The Promise.allSettled() method accepts an array (or any other iterable) of promises as a parameter. It returns a Promise object that is fulfilled with an array of settlement objects. Each settlement object describes the settlement of the corresponding input promise.
Notice that the Promise object returned from the Promise.allSettled() method is only rejected if there's an error iterating over the input promises. In all other cases, it is fulfilled.
The Promise.allSettled() method is useful when you want to wait for multiple promises to settle, no matter whether they'll be fulfilled or rejected.
First thing first, let's understand what is promise state:
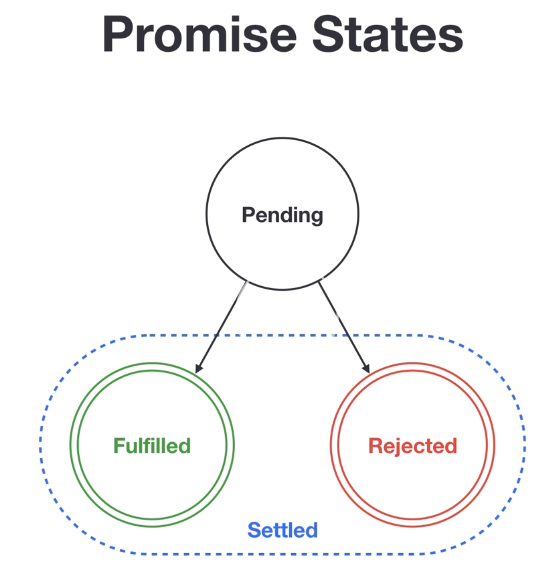
'Settled' means both 'Resolved' or 'Rejected'. So in most cases, Promise.settled() alwasy resolved. But if you do:
Promise.allSettled({})
It will throw error. Because {} is not iterable.
Why we need to use Promise.allSettled()?
Remeber Promise.all([..]), one promise rejected will cause the whole Promise get rejected. It is always a problem which cause a not user-friendly case.
Promise.allSettled([...]) is good a handling this case:
const API_URL = "https://starwars.egghead.training/"; const output = document.getElementById("output"); const spinner = document.getElementById("spinner"); function queryAPI(endpoint) { return fetch(API_URL + endpoint).then(response => { return response.ok ? response.json() : Promise.reject(Error("Unsuccessful response")); }); } Promise.allSettled([ queryAPI("films").then(f => `${f.length} films`), queryAPI("planets").then(p => `${p.length} planets`), queryAPI("species").then(s => `${s.length} species`), queryAPI("vehicles").then(v => `${v.length} vehicles`) ]) .then(results => { const statistics = results .filter(result => result.status === "fulfilled") .map(result => result.value); output.innerText = statistics.length === 0 ? "Failed to load statistics :(" : statistics.join(" "); }) .catch(error => { console.warn(error); output.innerText = ":("; }) .finally(() => { spinner.remove(); });
The ressuls comes back from Promise.allSettled()
