Global Statistics:
Common seen methods as such
1. Mean
2. Median
3. Standard deviation: the larger the number means it various a lot.
4. Sum.
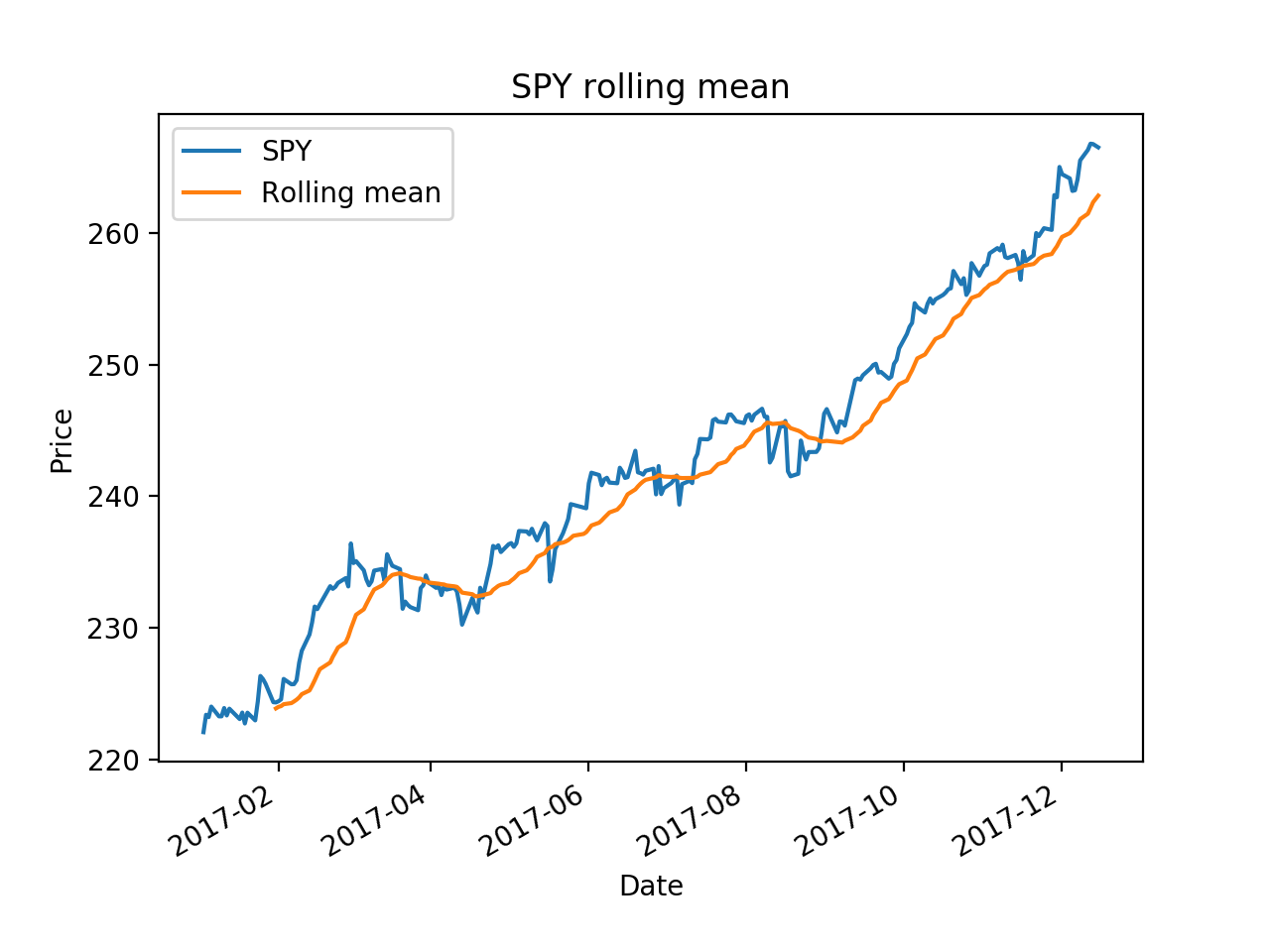
Rolling Statistics:
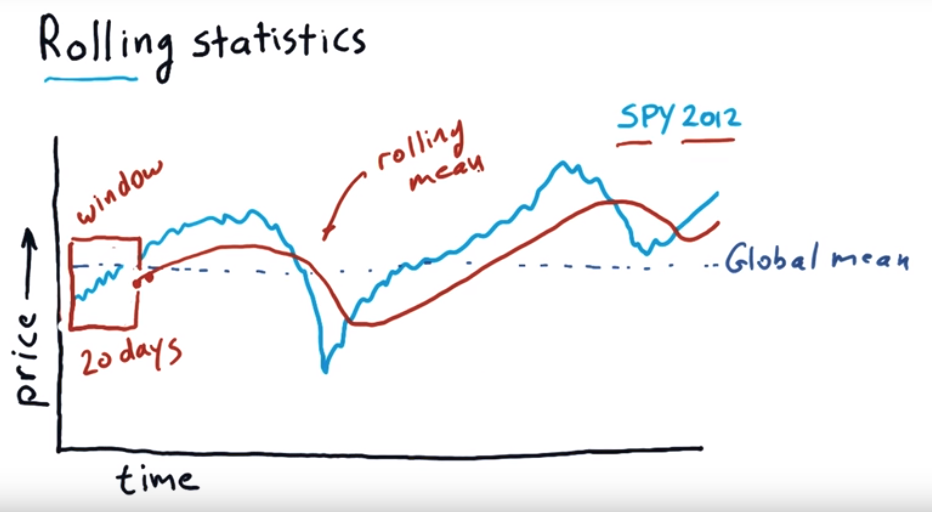
It use a time window, moving forward each day to calculate the mean value of those window periods.
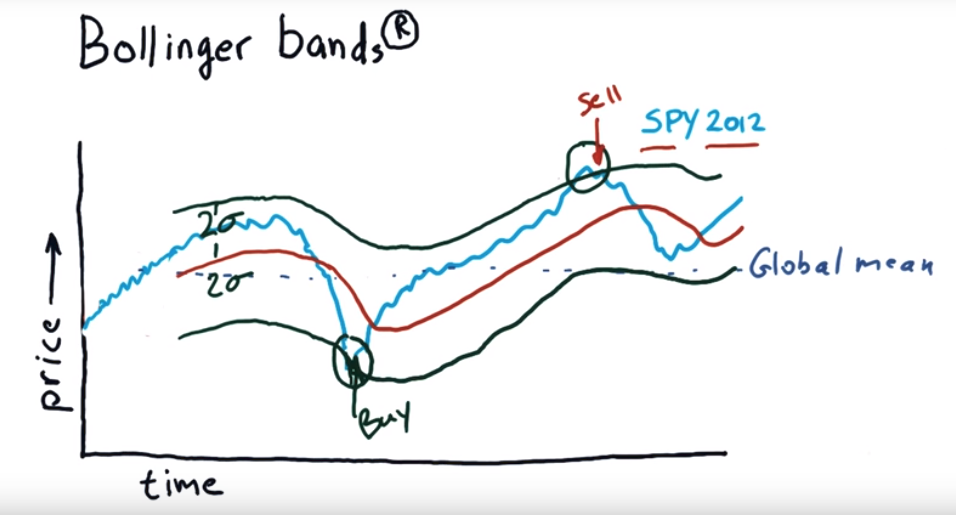
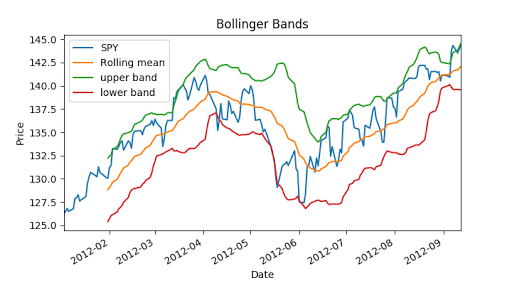
To find which day is good to buy which day is good for sell, we can use Bollinger bands.
Bollinger bands:
import os import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def test_run(): start_date='2017-01-01' end_data='2017-12-15' dates=pd.date_range(start_date, end_data) # Create an empty data frame df=pd.DataFrame(index=dates) symbols=['SPY', 'AAPL', 'IBM', 'GOOG', 'GLD'] for symbol in symbols: temp=getAdjCloseForSymbol(symbol) df=df.join(temp, how='inner') return df if __name__ == '__main__': df=test_run() # data=data.ix['2017-12-01':'2017-12-15', ['IBM', 'GOOG']] # df=normalize_data(df) ax = df['SPY'].plot(title="SPY rolling mean", label='SPY') rm = df['SPY'].rolling(20).mean() rm.plot(label='Rolling mean', ax=ax) ax.set_xlabel('Date') ax.set_ylabel('Price') ax.legend(loc="upper left") plt.show()
Now we can calculate Bollinger bands, it is 2 times std value.
"""Bollinger Bands.""" import os import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def symbol_to_path(symbol, base_dir="data"): """Return CSV file path given ticker symbol.""" return os.path.join(base_dir, "{}.csv".format(str(symbol))) def get_data(symbols, dates): """Read stock data (adjusted close) for given symbols from CSV files.""" df = pd.DataFrame(index=dates) if 'SPY' not in symbols: # add SPY for reference, if absent symbols.insert(0, 'SPY') for symbol in symbols: df_temp = pd.read_csv(symbol_to_path(symbol), index_col='Date', parse_dates=True, usecols=['Date', 'Adj Close'], na_values=['nan']) df_temp = df_temp.rename(columns={'Adj Close': symbol}) df = df.join(df_temp) if symbol == 'SPY': # drop dates SPY did not trade df = df.dropna(subset=["SPY"]) return df def plot_data(df, title="Stock prices"): """Plot stock prices with a custom title and meaningful axis labels.""" ax = df.plot(title=title, fontsize=12) ax.set_xlabel("Date") ax.set_ylabel("Price") plt.show() def get_rolling_mean(values, window): """Return rolling mean of given values, using specified window size.""" return values.rolling(window=window).mean() def get_rolling_std(values, window): """Return rolling standard deviation of given values, using specified window size.""" # TODO: Compute and return rolling standard deviation return values.rolling(window=window).std() def get_bollinger_bands(rm, rstd): """Return upper and lower Bollinger Bands.""" # TODO: Compute upper_band and lower_band upper_band = rstd * 2 + rm lower_band = rm - rstd * 2 return upper_band, lower_band def test_run(): # Read data dates = pd.date_range('2012-01-01', '2012-12-31') symbols = ['SPY'] df = get_data(symbols, dates) # Compute Bollinger Bands # 1. Compute rolling mean rm_SPY = get_rolling_mean(df['SPY'], window=20) # 2. Compute rolling standard deviation rstd_SPY = get_rolling_std(df['SPY'], window=20) # 3. Compute upper and lower bands upper_band, lower_band = get_bollinger_bands(rm_SPY, rstd_SPY) # Plot raw SPY values, rolling mean and Bollinger Bands ax = df['SPY'].plot(title="Bollinger Bands", label='SPY') rm_SPY.plot(label='Rolling mean', ax=ax) upper_band.plot(label='upper band', ax=ax) lower_band.plot(label='lower band', ax=ax) # Add axis labels and legend ax.set_xlabel("Date") ax.set_ylabel("Price") ax.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show() if __name__ == "__main__": test_run()
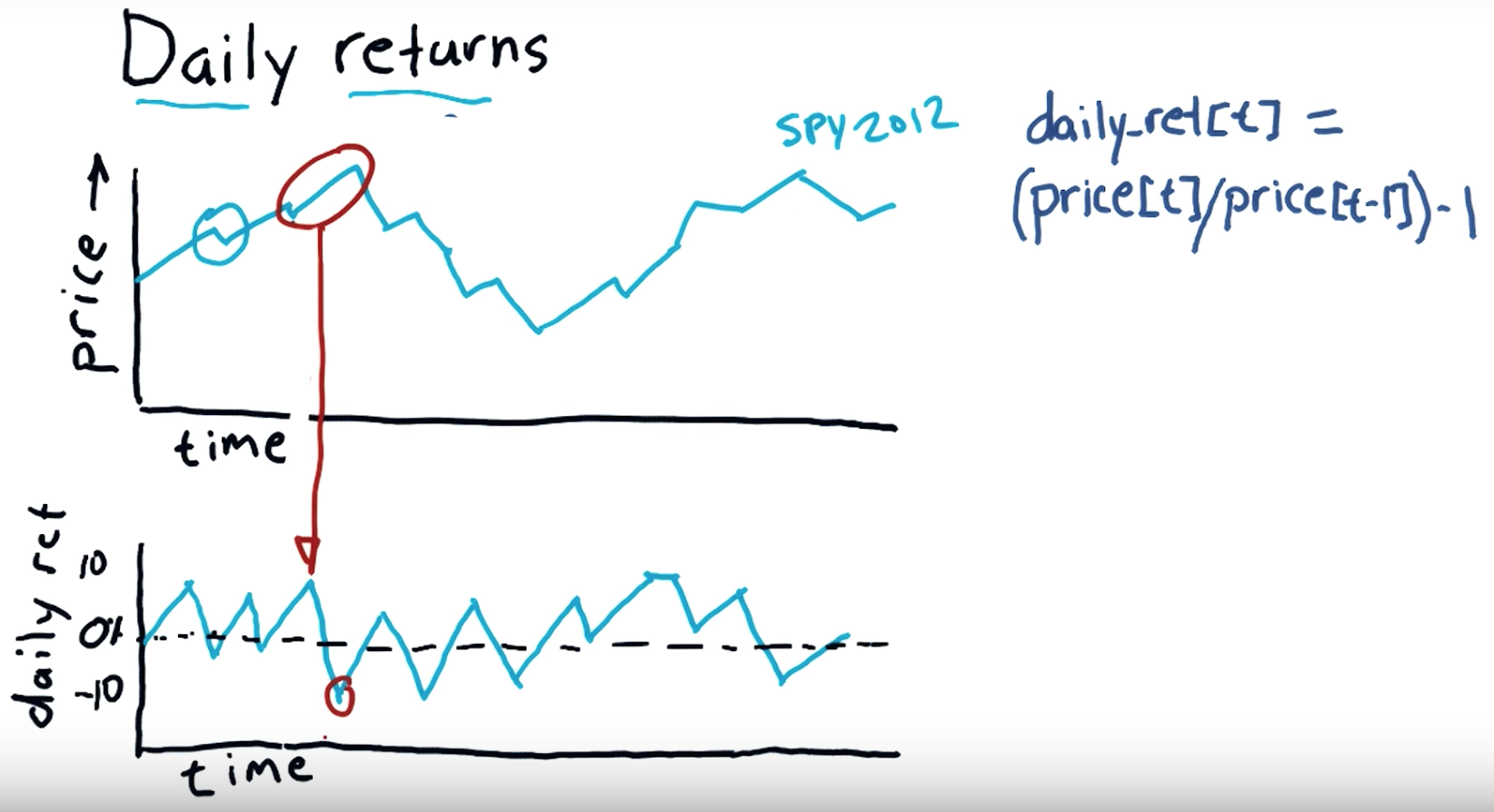
Daily return:
Subtract the previous day's closing price from the most recent day's closing price. In this example, subtract $35.50 from $36.75 to get $1.25. Divide your Step 4 result by the previous day's closing price to calculate the daily return. Multiply this result by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
"""Compute daily returns.""" import os import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def symbol_to_path(symbol, base_dir="data"): """Return CSV file path given ticker symbol.""" return os.path.join(base_dir, "{}.csv".format(str(symbol))) def get_data(symbols, dates): """Read stock data (adjusted close) for given symbols from CSV files.""" df = pd.DataFrame(index=dates) if 'SPY' not in symbols: # add SPY for reference, if absent symbols.insert(0, 'SPY') for symbol in symbols: df_temp = pd.read_csv(symbol_to_path(symbol), index_col='Date', parse_dates=True, usecols=['Date', 'Adj Close'], na_values=['nan']) df_temp = df_temp.rename(columns={'Adj Close': symbol}) df = df.join(df_temp) if symbol == 'SPY': # drop dates SPY did not trade df = df.dropna(subset=["SPY"]) return df def plot_data(df, title="Stock prices", xlabel="Date", ylabel="Price"): """Plot stock prices with a custom title and meaningful axis labels.""" ax = df.plot(title=title, fontsize=12) ax.set_xlabel(xlabel) ax.set_ylabel(ylabel) plt.show() def compute_daily_returns(df): """Compute and return the daily return values.""" # TODO: Your code here # Note: Returned DataFrame must have the same number of rows return df / df.shift(-1) -1 def test_run(): # Read data dates = pd.date_range('2012-07-01', '2012-07-31') # one month only symbols = ['SPY','XOM'] df = get_data(symbols, dates) plot_data(df) # Compute daily returns daily_returns = compute_daily_returns(df) plot_data(daily_returns, title="Daily returns", ylabel="Daily returns") if __name__ == "__main__": test_run()
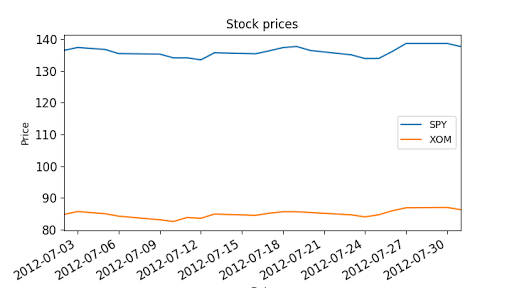
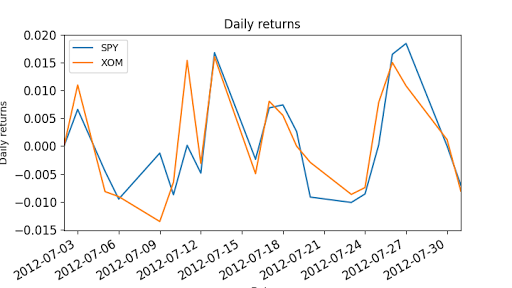
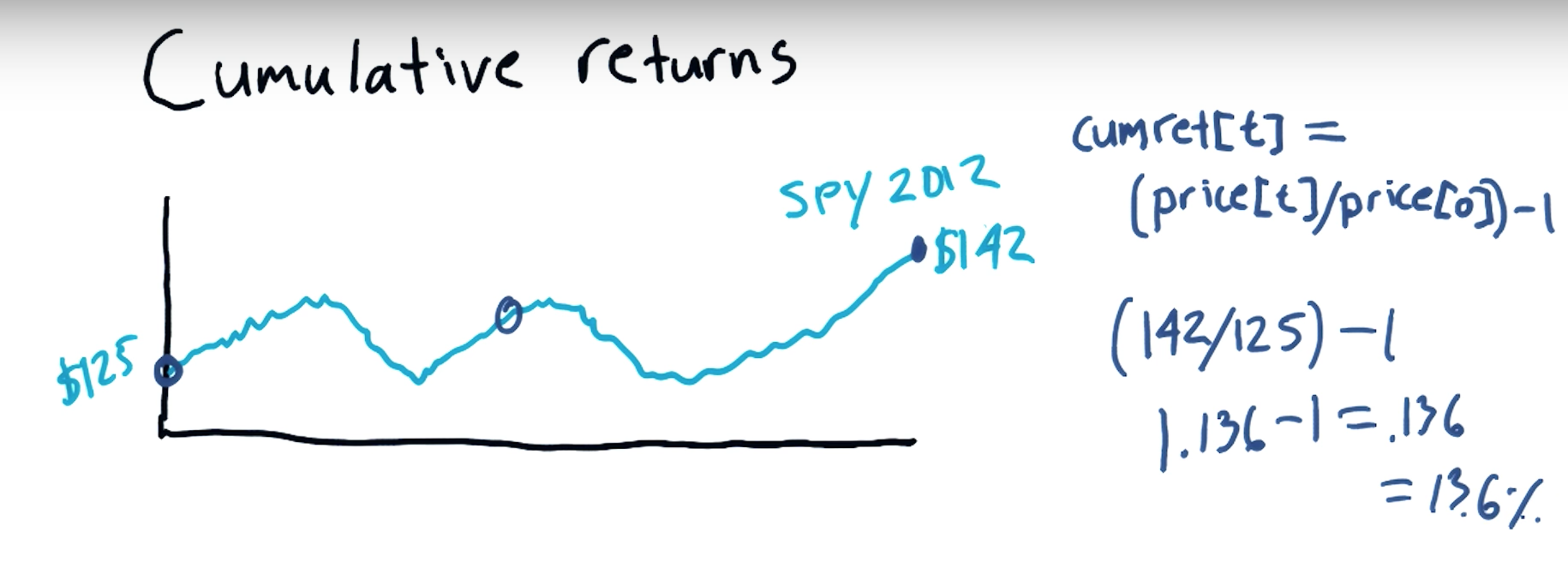
Cumulative return:
an investment relative to the principal amount invested over a specified amount of time. ... To calculate cumulative return, subtract the original price of the investment from the current price and divide that difference by the original price.