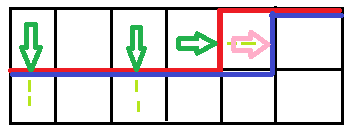
对于两个相邻的插头就直接连起来即可(如下图)。最后的答案就是在最后一个能走的格子中两个插头这样连起来的方案数(当然这时候这条轮廓线前面的那些绿色插头都是不存在的)。

任意条回路的方案数就很容易的求完了。
如果只有一条回路,就不能随便把两个插头连起来了(上一段加黑的部分)。因为两个插头代表的路径可能已经联通了,再相连的话就会提前形成一个回路(如下图,上方灰色的条路径使两个插头已经联通,再把浅绿的相连就形成回路了)。
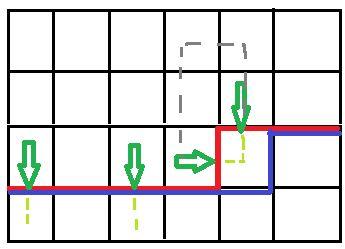
但如果是这样的路径连起来就是合法的,因为这两个插头一开始在灰色路径中并没有联通
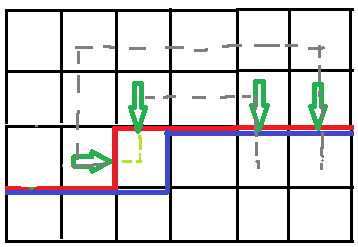
两种常用的处理办法:
1、最小表示法,我还没写过,不过NOI2007那道题构造转移的时候也是用最小表示法表示联通关系的,大概差不多吧
2、括号序列
这样的联通关系显然是构成括号序列的,那么只需要把二进制变成三进制,每个插头区分是左括号还是右括号就好了
转移的时候,b1,b2代表绿箭头指的两条轮廓线上的插头情况
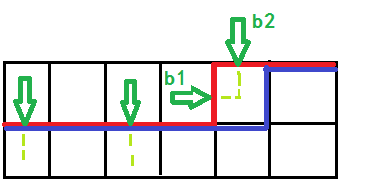
只有一个插头的情况连通性不改变,很好处理,主要需要注意这种转移(其余请转移参考最上面大佬的博客,主要是我懒得写了。。。)
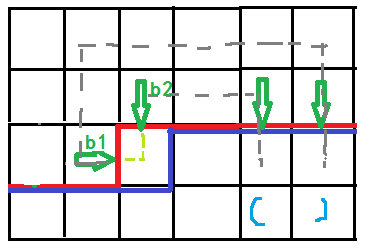
蓝色的是原来的括号序列,当用浅绿色把两个插头连起来时,联通性改变

括号序列就变成了这样,也就是找到右边对应的第一个右括号改成左括号即可,如下图。和这种转移对称的找左括号的转移同理。
Eat the Trees
真-最简单的插头dp入门题,因为不需要维护插头的连通性,每条线上只需要记有无插头,或许直接叫轮廓线dp比较合适。

1 //Achen
2 #include<algorithm>
3 #include<iostream>
4 #include<cstring>
5 #include<cstdlib>
6 #include<vector>
7 #include<cstdio>
8 #include<queue>
9 #include<cmath>
10 #include<set>
11 #include<map>
12 #define Formylove return 0
13 #define For(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
14 #define Rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
15 const int N=4107;
16 typedef long long LL;
17 typedef double db;
18 using namespace std;
19 int Cas,n,m,a[15][15],ex,ey;
20 LL ans,f[2][N];
21
22 template<typename T>void read(T &x) {
23 char ch=getchar(); x=0; T f=1;
24 while(ch!='-'&&(ch<'0'||ch>'9')) ch=getchar();
25 if(ch=='-') f=-1,ch=getchar();
26 for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; x*=f;
27 }
28
29 LL solve() {
30 LL rs=0;
31 int up=(1<<(m+1))-1,o=0;
32 For(i,0,up) f[o][i]=0;
33 f[o][0]=1;
34 For(i,1,n) {
35 For(j,1,m) {
36 o^=1;
37 For(s,0,up) f[o][s]=0;
38 For(s,0,up) if(f[o^1][s]) {
39 int ls=j==1?(s<<1):s,b1=(ls&(1<<(j-1))),b2=(ls&(1<<j));
40 if(!b1&&!b2&&!a[i][j]) f[o][ls]+=f[o^1][s];
41 else if(!b1&&!b2) {
42 if(a[i+1][j]&&a[i][j+1])
43 f[o][ls|(1<<(j-1))|(1<<j)]+=f[o^1][s];
44 }
45 else if(!b1) {
46 if(a[i+1][j])
47 f[o][(ls|(1<<(j-1)))^(1<<j)]+=f[o^1][s];
48 if(a[i][j+1])
49 f[o][ls]+=f[o^1][s];
50 }
51 else if(!b2) {
52 if(a[i+1][j])
53 f[o][ls]+=f[o^1][s];
54 if(a[i][j+1])
55 f[o][(ls^(1<<(j-1)))|(1<<j)]+=f[o^1][s];
56 }
57 else {
58 if(a[i][j]) {
59 f[o][ls^(1<<(j-1))^(1<<j)]+=f[o^1][s];
60 if(i==ex&&j==ey&&(ls^(1<<(j-1))^(1<<j))==0) {
61 rs+=f[o^1][s];
62 }
63 }
64 }
65 }
66 }
67 }
68 return rs;
69 }
70
71 int main() {
72 #ifdef ANS
73 freopen(".in","r",stdin);
74 freopen(".out","w",stdout);
75 #endif
76 read(Cas);
77 For(cas,1,Cas) {
78 read(n); read(m);
79 For(i,1,n) For(j,1,m){
80 read(a[i][j]);
81 if(a[i][j]) ex=i,ey=j;
82 }
83 ans=solve();
84 printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.
",cas,ans);
85 }
86 Formylove;
87 }
Formula1
需要维护连通性的真-插头dp. hasn的时候找到了没有return而是break和把Rep写成For调了半个小时。。。

1 //Achen
2 #include<algorithm>
3 #include<iostream>
4 #include<cstring>
5 #include<cstdlib>
6 #include<vector>
7 #include<cstdio>
8 #include<queue>
9 #include<cmath>
10 #include<set>
11 #include<map>
12 #define Formylove return 0
13 #define For(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
14 #define Rep(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
15 const int N=1594327,p=299983;
16 typedef long long LL;
17 typedef double db;
18 using namespace std;
19 int n,m,a[15][15],ex,ey,power[20];
20 char mp[15];
21
22 template<typename T>void read(T &x) {
23 char ch=getchar(); x=0; T f=1;
24 while(ch!='-'&&(ch<'0'||ch>'9')) ch=getchar();
25 if(ch=='-') f=-1,ch=getchar();
26 for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0'; x*=f;
27 }
28
29 LL f[2][N];
30 int S[2][N];
31
32 int o,fir[p+10],nxt[N],tot[2];
33 void ins(int s,LL val) {
34 int tp=s%p+1;
35 for(int i=fir[tp];i;i=nxt[i]) if(S[o][i]==s) {
36 f[o][i]+=val; return;
37 }
38 nxt[++tot[o]]=fir[tp]; fir[tp]=tot[o];
39 S[o][tot[o]]=s; f[o][tot[o]]=val;
40 }
41
42 //f 方案数 S hash前的状态 (4进制)
43 LL solve() {
44 LL rs=0;
45 o=1;
46 S[o][++tot[o]]=0;
47 f[o][tot[o]]=1;
48 For(i,1,n) For(j,1,m) {
49 o^=1;
50 tot[o]=0;
51 memset(fir,0,sizeof(fir));
52 For(zt,1,tot[o^1]) {
53 int s=j==1?(S[o^1][zt]<<2):S[o^1][zt];
54 LL num=f[o^1][zt];
55 int b1=(s>>(2*j-2))%4,b2=(s>>(2*j))%4;
56 if(!a[i][j]) {
57 if(!b1&&!b2) ins(s,num);
58 }
59 else if(!b1&&!b2) {
60 if(a[i+1][j]&&a[i][j+1]) ins(s+power[j-1]+power[j]*2,num);
61 }
62 else if(!b1) {
63 if(a[i+1][j]) ins(s+b2*power[j-1]-b2*power[j],num);
64 if(a[i][j+1]) ins(s,num);
65 }
66 else if(!b2) {
67 if(a[i][j+1]) ins(s-b1*power[j-1]+b1*power[j],num);
68 if(a[i+1][j]) ins(s,num);
69 }
70 else if(b1==1&&b2==1) {
71 int kl=1;
72 For(t,j+1,m) {
73 if((s>>(2*t))%4==1) kl++;
74 if((s>>(2*t))%4==2) kl--;
75 if(!kl) {
76 ins(s-power[j-1]-power[j]-power[t],num);
77 break;
78 }
79 }
80 }
81 else if(b1==2&&b2==2) {
82 int kl=1;
83 Rep(t,j-2,0) {
84 if((s>>(2*t))%4==2) kl++;
85 if((s>>(2*t))%4==1) kl--;
86 if(!kl) {
87 ins(s-2*power[j-1]-2*power[j]+power[t],num);
88 break;
89 }
90 }
91 }
92 else if(b1==2&&b2==1) ins(s-2*power[j-1]-power[j],num);
93 else if(b1==1&&b2==2&&i==ex&&j==ey)
94 rs+=num;
95 }
96 }
97 return rs;
98 }
99
100 int main() {
101 #ifdef ANS
102 freopen(".in","r",stdin);
103 freopen(".out","w",stdout);
104 #endif
105 read(n); read(m);
106 For(i,1,n) {
107 scanf("%s",mp+1);
108 For(j,1,m) if(mp[j]=='.') {
109 a[i][j]=1;
110 ex=i; ey=j;
111 }
112 }
113 power[0]=1;
114 For(i,1,15) power[i]=(power[i-1]<<2);
115 LL ans=solve();
116 printf("%lld
",ans);
117 Formylove;
118 }
