Continuous Integration
Integrating or mergin the code changes frequently - at least once per day. (CodeCommit / GitHub)
Continuous Delivery
Automating the build, test and deployment functions. (CodeBuild and CodeDeploy)
Continuous Deployment
Fully automated release process, code is deployed into Staging or Production as soon as it has successfully passed through the release pipeline. (CodePipeline)

Lab: CodeCommit From CLI
CodeDeploy
Work with EC2 instances, on-premises & Lambda
- Quickly release new features
- Avoid downtime during deployments
- Avoid the risks associated with manual processes.
Deployment Approaches
1. In-Place
The application is stopped on each instance and the new release is installed. Also known as Rolling update.
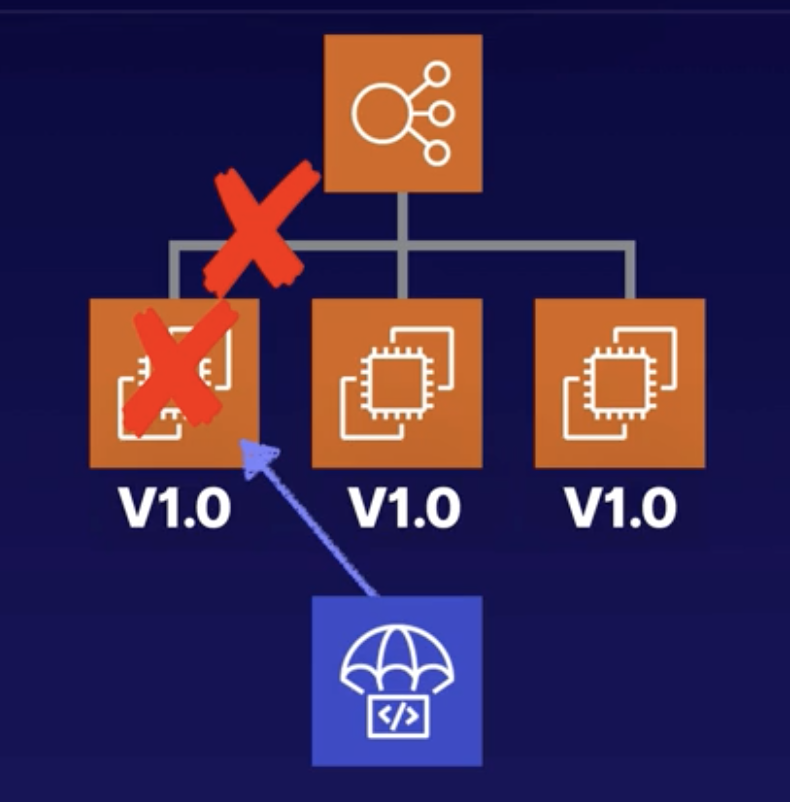
For example, a Load balancer has three instances. When doing the In-placed deployment.
- The application is stopped on the first instance.
- The instance will be out of service during the deployment so capacity is reduced.
- You should configure your Elastic Load Balancer to stop sending requests to the instance.
Rollback
No easy way to rollback, you need to deploy previous version all over again. Cause a big downtime.
When to use?
Great when deploying the first time. Because there is no second version during the first time.
2. Blue / Green
New instances are provisioned and new release is installed on the new instances. Blue represents the active deployment, green is the new release.
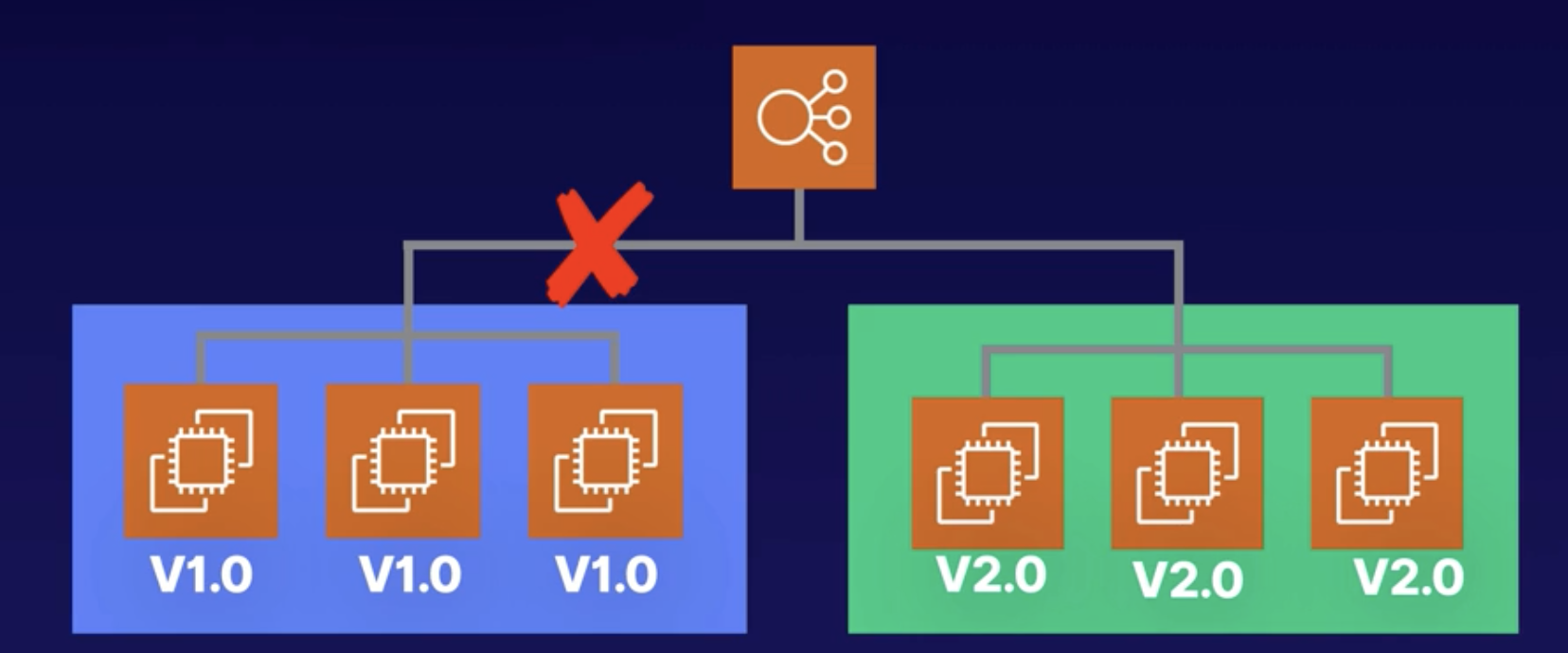
- Blue represents the current version of our application.
- CodeDeploy provisions new instances in green.
- The new Revision is deployed to the Green environment.
- The Green instances are registered with the Elastic Load Balancer
- Traffic is routed away from the old enironment.
- Blue environment is eventually terminated.
Rollback
It is easy because we just need to switch the Load Balacner to Blue env from Green env again. Only works if you didn't already terminate your old environment!

CodeDeploy AppSpec File

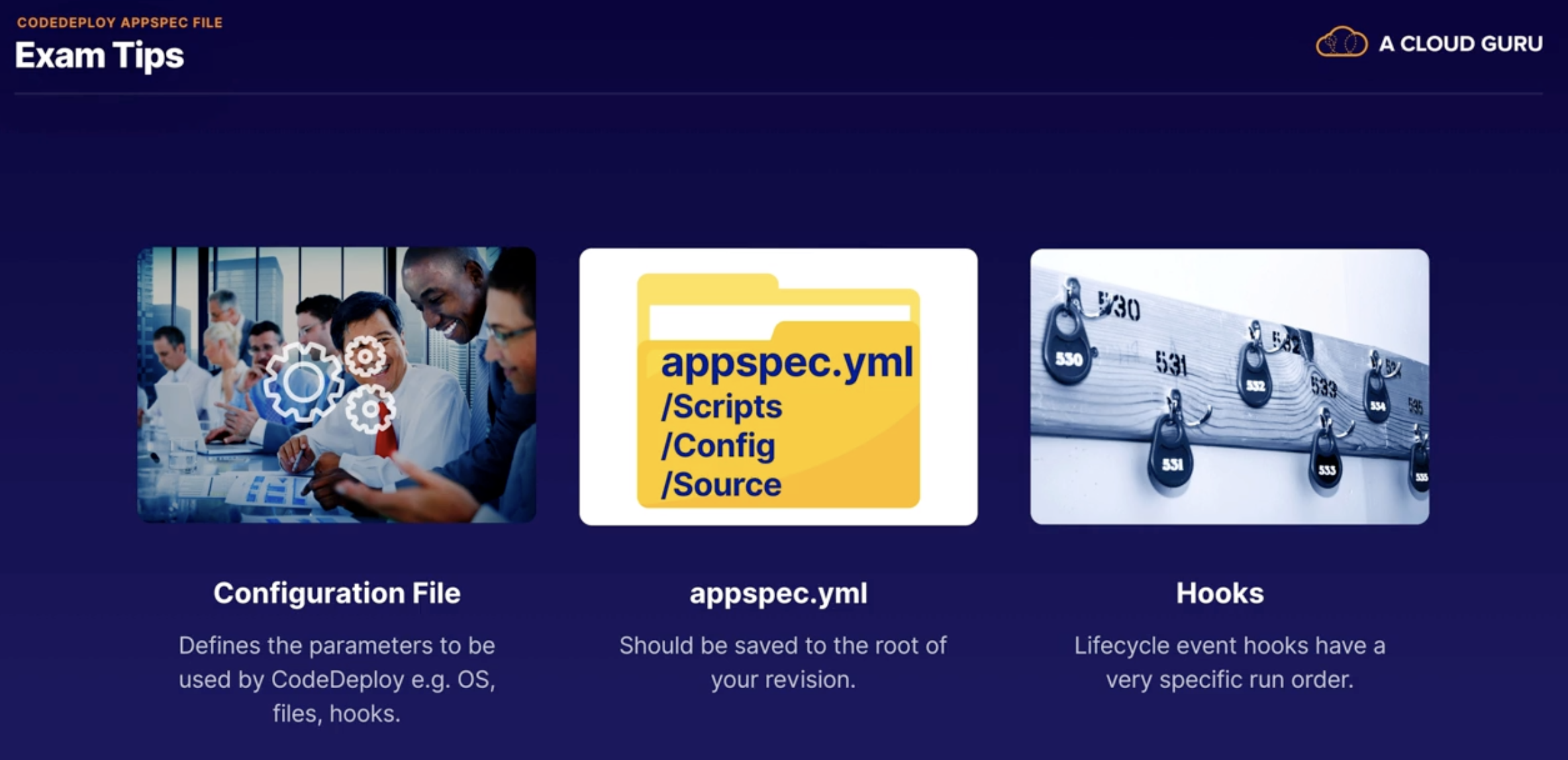
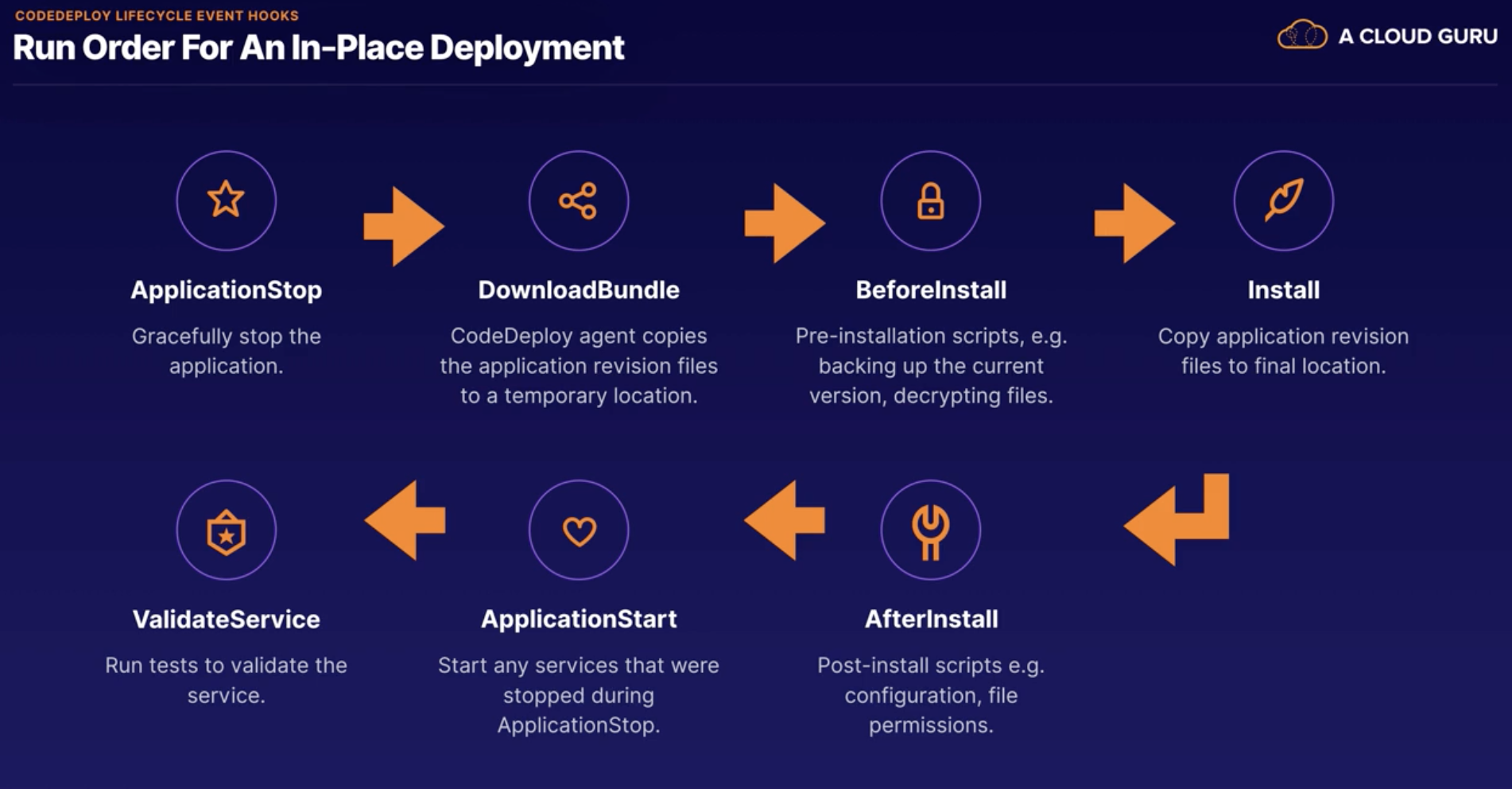
CodeDeploy Lifecycle Event Hooks
Mainly needed for In-Placed deployment
Divide into three main Phases
- De-register instances from a Load Balancer
- The real nuts & bolts of the application deployemnt
- Re-register instances with the Load Balancer

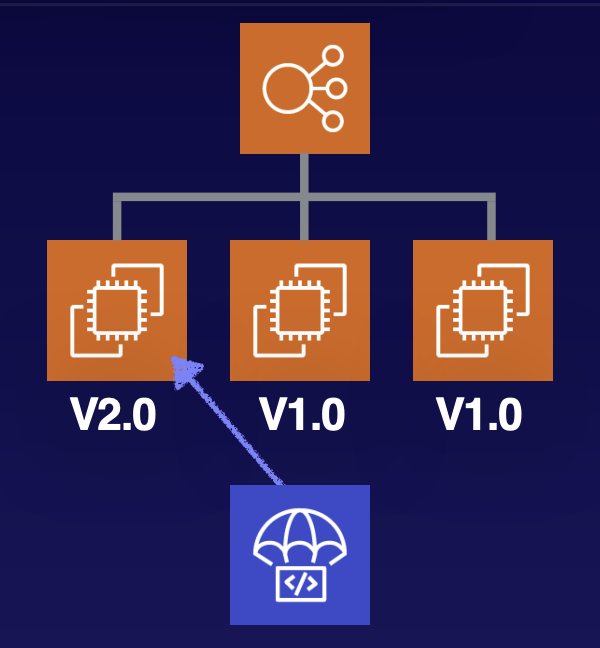
It makes senses, you need to first stop traffic go to V1.0 from load balacner; then install Revision; Last register load balancer to V2.
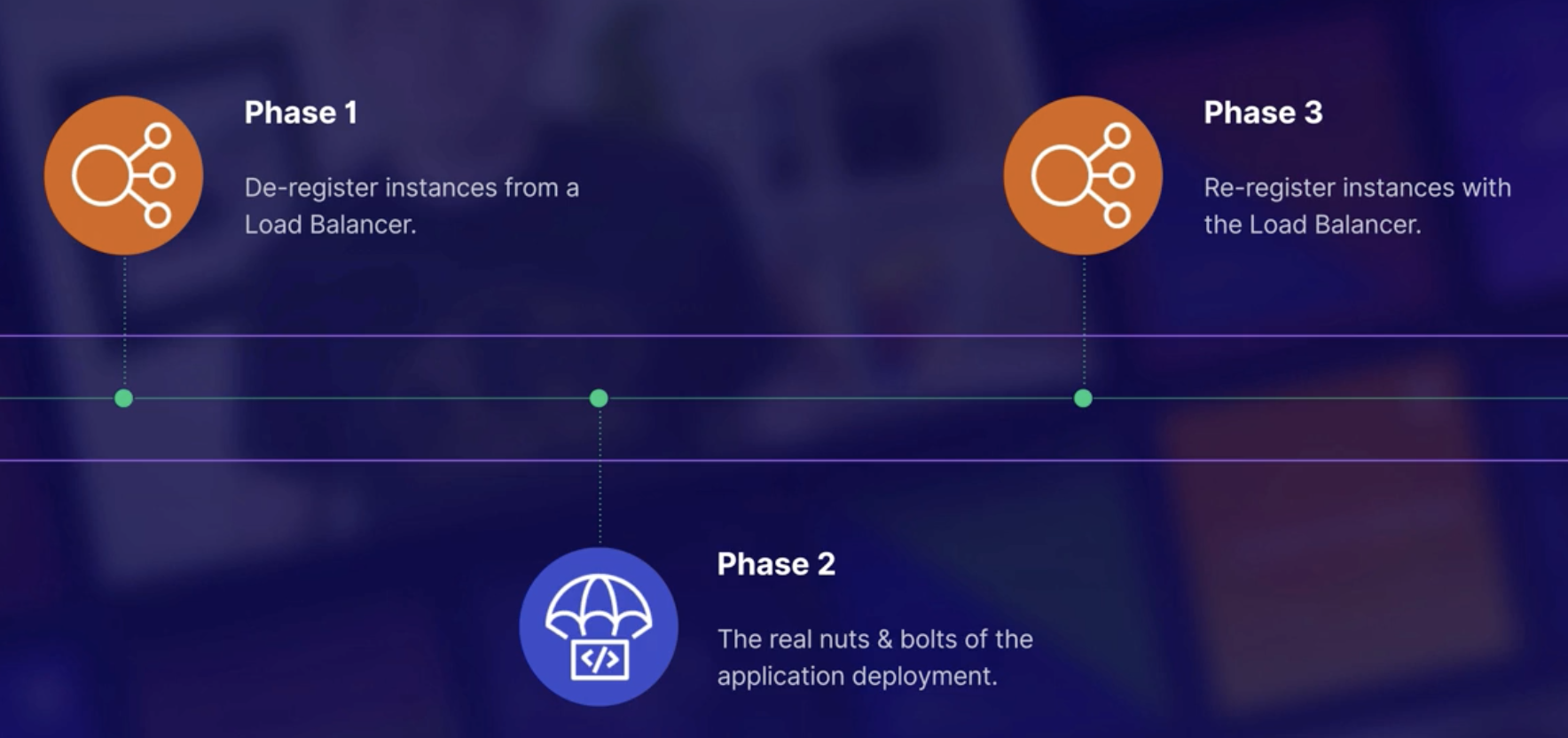
Phase1
What it does is mainly Block Traffic.

Phase2
What it does is stop previous running application, download new version, install new version, running new application and Validate/testing.
Phase3
What it does is connect load balancer


CodePipeline
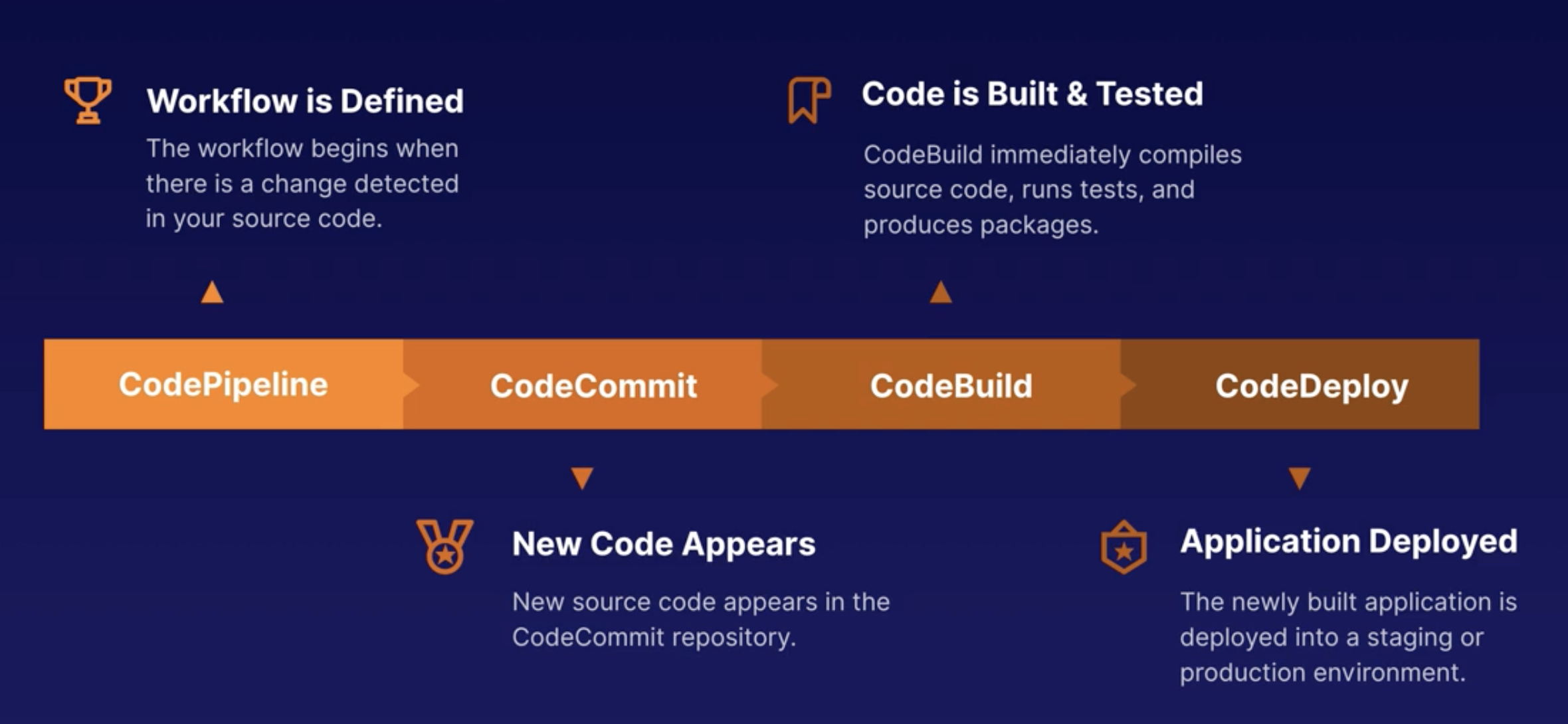
- Integrates with AWS & Third-Party Tools
ECS

Elastic Beanstalk

CloudFormation
Infrastructure As Code
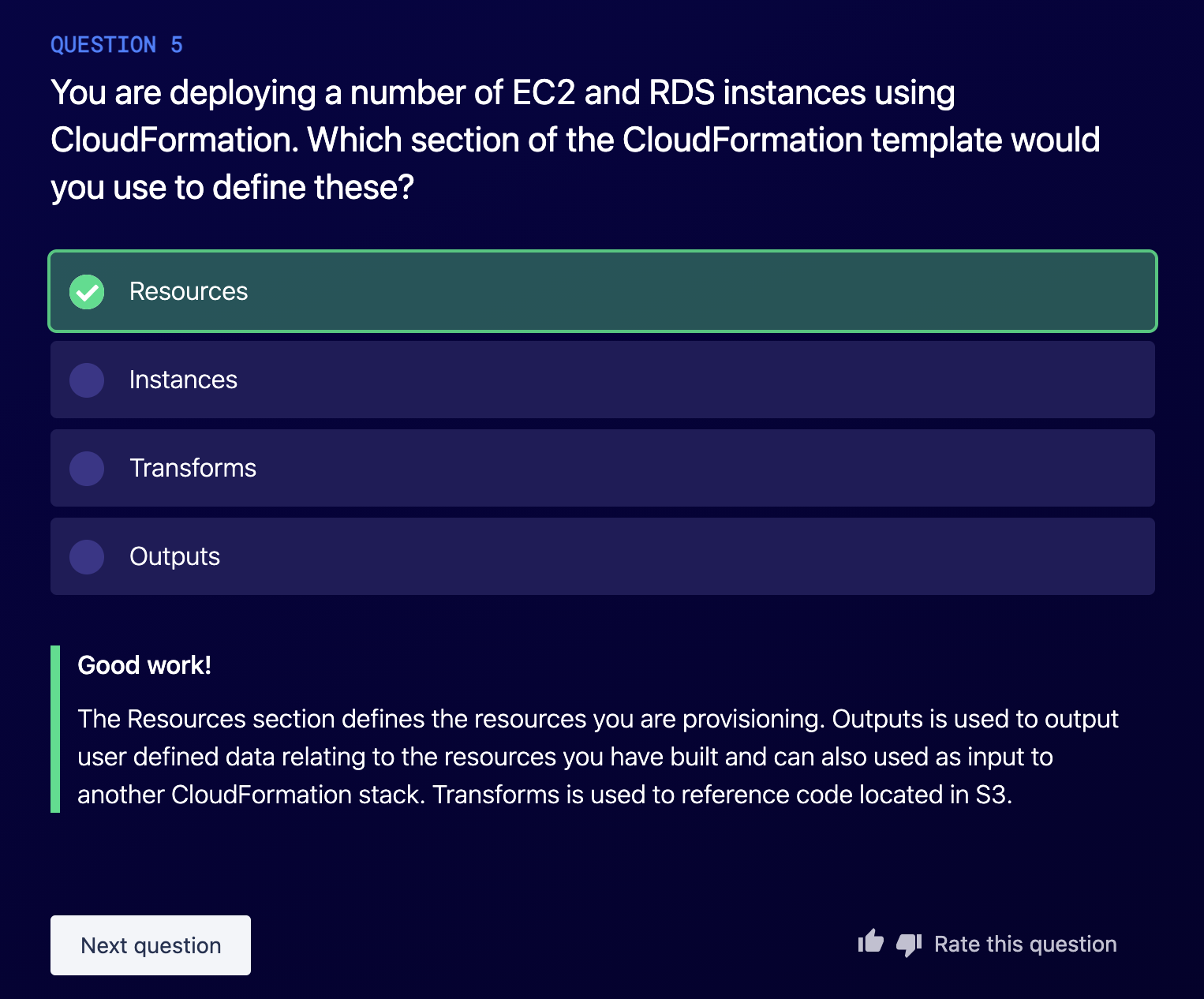
CloudFormation allows you to manage, configure, and provision AWS infrastructue as YAML or JSON code.
- The Resource Section is the only Mandatory of CloudFormation template.
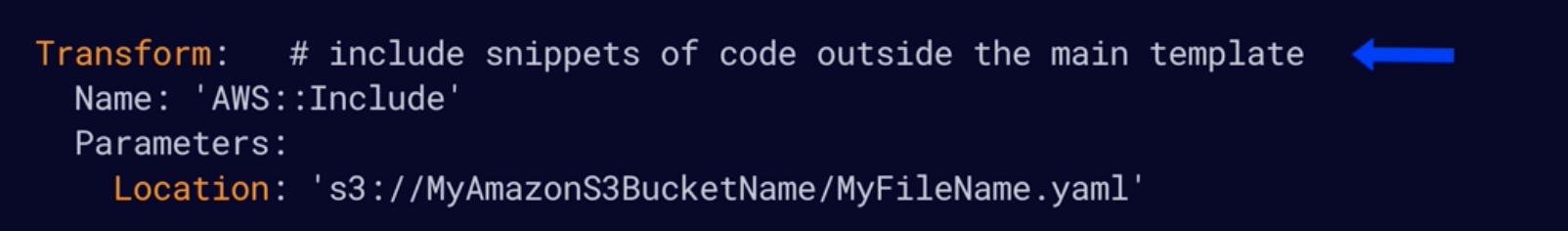
- The Transform section is used to reference additional code stored in S3, allowing for code re-use. E.g Lambda code or template nippets / reusable pieces of CloudFormation code.
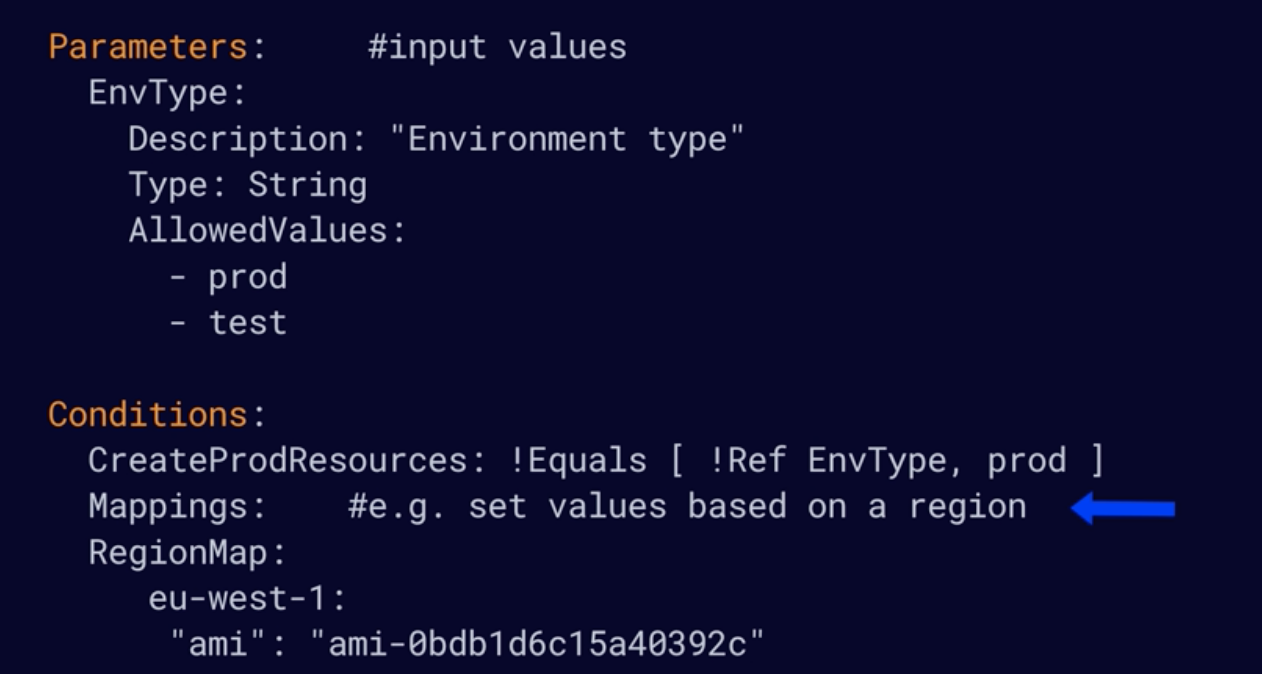
- The Parameters section is used to Input custom values
- The Conditions section is used for provision resources based on environment.
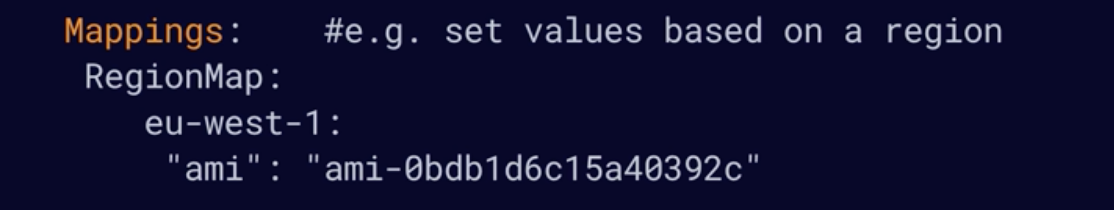
- The Mappings section allows you to create custom mappings like Region: AMI
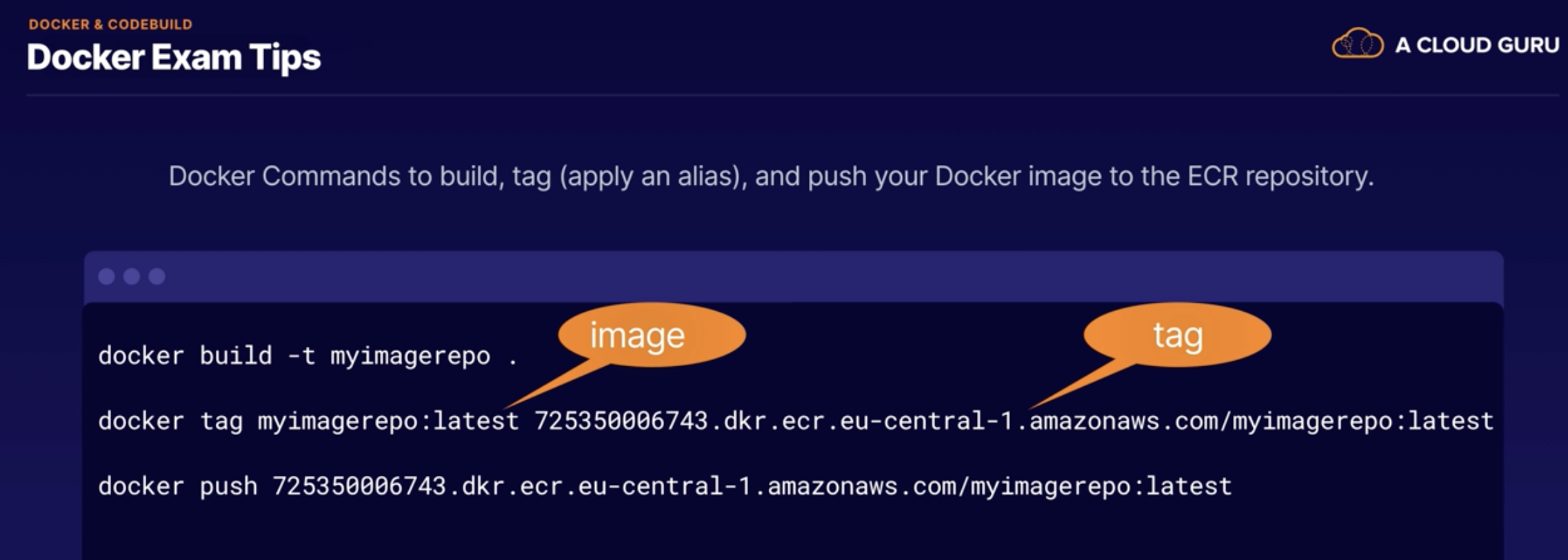
Exampe YML template:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09 Description: Template to create an EC2 instance and enable SSH Parameters: KeyName: Description: Name of SSH KeyPair Type: 'AWS::EC2::KeyPair::KeyName' ConstraintDescription: Provide the name of an existing SSH key pair Resources: MyEC2Instance: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Instance' Properties: InstanceType: t2.micro ImageId: ami-0bdb1d6c15a40392c KeyName: !Ref KeyName SecurityGroups: - Ref: InstanceSecurityGroup Tags: - Key: Name Value: My CF Instance InstanceSecurityGroup: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup' Properties: GroupDescription: Enable SSH access via port 22 SecurityGroupIngress: IpProtocol: tcp FromPort: 22 ToPort: 22 CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0 Outputs: InstanceID: Description: The Instance ID Value: !Ref MyEC2Instance

You can find `ImageId` when you create a new EC2 instances and remember to choose the correct region.
Serverless Application Model
Define and provision serverless applications using CloudFormation
SAM CLI
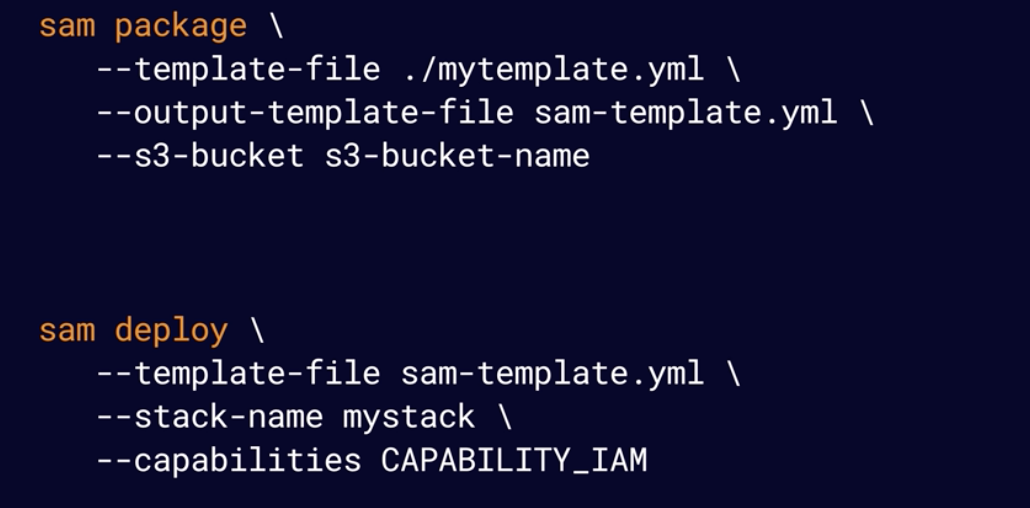
sam package: Packages your application and uploads to S3
sam deploy: Deploys your serverless app using CloudFormation.
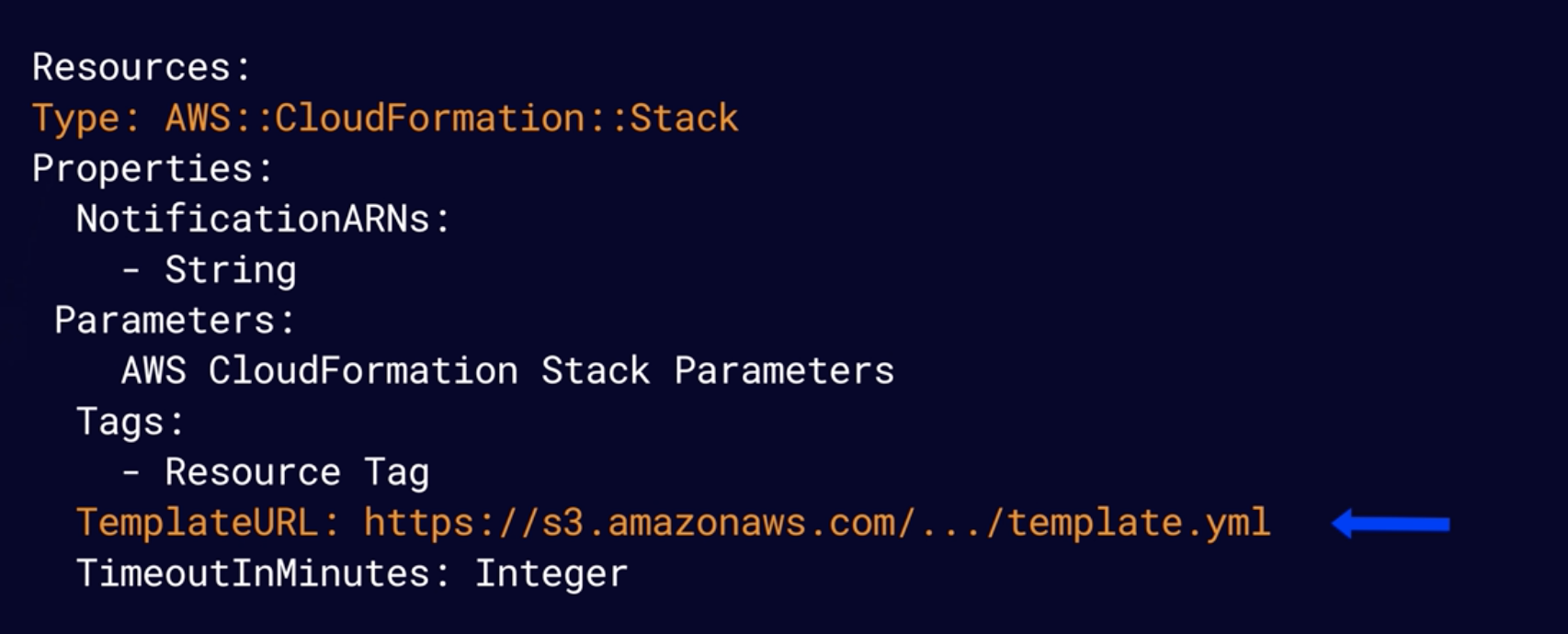
Nested CloudFormation Stacks
Enable re-use of CloudFormation code for common use cases: For example, you have a load balancer which used again and again.
Instead of copying out the code each time, create a standard template for each commn use case and reference from within your CloudFormation tempalte.

Lab: CloudFormation Nested Stack

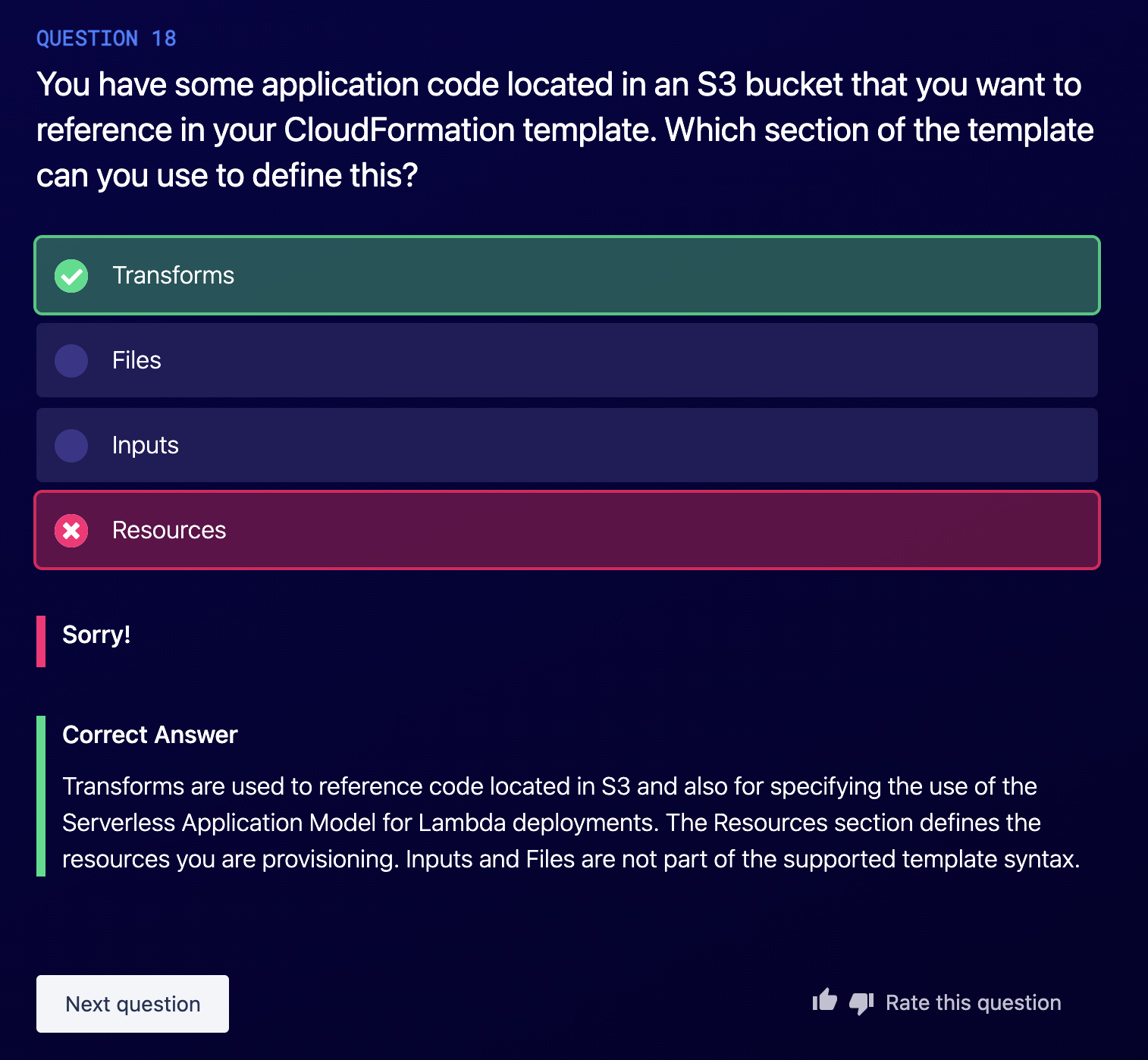

Transform: Reuse code and reference Lambda code snippet.

For serverless related, Lambda is in Transform section