作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明。谢谢!
二叉搜索树的深度与搜索效率
我们在树, 二叉树, 二叉搜索树中提到,一个有n个节点的二叉树,它的最小深度为log(n),最大深度为n。比如下面两个二叉树:
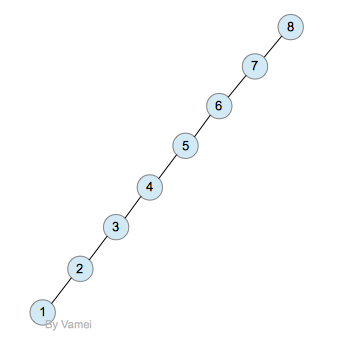
深度为n的二叉树
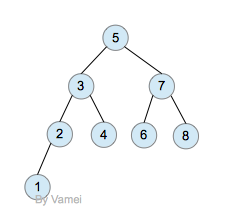
深度为log(n)的二叉树
这两个二叉树同时也是二叉搜索树(参考树, 二叉树, 二叉搜索树)。注意,log以2为基底。log(n)是指深度的量级。根据我们对深度的定义,精确的最小深度为floor(log(n)+1)。
我们将处于同一深度的节点归为一层。如果除最后一层外的其他层都被节点填满时,二叉树有最小深度log(n)。
二叉搜索树的深度越小,那么搜索所需要的运算时间越小。一个深度为log(n)的二叉搜索树,搜索算法的时间复杂度也是log(n)。然而,我们在二叉搜索树中已经实现的插入和删除操作并不能让保持log(n)的深度。如果我们按照8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1的顺序插入节点,那么就是一个深度为n的二叉树。那么,搜索算法的时间复杂度为n。
n和log(n)的时间复杂度意味着什么呢?时间复杂度代表了完成算法所需要的运算次数。时间复杂度越小,算法的速度越快。
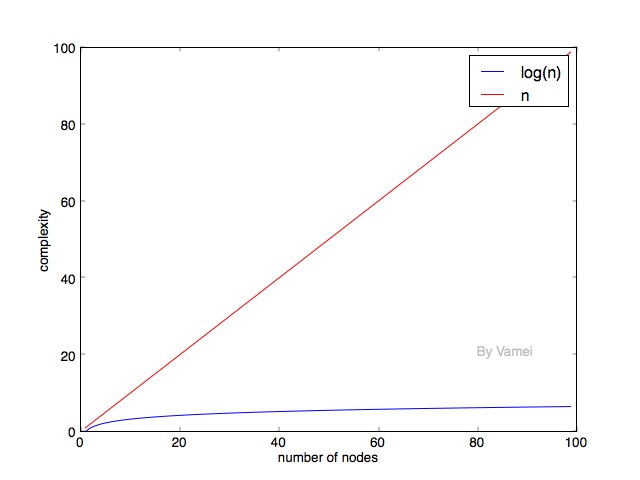
可以看到,随着元素的增加,log(n)的时间复杂度的增长要远小于n。所以,我们自然希望二叉搜索树能尽可能保持log(n)的深度。在上面深度为n的例子中,我们发现,每个节点只有左节点被填满。树的每一层都有很多空位。能不能尽可能减少每一层的空位呢? (相应的,减少树的深度)

“紧致”的树
一种想法是先填满一层,再去填充下一层,这样就是一个完全二叉树(complete binary tree)。这样的二叉树实现插入算法会比较复杂。我们将介绍一种思路相似,但比较容易实现的树状数据结构——AVL树。
AVL树
AVL树是根据它的发明者G. M. Adelson-Velskii和E. M. Landis命名的。它是一种特殊的二叉搜索树。AVL树要求: 任一节点的左子树深度和右子树深度相差不超过1
(空树的深度为0。注意,有的教材中,采用了不同的深度定义方法,所以空树的深度为-1)
下面是AVL树:
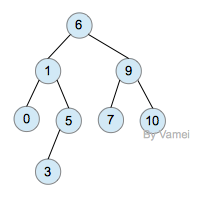
AVL树
AVL树的特性让二叉搜索树的节点实现平衡(balance):节点相对均匀分布,而不是偏向某一侧。因此,AVL树的搜索算法复杂度是log(n)的量级。
我们在二叉搜索树中定义的操作,除了插入,都可以用在AVL树上 (假设使用懒惰删除)。如果进行插入操作,有可能会破坏AVL树的性质,比如:
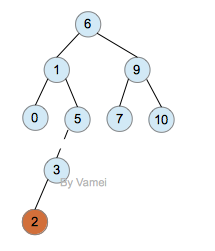
插入2: 破坏AVL树
观察节点5,它的左子树深度为2,右子树深度为0,所以左右两个子树深度相差为2,不再是AVL树。由于2的加入,从节点6,1,5,3到2的层数都增加1。6, 1, 5节点的AVL性质都被破坏。如果从节点2向上回溯,节点5是第一个被破坏的。从节点3开始的子树深度加1,这是造成6, 1, 5的AVL性质被破坏的本质原因。我们将5和3之间的路径画成虚线(就好像挂了重物,边被拉断一样)。
我们可以通过单旋照(single rotation),调整以5为根节点的子树,来修正因为插入一个元素而引起的对AVL性质的破坏。如下:
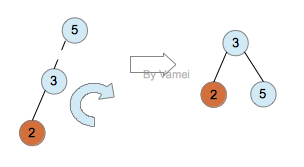
Single rotation: 左侧超重,向右转
通过单旋转,3成为新的根节点,2,5称为3的左右子节点。子树重新成为AVL树。该子树的深度减小1,这将自动修正2带给节点6,1的“超负荷”。
单旋转效果如下:
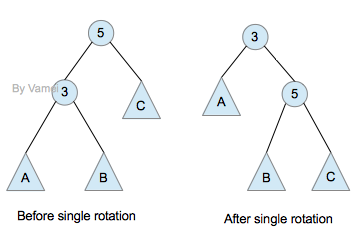 向右单旋转
向右单旋转
特别要注意的是,为了保持二叉树的性质,子树B过继给了节点5。
向左单旋转与之类似。作为练习,可以尝试绘制向左单旋转的示意图。
但如果插入的节点不是2,而是4,会是如何呢?

插入4
尝试单旋转,会发现无法解决问题。以5为根节点的子树向右单旋转后,树将以3为根节点,4,5为子节点。4比3大,却是3的左子节点,显然,这依然不符合二叉搜索树的性质。但基于和上面相似的原则(调整以5为根节点的树),我们发现有一个简单的解决方式:

double rotation
上面的操作被称作双旋转(double rotation)。双旋转实际上是进行两次单旋转: 4为根节点的子树先进行一次向左的单旋转,然后将5为根节点的子树进行了一次向右的单旋转。这样恢复了树的ACL性质。
对于AVL树,可以证明,在新增一个节点时,总可以通过一次旋转恢复AVL树的性质。
当我们插入一个新的节点时,在哪里旋转?是用单旋转还是双旋转?
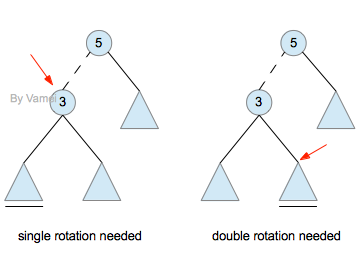
我们按照如下基本步骤进行:
1. 按照二叉搜索树的方式增加节点,新增节点称为一个叶节点。
2. 从新增节点开始,回溯到第一个失衡节点(5)。
(如果回溯到根节点,还没有失衡节点,就说明该树已经符合AVL性质。)
3. 找到断的边(5->3),并确定断弦的方向(5的左侧)
4. 以断边下端(3)为根节点,确定两个子树中的哪一个深度大(左子树还是右子树)。
(这两棵子树的深度不可能相等,而且深度大的子树包含有新增节点。想想为什么)
5. 如果第2和第3步中的方向一致(都为左或者都为右),需要单旋转以失衡节点为根节点的子树。
否则,双旋转以失衡节点为根节点的子树。
下面是AVL树的插入算法实现如下:
/* By Vamei */
/* binary search tree */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node *position;
typedef int ElementTP;
struct node {
int depth;
position parent;
ElementTP element;
position lchild;
position rchild;
};
/* pointer => root node of the tree */
typedef struct node *TREE;
position insert_value(TREE, ElementTP);
int depth(TREE);
static void insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(TREE, position);
static void update_root_depth(TREE);
static TREE recover_avl(TREE, position);
static int depth_diff(TREE);
static position insert_leaf(TREE, ElementTP);
static void insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(TREE, position);
static TREE left_single_rotate(TREE);
static TREE left_double_rotate(TREE);
static TREE right_single_rotate(TREE);
static TREE right_double_rotate(TREE);
void main(void)
{
TREE tr;
position np;
ElementTP element;
tr = NULL;
tr = insert_value(tr, 18);
tr = insert_value(tr, 5);
printf("root: %d
", tr->element);
printf("depth: %d
", depth(tr));
tr = insert_value(tr, 2);
printf("root: %d
", tr->element);
printf("depth: %d
", depth(tr));
tr = insert_value(tr, 4);
printf("root: %d
", tr->element);
printf("depth: %d
", depth(tr));
printf("root->lchild: %d
", tr->lchild->element);
tr = insert_value(tr, 3);
printf("root: %d
", tr->element);
printf("depth: %d
", depth(tr));
printf("root->lchild: %d
", tr->lchild->element);
printf("root->lchild->lchild: %d
", tr->lchild->lchild->element);
}
/*
* insert value
*
*/
position insert_value(TREE tr, ElementTP value)
{
position new;
/* insert a value to a binary search tree */
new = insert_leaf(tr, value);
update_root_depth(new);
if (tr == NULL) {
tr = new;
}
else {
tr = recover_avl(tr, new);
}
return tr;
}
/*
* get the depth of the tree
* use this function to access depth
*/
int depth(TREE tr) {
if (tr == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
return tr->depth;
}
}
//========================================
// static functions: for internal use
/*
* traverse the path from new node to root node
* make one rotation, recover AVL and stop
*/
static TREE recover_avl(TREE tr, position np)
{
int myDiff;
while (np != NULL) {
update_root_depth(np);
myDiff = depth_diff(np);
if (myDiff > 1 || myDiff < -1) {
if (myDiff > 1) {
/* left rotate needed */
if(depth_diff(np->rchild) > 0) {
np = left_single_rotate(np);
}
else {
np = left_double_rotate(np);
}
}
if (myDiff < -1) {
if(depth_diff(np->lchild) < 0) {
np = right_single_rotate(np);
}
else {
np = right_double_rotate(np);
}
}
/* if rotation changes root node */
if (np->parent == NULL) tr = np;
break;
}
np = np->parent;
}
return tr;
}
/*
* difference of rchild->depth and lchild->depth
*/
static int depth_diff(TREE tr)
{
if (tr == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
return depth(tr->rchild) - depth(tr->lchild);
}
}
/*
* left single rotation
* return the new root
*/
static TREE left_single_rotate(TREE tr)
{
TREE newRoot, parent;
parent = tr->parent;
newRoot = tr->rchild;
/* detach & attach */
if (newRoot->lchild != NULL) newRoot->lchild->parent = tr;
tr->rchild = newRoot->lchild;
update_root_depth(tr);
/* raise new root node */
newRoot->lchild = tr;
newRoot->parent = parent;
if (parent != NULL) {
if (parent->lchild == tr) {
parent->lchild = newRoot;
}
else {
parent->rchild = newRoot;
}
}
tr->parent = newRoot;
update_root_depth(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
/*
* right single rotation
* return the new root
*/
static TREE right_single_rotate(TREE tr)
{
TREE newRoot, parent;
parent = tr->parent;
newRoot = tr->lchild;
/* detach & attach */
if (newRoot->rchild != NULL) newRoot->rchild->parent = tr;
tr->lchild = newRoot->rchild;
update_root_depth(tr);
/* raise new root node */
newRoot->rchild = tr;
newRoot->parent = parent;
if (parent != NULL) {
if (parent->lchild == tr) {
parent->lchild = newRoot;
}
else {
parent->rchild = newRoot;
}
}
tr->parent = newRoot;
update_root_depth(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
/*
* left double rotation
* return
*/
static TREE left_double_rotate(TREE tr)
{
right_single_rotate(tr->rchild);
return left_single_rotate(tr);
}
/*
* right double rotation
* return
*/
static TREE right_double_rotate(TREE tr)
{
left_single_rotate(tr->lchild);
return right_single_rotate(tr);
}
/*
* update tr->depth
* assume lchild->depth and rchild->depth are correct
*/
static void update_root_depth(TREE tr)
{
int maxChildDepth;
int depLChild, depRChild;
if (tr==NULL) return;
else {
depLChild = depth(tr->lchild);
depRChild = depth(tr->rchild);
maxChildDepth = depLChild > depRChild ? depLChild : depRChild;
tr->depth = maxChildDepth + 1;
}
}
/*
* insert a new value into the tree as a leaf
* return address of the new node
*/
static position insert_leaf(TREE tr, ElementTP value)
{
position np;
/* prepare the node */
np = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
np->element = value;
np->parent = NULL;
np->lchild = NULL;
np->rchild = NULL;
if (tr != NULL) {
insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(tr, np);
}
return np;
}
/*
* insert a node to a non-empty tree
* called by insert_value()
*/
static void insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(TREE tr, position np)
{
/* insert the node */
if(np->element <= tr->element) {
if (tr->lchild == NULL) {
/* then tr->lchild is the proper place */
tr->lchild = np;
np->parent = tr;
return;
}
else {
insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(tr->lchild, np);
}
}
else if(np->element > tr->element) {
if (tr->rchild == NULL) {
tr->rchild = np;
np->parent = tr;
return;
}
else {
insert_node_to_nonempty_tree(tr->rchild, np);
}
}
}
输出如下:
root: 18
depth: 2
root: 5
depth: 2
root: 5
depth: 3
root->lchild: 2
depth: 3
root->lchild: 3
root->lchild->lchild: 2
(空行是额外加的)
总结:
AVL树: 平衡,深度相差不超过1
单旋转,双旋转
