这里介绍下,
- 如何下载和编译 OpenVINO
- 利用 Benchmark 进行性能评估
- 如何利用 OpenVINO 提供的 Mutli-device Plugin 将模型加载到多个设备上
OpenVINO 专注于物联网场景,对于一些边缘端的低算力设备,借助 OpenVINO 可以通过调度 MKLDNN 库 CLDNN 库来在 CPU,iGPU,FPGA 以及其他设备上,加速部署的模型推理的速度;
一个标准的边缘端的推理过程可以分为以下几步:编译模型,优化模型,部署模型;
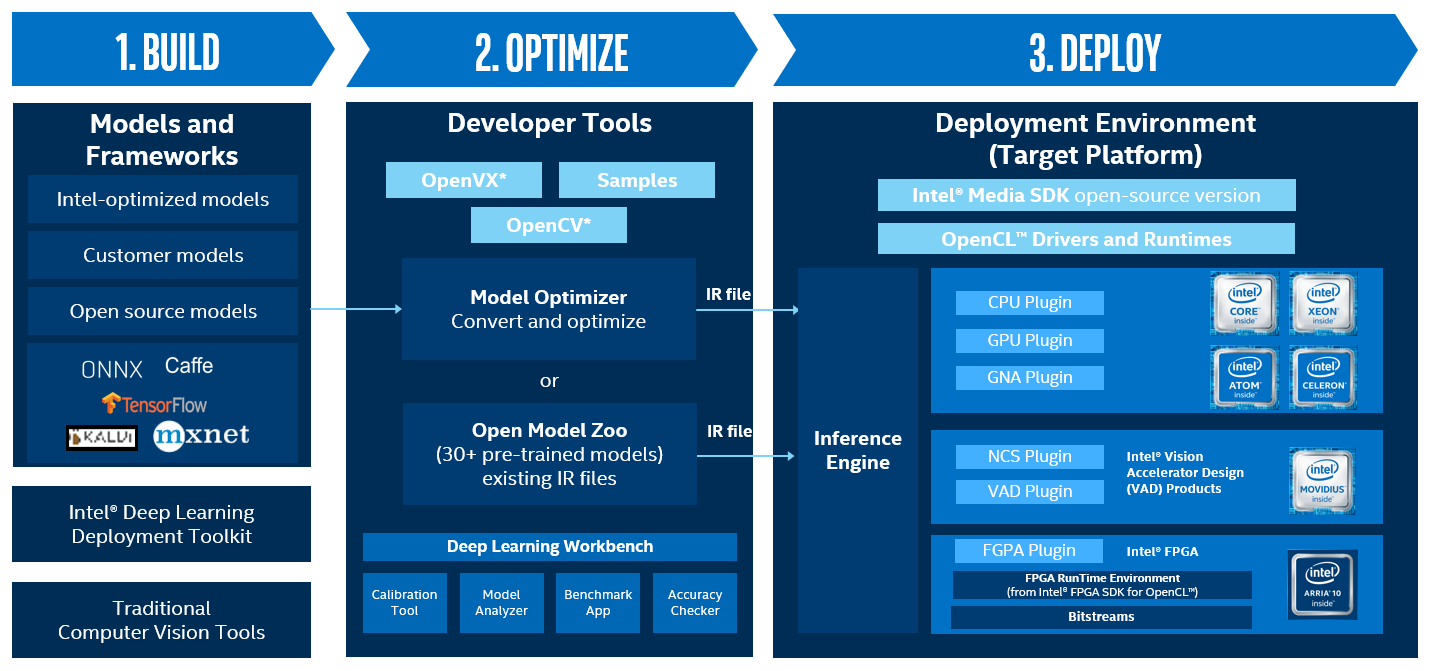
1. 下载和编译 OpenVINO
需要 clone 代码并且编译源码:
# 1. clone OpenVINO 源码 $ git clone https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino.git $ cd openvino $ git submodule update --init --recursive $ chmod +x install_dependencies.sh $ ./install_dependencies.sh # 2. 编译源码 $ cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DENABLE_PYTHON=ON -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3.6 .. $ make --jobs=$(nproc --all) # 3. 安装 $ cmake --install . --prefix /opt/intel/coneypo_test/ # 4. 启用 OpenVINO 环境 $ source /opt/intel/coneypo_test/bin/setupvars.sh # 注意配置 OpenCV 的环境,export 到 openvino 的路径 $ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/hddl/code/openvino/inference-engine/temp/opencv_4.5.2_ubuntu18/opencv/lib/
2. 通过 Benchmark app 来进行性能评估
2.1 硬件配置
我这边测试的主机硬件配置:
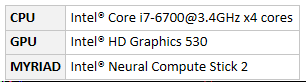
2.2 下载和转换模型
2.2.1 下载模型
以 alexnet 网络为例,借助 OpenVINO 提供工具,从 open model zoo,通过模型名称检索来进行下载:
$ cd /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/
$ /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader# python3 downloader.py --name alexnet ################|| Downloading models ||################ ========== Downloading /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/public/alexnet/alexnet.prototxt ... 100%, 3 KB, 36857 KB/s, 0 seconds passed ========== Downloading /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/public/alexnet/alexnet.caffemodel ... 100%, 238146 KB, 13041 KB/s, 18 seconds passed ################|| Post-processing ||################ ========== Replacing text in /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/public/alexnet/alexnet.prototxt
2.2.2 转换模型
需要将 caffe 模型转换成 OpenVINO 的 IR 文件:
$ cd /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer
$ python3 mo.py --input_model /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tool Model Optimizer arguments: Common parameters: - Path to the Input Model: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/public/alexnet/alexnet.caffemodel - Path for generated IR: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/. - IR output name: alexnet - Log level: ERROR - Batch: Not specified, inherited from the model - Input layers: Not specified, inherited from the model - Output layers: Not specified, inherited from the model - Input shapes: Not specified, inherited from the model - Mean values: Not specified - Scale values: Not specified - Scale factor: Not specified - Precision of IR: FP32 - Enable fusing: True - Enable grouped convolutions fusing: True - Move mean values to preprocess section: None - Reverse input channels: False Caffe specific parameters: - Path to Python Caffe* parser generated from caffe.proto: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo/utils/../front/caffe/proto - Enable resnet optimization: True - Path to the Input prototxt: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/open_model_zoo/tools/downloader/public/alexnet/alexnet.prototxt - Path to CustomLayersMapping.xml: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo/utils/../../extensions/front/caffe/CustomLayersMappin - Path to a mean file: Not specified - Offsets for a mean file: Not specified - Inference Engine found in: /opt/intel/zt_auto/python/python3.6/openvino Inference Engine version: 2.1.custom_zt/AutoPlugin_c6e9314a9e96f74183023323dc6a026cd0b4549e Model Optimizer version: custom_zt/AutoPlugin_c6e9314a9e96f74183023323dc6a026cd0b4549e [ SUCCESS ] Generated IR version 10 model. [ SUCCESS ] XML file: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/alexnet.xml [ SUCCESS ] BIN file: /opt/intel/zt_debug/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/alexnet.bin [ SUCCESS ] Total execution time: 19.84 seconds. [ SUCCESS ] Memory consumed: 1513 MB.
alexnet.xml 和 alexnet.bin 就是 OpenVINO 所需要的模型 IR 文件;
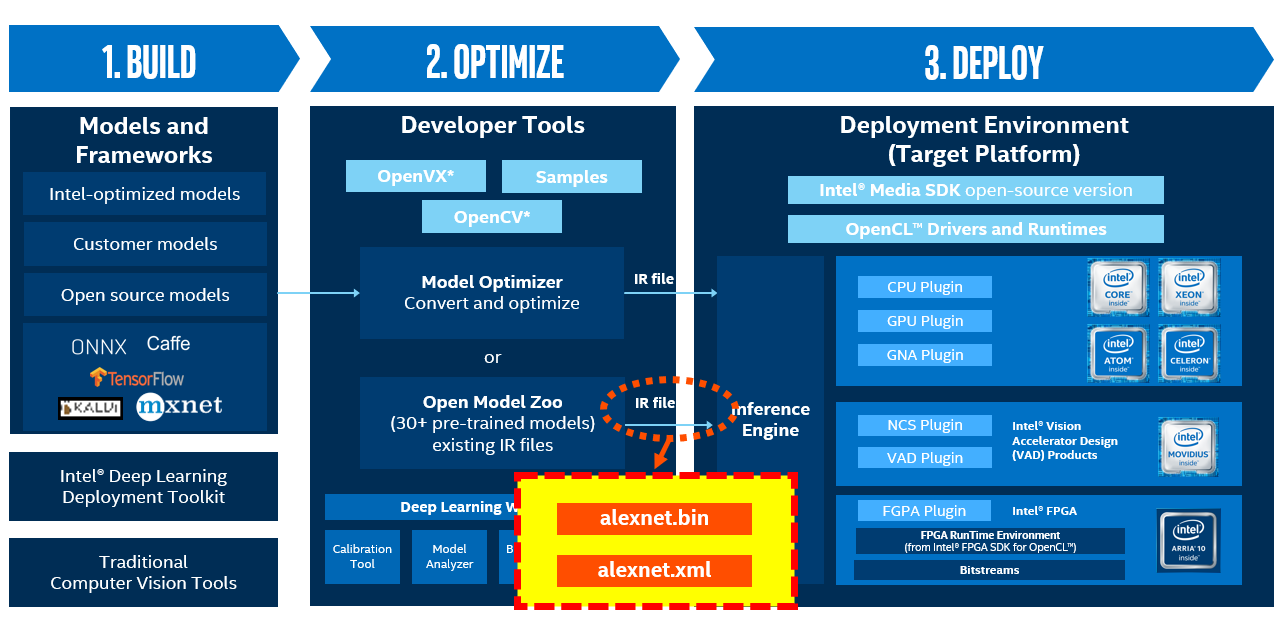
2.3 Benchmark
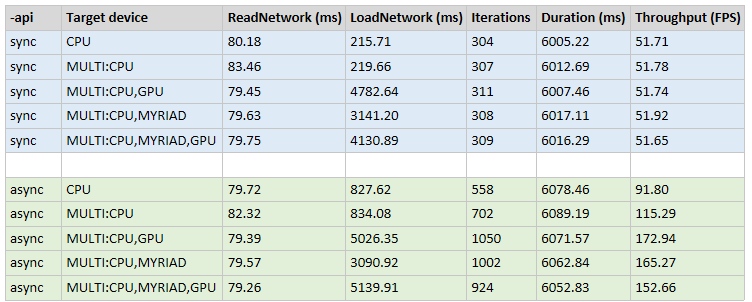
然后通过同步或者异步的方式,将 alexnet 模型通过 Multi-device plugin 加载到不同的设备上,然后利用 OpenVINO 提供的 benchmark_app 来评估性能:
$ cd /home/test/code/openvino/bin/intel64/Release
# sync, 使用 CPU 和 GPU $ ./benchmark_app -m /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/alexnet.xml -i /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/inference_engine/samples/python/hello_classification/images/cat_1.png -api sync -d "MULTI:CPU,GPU" # async,使用 CPU 和 MYRIAD $ ./benchmark_app -m /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/alexnet.xml -i /opt/intel/coneypo_test/deployment_tools/inference_engine/samples/python/hello_classification/images/cat_1.png -api async -d "MULTI:CPU,MYRIAD"
可以看到 sync 模式下,性能表现差不太多;
走异步的话,可以看到使用 MUTLI device plugin ,加载到多个设备上面异步做推理,会显著提高 FPS:
2.4 加载流程
具体实现:

以 ./benchmark_app
-m alexnet.xml
-i cat_1.png
-api sync
-d MULTI:CPU,GPU,MYRIAD
为例:
2.4.1 解析和验证输入
输入的 IR 文件,不是 .blob,isNetworkCompiled 为 false:
bool isNetworkCompiled = fileExt(FLAGS_m) == "blob";
2.4.2 加载推理引擎(Inference Engine)
Core ie;
需要使用 CPU, MKLDNN 库作为一个共享库被加载:
const auto extension_ptr = std::make_shared<InferenceEngine::Extension>(FLAGS_l);
ie.AddExtension(extension_ptr);
需要使用 iGPU,加载 clDNN 库;
auto ext = config.at("GPU").at(CONFIG_KEY(CONFIG_FILE)); ie.SetConfig({{CONFIG_KEY(CONFIG_FILE), ext}}, "GPU");
2.4.3 配置设备
2.4.4 读取 IR 文件
CNNNetwork cnnNetwork = ie.ReadNetwork(input_model);
2.4.5 调整网络大小,来匹配输入图像尺寸和 batch size
cnnNetwork.reshape(shapes);
batchSize = (!FLAGS_layout.empty()) ? getBatchSize(app_inputs_info) : cnnNetwork.getBatchSize();
2.4.6 配置网络输入输出
2.4.7 将模型加载到设备上
注意这里 "device_name" 传进去的是 ”MULTI:CPU,GPU,MYRIAD" 这种字段,还没有进行解析;
exeNetwork = ie.LoadNetwork(cnnNetwork, device_name);
因为使用了 "-d MULTI:CPU,GPU,MYRIAD",所以走到了 MULTI Plugin 里;
通过 openvino/inference-engine/src/multi_device/multi_device_plugin.cpp 的 MultiDeviceInferencePlugin::LoadExeNetworkImpl() 去实现加载网络;
对于每个 device:CPU, GPU, MYRIAD,都要 LoadNetwork 一遍:
ExecutableNetworkInternal::Ptr MultiDeviceInferencePlugin::LoadExeNetworkImpl() { ... for (auto& p : metaDevices) { ... auto exec_net = GetCore()->LoadNetwork(network, deviceName, deviceConfig); ... } ... return std::make_shared<MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork>(executableNetworkPerDevice, metaDevices, multiNetworkConfig, enablePerfCounters); }
上个函数 LoadExeNetworkImpl 中会创建 MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork 对象;
这里面会对于每个设备,networkValue.first = CPU/GPU/MYRIAD, networkValue.second = AlexNet/AlexNet/AlexNet;
如果传入的 -d 没有为设备配置 nireq,会通过 GetMetric() 拿到这个设备的 optimalNum,这个值是这个设备的最优的,处理推理请求的个数;
MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork() { for (auto&& networkValue : _networksPerDevice) { ... auto numRequests = (_devicePriorities.end() == itNumRequests || itNumRequests->numRequestsPerDevices == -1) ? optimalNum : itNumRequests->numRequestsPerDevices; ... for (auto&& workerRequest : workerRequests) { ... workerRequest._inferRequest = network.CreateInferRequest(); ... } } }
注意这里 network.CreateInferRequest() ,是在 openvino/inference-engine/src/inference_engine/cpp/ie_executable_network.cpp 里面实现的,并不是调用 Multi-plugin 的里面的 CreateInferRequest(),
如果我们给定 nireq=6,创建六个推理请求,可以看到对于设备 CPU/GPU/MYRIAD, workerRequests 的大小分别是 2/1/4,所以会分别启动 2/1/4 个 workerRequest;
关于 idleWorkerRequests 和 workerRequests 的定义:
DeviceMap<NotBusyWorkerRequests> _idleWorkerRequests;
DeviceMap<std::vector<WorkerInferRequest>> _workerRequests;
之后会详细介绍 WorkerInferRequest 的工作原理;
2.4.8 配置最优化参数
如果已经配置了推理个数,会跳过这一步;
如果没有配置,就会通过 GetMetric(METRIC_KEY(OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS)) 拿到这个网络最优的 nireq:
nireq = exeNetwork.GetMetric(key).as<unsigned int>();
2.4.9 创建推理请求(Infer Requests)
通过 InferRequestsQueue 来将 nireq 个推理请求下发到要执行的网络,创建了 nireq 个 InferReqWrap 对象:
InferRequestsQueue inferRequestsQueue(exeNetwork, nireq);
可以在 openvino/inference-engine/samples/benchmark_app/infer_request_wrap.hpp 看到 InferRequestsQueue 这个类的定义:
InferRequestsQueue(InferenceEngine::ExecutableNetwork& net, size_t nireq) { for (size_t id = 0; id < nireq; id++) { requests.push_back( std::make_shared<InferReqWrap>(net, id, std::bind(&InferRequestsQueue::putIdleRequest, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2))); _idleIds.push(id); } resetTimes(); }
InferReqWrap 里面会通过 net.CreateInferRequest()来创建推理请求:
explicit InferReqWrap(InferenceEngine::ExecutableNetwork& net, size_t id, QueueCallbackFunction callbackQueue) : _request(net.CreateInferRequest()), _id(id), _callbackQueue(callbackQueue) { _request.SetCompletionCallback([&]() { _endTime = Time::now(); _callbackQueue(_id, getExecutionTimeInMilliseconds()); }); }
比如我们配置 nireq=6,需要创建六个推理请求,通过 openvino/inference-engine/src/multi_device/multi_device_exec_network.cpp 里面的 CreateInferRequest 来创建:
IInferRequestInternal::Ptr MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::CreateInferRequest() { auto syncRequestImpl = CreateInferRequestImpl(_networkInputs, _networkOutputs); syncRequestImpl->setPointerToExecutableNetworkInternal(shared_from_this()); return std::make_shared<MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest>(std::static_pointer_cast<MultiDeviceInferRequest>(syncRequestImpl), _needPerfCounters, std::static_pointer_cast<MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork>(shared_from_this()), _callbackExecutor); }
CreateInferRequestImpl() 会根据推理个数,构建 request_to_share_blobs_with,然后分配到各个设备上面;
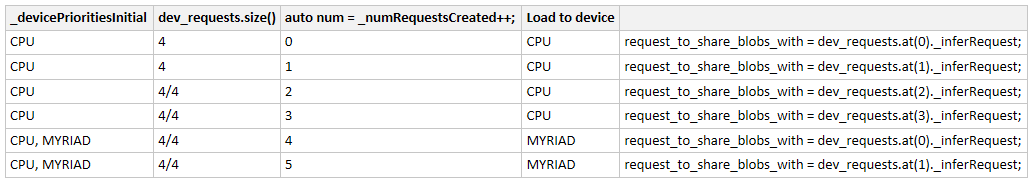
不断更新 _devicePrioritiesInitial 来决定将当前的 Infer Request 加载到哪个设备上面去;
InferenceEngine::IInferRequestInternal::Ptr MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::CreateInferRequestImpl(InferenceEngine::InputsDataMap networkInputs, InferenceEngine::OutputsDataMap networkOutputs) { auto num = _numRequestsCreated++; ... for (const auto& device : _devicePrioritiesInitial) { auto& dev_requests = _workerRequests[device.deviceName]; ... if ((num - sum) < dev_requests.size()) { request_to_share_blobs_with = dev_requests.at(num - sum)._inferRequest; break; } sum += dev_requests.size(); } return std::make_shared<MultiDeviceInferRequest>(networkInputs, networkOutputs, request_to_share_blobs_with); }
这个函数会去创建 MultiDeviceInferRequest 对象,而这个类是在 openvino/inference-engine/src/multi_device/multi_device_infer_request.cpp 里面定义的;
创建 MultiDeviceInferRequest 对象,会去配置这个 Infer Request,给到网络的输入输出:
MultiDeviceInferRequest::MultiDeviceInferRequest(const InputsDataMap& networkInputs, const OutputsDataMap& networkOutputs, InferRequest request_to_share_blobs_with) : IInferRequestInternal(networkInputs, networkOutputs) { if (request_to_share_blobs_with) { for (const auto &it : _networkInputs) { _inputs[it.first] = request_to_share_blobs_with.GetBlob(it.first); } for (const auto &it : _networkOutputs) _outputs[it.first] = request_to_share_blobs_with.GetBlob(it.first); return; } // Allocate all input blobs for (const auto &it : networkInputs) { Layout l = it.second->getLayout(); Precision p = it.second->getPrecision(); SizeVector dims = it.second->getTensorDesc().getDims(); TensorDesc desc = TensorDesc(p, dims, l); _inputs[it.first] = make_blob_with_precision(desc); _inputs[it.first]->allocate(); } // Allocate all output blobs for (const auto &it : networkOutputs) { Layout l = it.second->getLayout(); Precision p = it.second->getPrecision(); SizeVector dims = it.second->getTensorDesc().getDims(); TensorDesc desc = TensorDesc(p, dims, l); _outputs[it.first] = make_blob_with_precision(desc); _outputs[it.first]->allocate(); } }
关于 OpenVINO 里面 GetBlob() 的定义:
Get blobs allocated by an infer request using InferenceEngine::InferRequest::GetBlob() and feed an image and the input data to the blobs.
意思就是说,OpenVINO 中推理请求(Infer request)会通过 InferenceEngine::InferRequest::GetBlob() 来将网络输入的数据喂给网络;
MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::CreateInferRequest() 的返回值还会创建 MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest 对象;
这个类是在 openvino/inference-engine/src/multi_device/multi_device_async_infer_request.cpp 里面定义的:
MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest::MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest( const MultiDeviceInferRequest::Ptr& inferRequest, const bool needPerfCounters, const MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::Ptr& multiDeviceExecutableNetwork, const ITaskExecutor::Ptr& callbackExecutor) : AsyncInferRequestThreadSafeDefault(inferRequest, nullptr, callbackExecutor), _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork{multiDeviceExecutableNetwork}, _inferRequest{inferRequest}, _needPerfCounters{needPerfCounters} { // this executor starts the inference while the task (checking the result) is passed to the next stage struct ThisRequestExecutor : public ITaskExecutor { explicit ThisRequestExecutor(MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest* _this_) : _this{_this_} {} void run(Task task) override { auto workerInferRequest = _this->_workerInferRequest; workerInferRequest->_task = std::move(task); workerInferRequest->_inferRequest.StartAsync(); }; MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest* _this = nullptr; }; _pipeline = { // if the request is coming with device-specific remote blobs make sure it is scheduled to the specific device only: { /*TaskExecutor*/ std::make_shared<ImmediateExecutor>(), /*task*/ [this] { // by default, no preferred device: _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->_thisPreferredDeviceName = ""; // if any input is remote (e.g. was set with SetBlob), let' use the corresponding device for (const auto &it : _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->GetInputsInfo()) { auto b = _inferRequest->GetBlob(it.first); auto r = b->as<RemoteBlob>(); if (r) { const auto name = r->getDeviceName(); const auto res = std::find_if( _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->_devicePrioritiesInitial.cbegin(), _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->_devicePrioritiesInitial.cend(), [&name](const MultiDevicePlugin::DeviceInformation& d){ return d.deviceName == name; }); if (_multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->_devicePrioritiesInitial.cend() == res) { IE_THROW() << "None of the devices (for which current MULTI-device configuration was " "initialized) supports a remote blob created on the device named " << name; } else { // it is ok to take the c_str() here (as pointed in the multi_device_exec_network.hpp we need to use const char*) // as the original strings are from the "persistent" vector (with the right lifetime) _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork->_thisPreferredDeviceName = res->deviceName.c_str(); break; } } } }}, // as the scheduling algo may select any device, this stage accepts the scheduling decision (actual workerRequest) // then sets the device-agnostic blobs to the actual (device-specific) request { /*TaskExecutor*/ _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork, /*task*/ [this] { _workerInferRequest = MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::_thisWorkerInferRequest; _inferRequest->SetBlobsToAnotherRequest(_workerInferRequest->_inferRequest); }}, // final task in the pipeline: { /*TaskExecutor*/std::make_shared<ThisRequestExecutor>(this), /*task*/ [this] { auto status = _workerInferRequest->_status; if (InferenceEngine::StatusCode::OK != status) { if (nullptr != InferenceEngine::CurrentException()) std::rethrow_exception(InferenceEngine::CurrentException()); else IE_EXCEPTION_SWITCH(status, ExceptionType, InferenceEngine::details::ThrowNow<ExceptionType>{} <<= std::stringstream{} << IE_LOCATION << InferenceEngine::details::ExceptionTraits<ExceptionType>::string()); } if (_needPerfCounters) _perfMap = _workerInferRequest->_inferRequest.GetPerformanceCounts(); }} }; }
2.4.10 进行推理
根据是 sync 还是 async,来对创建的 inferRequest 进行推理;
if (FLAGS_api == "sync") { inferRequest->infer(); } else { inferRequest->wait(); inferRequest->startAsync(); }
如果是 sync,会去执行 InferReqWrap 类里面定义的 infer():
void infer() { _startTime = Time::now(); _request.Infer(); _endTime = Time::now(); _callbackQueue(_id, getExecutionTimeInMilliseconds()); }
会去执行之前 MultiDeviceAsyncInferRequest 类里面,pipeline 里面创建的任务,去执行 SetBlobsToAnotherRequest:
{ /*TaskExecutor*/ _multiDeviceExecutableNetwork, /*task*/ [this] { _workerInferRequest = MultiDeviceExecutableNetwork::_thisWorkerInferRequest; _inferRequest->SetBlobsToAnotherRequest(_workerInferRequest->_inferRequest); }},
而 SetBlobsToAnotherRequest() 里面就是真正的去 GetBlob() 来做推理:
void MultiDeviceInferRequest::SetBlobsToAnotherRequest(InferRequest& req) { for (const auto &it : _networkInputs) { auto &name = it.first; // this request is already in BUSY state, so using the internal functions safely auto blob = GetBlob(name); if (req.GetBlob(name) != blob) { req.SetBlob(name, blob); } } for (const auto &it : _networkOutputs) { auto &name = it.first; // this request is already in BUSY state, so using the internal functions safely auto blob = GetBlob(name); if (req.GetBlob(name) != blob) { req.SetBlob(name, blob); } } }
如果我们指定 -d "MULTI:CPU(1),MYRIAD(3),GPU(2)",分别在 CPU/MYRIAD/GPU 上面创建 1/3/2 个推理请求:
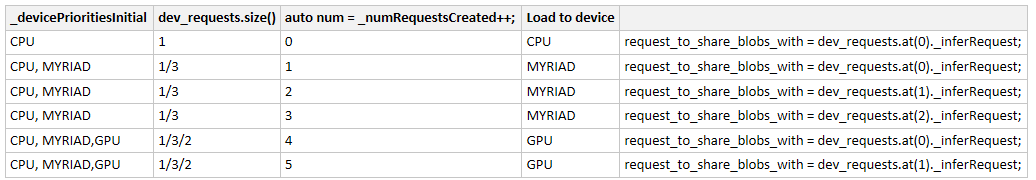
如果我们指定 -d "MULTI:CPU,MYRIAD,GPU",但是没有给每个设备指定 Infer request;
会按照设备顺序,先在 CPU 上面创建 Infer request, 在 async 的情况下,因为有四个物理核,所以可以创建四个,剩下的两个 Infer request 就会创建到第二个设备, MYRIAD 上面: