主要内容:
1、显性和隐性行为
2、基于物品的协同过滤
3、python实现
4、基于用户和基于物品的协同过滤应用
一、显性和隐性行为:
了解用户喜好的途径有两种:
1、显式的标记,即对物品进行“踩”/"赞"或打分等明显行为,例如购物网站对商品的评分等;
2、隐式的跟踪,即跟踪用户对物品的行为,如点击、浏览等隐藏行为,例如购物网站中的“浏览过该商品的用户还浏览了”等;
那么显式的标记和隐式的跟踪,哪个更好呢?
也许我们会觉得显示的标记会更准确一点,其实很多时候不然,下面列举几点:1、人都是懒的,很少人会对商品进行评分;2、评分也存在虚假和片面的信息;3、评分有时需要更新,而很多人没有这么做;
那么,隐式的跟踪可以用来做什么呢?诸如根据用户购物浏览记录了解用户喜好来推荐物品、根据用户的网页点击浏览记录进行新闻推荐、根据用户的听歌记录(播放or跳过)来推荐歌曲等。
问题在于:
如果利用之前介绍的基于用户的协同过滤来推荐物品,那么如果用户超级多,那么来一个新用户,找到最近邻的用户的所需内存和计算量将是无法想象的;其次,用户的特征向量是稀疏的,即每个人评分的物品寥寥无几。
基于此,下面介绍基于物品的协同过滤(Item-based collaborative filtering, Item CF)。
二、基于物品的协同过滤
基于用户的协同过滤是根据用户的相似度来进行过滤推荐,很明显,基于物品的协同过滤自然是根据物品的相似度与用户的历史记录来进行过滤推荐,
即根据物品与物品之间的相似性,来预测用户对某物品的评分,选出评分最高的物品作为推荐。
优点:
1、基于物品的协同过滤采用的用户-物品的倒排表,因为物品的相对特征固定,因此物品与物品之间的相似性可以预先计算保存起来,这样在推荐时可以大大降低计算量。
2、基于物品的协同过滤容易提供推荐的理由,例如给你推荐《机器学习》是因为你之前买过《数据挖掘》,这样能增加信任度,提高用户和推荐系统的交互,进一步增强个性化推荐
这里介绍两种基于物品的协同过滤方法,所谓不同的方法,就是不同的相似度衡量方法或者评分预测方法。
1、调整后的cosine相似度Adjusted Cosine Similarity
物品与物品的相似度公式:
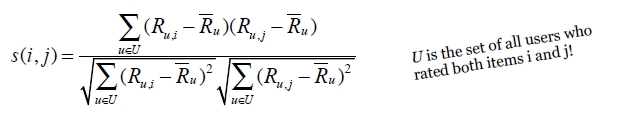
用户对某物品的预测评分公式:
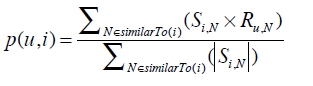
如果出现用户评分尺度不一致,可以预先进行归一化处理,然后再变换回来:
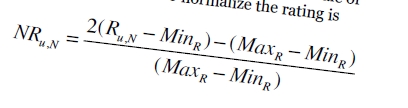
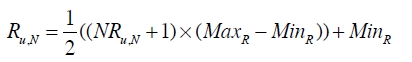
2、Slope One
原理:简单来说,求某人对某个物品的评分,可以转换为:通过所有数据来找到某人u评分过的物品i与该物品j的分数差,根据分数差和物品i的权重关系来确定某人u对物品j的分数。
具体:参考http://www.cppblog.com/AutomateProgram/archive/2010/07/19/120790.html
这里只贴出公式:
计算物品i与物品j的分数差:
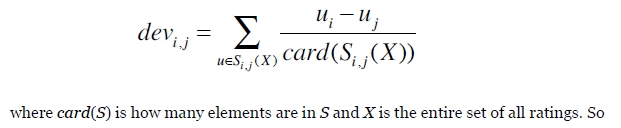
预测用户u对物品j的评分:

三、python实现
这里只实现了slope one
import codecs from math import sqrt users2 = {"Amy": {"Taylor Swift": 4, "PSY": 3, "Whitney Houston": 4}, "Ben": {"Taylor Swift": 5, "PSY": 2}, "Clara": {"PSY": 3.5, "Whitney Houston": 4}, "Daisy": {"Taylor Swift": 5, "Whitney Houston": 3}} users = {"Angelica": {"Blues Traveler": 3.5, "Broken Bells": 2.0, "Norah Jones": 4.5, "Phoenix": 5.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 1.5, "The Strokes": 2.5, "Vampire Weekend": 2.0}, "Bill":{"Blues Traveler": 2.0, "Broken Bells": 3.5, "Deadmau5": 4.0, "Phoenix": 2.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 3.5, "Vampire Weekend": 3.0}, "Chan": {"Blues Traveler": 5.0, "Broken Bells": 1.0, "Deadmau5": 1.0, "Norah Jones": 3.0, "Phoenix": 5, "Slightly Stoopid": 1.0}, "Dan": {"Blues Traveler": 3.0, "Broken Bells": 4.0, "Deadmau5": 4.5, "Phoenix": 3.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 4.5, "The Strokes": 4.0, "Vampire Weekend": 2.0}, "Hailey": {"Broken Bells": 4.0, "Deadmau5": 1.0, "Norah Jones": 4.0, "The Strokes": 4.0, "Vampire Weekend": 1.0}, "Jordyn": {"Broken Bells": 4.5, "Deadmau5": 4.0, "Norah Jones": 5.0, "Phoenix": 5.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 4.5, "The Strokes": 4.0, "Vampire Weekend": 4.0}, "Sam": {"Blues Traveler": 5.0, "Broken Bells": 2.0, "Norah Jones": 3.0, "Phoenix": 5.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 4.0, "The Strokes": 5.0}, "Veronica": {"Blues Traveler": 3.0, "Norah Jones": 5.0, "Phoenix": 4.0, "Slightly Stoopid": 2.5, "The Strokes": 3.0} } class recommender: def __init__(self, data,n=5): """ initialize recommender currently, if data is dictionary the recommender is initialized to it. For all other data types of data, no initialization occurs k is the k value for k nearest neighbor metric is which distance formula to use n is the maximum number of recommendations to make""" self.n = n self.username2id = {} self.userid2name = {} self.productid2name = {} # # The following two variables are used for Slope One # self.frequencies = {} self.deviations = {} # for some reason I want to save the name of the metric #if self.metric == 'pearson': #self.fn = self.pearson # # if data is dictionary set recommender data to it # if type(data).__name__ == 'dict': self.data = data def convertProductID2name(self, id): """Given product id number return product name""" if id in self.productid2name: return self.productid2name[id] else: return id def userRatings(self, id, n): """Return n top ratings for user with id""" print ("Ratings for " + self.userid2name[id]) ratings = self.data[id] print(len(ratings)) ratings = list(ratings.items())[:n] ratings = [(self.convertProductID2name(k), v) for (k, v) in ratings] # finally sort and return ratings.sort(key=lambda artistTuple: artistTuple[1], reverse = True) # for rating in ratings: # print("%s %i" % (rating[0], rating[1])) def showUserTopItems(self, user, n): """ show top n items for user""" items = list(self.data[user].items()) items.sort(key=lambda itemTuple: itemTuple[1], reverse=True) for i in range(n): print("%s %i" % (self.convertProductID2name(items[i][0]), items[i][1])) def loadMovieLens(self, path=''): self.data = {} # # first load movie ratings # i = 0 # # First load book ratings into self.data # #f = codecs.open(path + "u.data", 'r', 'utf8') f = codecs.open(path + "u.data", 'r', 'ascii') # f = open(path + "u.data") for line in f: i += 1 #separate line into fields fields = line.split(' ') user = fields[0] movie = fields[1] rating = int(fields[2].strip().strip('"')) if user in self.data: currentRatings = self.data[user] else: currentRatings = {} currentRatings[movie] = rating self.data[user] = currentRatings f.close() # # Now load movie into self.productid2name # the file u.item contains movie id, title, release date among # other fields # #f = codecs.open(path + "u.item", 'r', 'utf8') f = codecs.open(path + "u.item", 'r', 'iso8859-1', 'ignore') #f = open(path + "u.item") for line in f: i += 1 #separate line into fields fields = line.split('|') mid = fields[0].strip() title = fields[1].strip() self.productid2name[mid] = title f.close() # # Now load user info into both self.userid2name # and self.username2id # #f = codecs.open(path + "u.user", 'r', 'utf8') f = open(path + "u.user") for line in f: i += 1 fields = line.split('|') userid = fields[0].strip('"') self.userid2name[userid] = line self.username2id[line] = userid f.close() print(i) def loadBookDB(self, path=''): """loads the BX book dataset. Path is where the BX files are located""" self.data = {} i = 0 # # First load book ratings into self.data # f = codecs.open(path + "BX-Book-Ratings.csv", 'r', 'utf8') for line in f: i += 1 # separate line into fields fields = line.split(';') user = fields[0].strip('"') book = fields[1].strip('"') rating = int(fields[2].strip().strip('"')) # if rating > 5: # print("EXCEEDING ", rating) if user in self.data: currentRatings = self.data[user] else: currentRatings = {} currentRatings[book] = rating self.data[user] = currentRatings f.close() # # Now load books into self.productid2name # Books contains isbn, title, and author among other fields # f = codecs.open(path + "BX-Books.csv", 'r', 'utf8') for line in f: i += 1 # separate line into fields fields = line.split(';') isbn = fields[0].strip('"') title = fields[1].strip('"') author = fields[2].strip().strip('"') title = title + ' by ' + author self.productid2name[isbn] = title f.close() # # Now load user info into both self.userid2name and # self.username2id # f = codecs.open(path + "BX-Users.csv", 'r', 'utf8') for line in f: i += 1 # separate line into fields fields = line.split(';') userid = fields[0].strip('"') location = fields[1].strip('"') if len(fields) > 3: age = fields[2].strip().strip('"') else: age = 'NULL' if age != 'NULL': value = location + ' (age: ' + age + ')' else: value = location self.userid2name[userid] = value self.username2id[location] = userid f.close() print(i) def computeDeviations(self): # for each person in the data: # get their ratings for ratings in self.data.values(): # for each item & rating in that set of ratings: for (item, rating) in ratings.items(): self.frequencies.setdefault(item, {}) self.deviations.setdefault(item, {}) # for each item2 & rating2 in that set of ratings: for (item2, rating2) in ratings.items(): if item != item2: # add the difference between the ratings to our # computation self.frequencies[item].setdefault(item2, 0) self.deviations[item].setdefault(item2, 0.0) self.frequencies[item][item2] += 1 self.deviations[item][item2] += rating - rating2 for (item, ratings) in self.deviations.items(): for item2 in ratings: ratings[item2] /= self.frequencies[item][item2] def slopeOneRecommendations(self, userRatings): recommendations = {} frequencies = {} # for every item and rating in the user's recommendations for (userItem, userRating) in userRatings.items(): # for every item in our dataset that the user didn't rate for (diffItem, diffRatings) in self.deviations.items(): if diffItem not in userRatings and userItem in self.deviations[diffItem]: freq = self.frequencies[diffItem][userItem] recommendations.setdefault(diffItem, 0.0) frequencies.setdefault(diffItem, 0) # add to the running sum representing the numerator # of the formula recommendations[diffItem] += (diffRatings[userItem] + userRating) * freq # keep a running sum of the frequency of diffitem frequencies[diffItem] += freq recommendations = [(self.convertProductID2name(k), v / frequencies[k]) for (k, v) in recommendations.items()] # finally sort and return recommendations.sort(key=lambda artistTuple: artistTuple[1], reverse = True) # I am only going to return the first 50 recommendations return recommendations[:5] if __name__ == '__main__': # users2 as dataset r=recommender(users2) r.computeDeviations() #print r.deviations g = users2['Ben'] print r.slopeOneRecommendations(g) # book dataset is too large to store ''' r=recommender(0) r.loadBookDB('BX-Dump/BX-Dump/') r.computeDeviations() print r.slopeOneRecommendations(r.data['171118']) ''' # movielen as dataset r = recommender(0) r.loadMovieLens('./') r.computeDeviations() print r.slopeOneRecommendations(r.data['1']) print r.slopeOneRecommendations(r.data['25'])
四、基于用户和基于物品的协同过滤应用
一般而言,
基于用户的协同过滤更适用于社交和群体类推荐,例如新闻、热点等;
而基于物品的协同过滤更适用于个性化推荐,例如个人电台、个人阅读等;