算法题整理
1.数组
1.1 剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution{
public int missingNumver(int[] nums){
int i=0,j = nums.length-1;
while(i<=j){
int m = (i+j)/2;
if(nums[m] == m){
i = m+1;
}else j = m-1;
}
}
}
解题:排序数组中的搜索问题,首先想到二分法解决
1.2 剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
解法有三种:
方法一:遍历数组 T O(n) S O(n)
利用集合的特性,把遍历的数组存到集合中,判断能否遇到重复数字
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums){
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
int repeat = -1;
for(int num : nums){
if(!set.add(num)){
repeat = num;
break;
}
}
return repeat;
}
}
方法二:原地置换 T O(n2) S O(1)
如果没有重复数字,那么正常排序后,数字i应该在下标为i的位置,所以思路是重头扫描数组,遇到下标为i的数字如果不是i的话,(假设为m),那么我们就拿与下标m的数字交换。在交换过程中,如果有重复的数字发生,那么终止返回ture.
class Solution{
public int fintRepeatNumber(int[] nums){
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
while(nums[i] != i){
if(nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]){
return nums[i];
}
temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[temp];
nums[temp]= temp;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
1.3 百度笔试:
给定一个存放整数的数组,重新排列数组使得数组左边为奇数,右边为偶数。 要求:空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度为O(n)
方法一:SO(n) TO(n)
void chongPai(int a[],int len){
int i,k,b[100];
b[100] = {0};
k = 0;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
if(a[i]%2 == 1)
{
b[k] = a[i];
k++;
}
}
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
if(a[i]%2 == 0)
{
b[k] = a[i];
k++;
}
}
}
方法二:首位双指针
- 定义头指针 leftleft ,尾指针 rightright
- leftleft 一直往右移,直到它指向的值为偶数
- rightright 一直往左移, 直到它指向的值为奇数
- 交换 nums[left] nums[left] 和 nums[right] nums[right]
- 重复上述操作,直到 left == right left==right
class Solution{
public vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums){
int left = 0,roght = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right){
if((nums[left] & 1) != 0){
left++;
continue;
}
if((nums[right] & 1) != 1){
rigeht--;
continue;
}
swap(nums[left++],nums[right--]);
}
return nums;
}
}
1.4 给定一个二进制串的位数,怎么枚举出所有情况
public class DecTBinary{
DecTBinary(int nData,int nByte){
int i = 0,j = 0;
int nArr[] new int[16];
while(nData != 0){
i = nData % 2;
nArr[j++] = i;
nData = nData /2;
}
j = nByte - 1;
for(;j >=0; j++){
System.out.print(nArr[j]);
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
double n = Math.pow(2.0,5);
System.out.println(n);
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
DecTBinary dec= new DecTBinary(i,5)
}
}
}
1.5 删除排序数组中的重复项
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
方法: 数组完成排序后,我们可以放置两个指针 i 和 j,其中 i 是慢指针,而 j 是快指针。只要 nums[i] = nums[j] ,我们就增加 j 以跳过重复项。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)O(n),假设数组的长度是 nn,那么 ii 和 jj 分别最多遍历 nn 步。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)O(1)。
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums){
if(nums.length == 0) return 0;
int i = 0;
for(int j=1;j<nums.length;j++){
if nums[j] != nums[i] {
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
}
2. 链表
2.1
一个数组插入删除查找和链表的效率对比?如果一个数组要反复插入删除怎么优化降低时间复杂度?(一开始 没想到,面试官提示其实就是垃圾回收的算法 原理就是“标记-查找”。每次删除的时候元素不是真的被删除了, 而是先标记,最后统一移动数组元素,减少移动次数)
2.2
ArrayList查询第一个跟最后一个复杂度一样么?(我说一样) 那LinkedList查询第一个跟最后一个复杂度一样 么?(我说不一样,因为链表是从头往后查,只有前一个才能记录后一个的位置) 你确定么? (想了下, LinkedList 是双向的,查询第一个跟最后一个是一样的) 那查询第一个跟倒数第二个呢?(这就不一样了,第 一个直接给了头结点,倒数第二个需要从倒数第一个开始查询,走两步) 腾讯
List特性:List底层是双向链表实现的,它的特点是:*查询效率低,增删效率高,线程不安全*。
2.3 arrayList底层原理 滴滴 字节跳动
ArrayList底层实现最大的几个特点就是:有序、元素能重复、线程不安全。其次,实际上ArrayList就是一个数组。没有想象中那么牛逼。直接看源代码可以得知但你NEW ArrayList 时候创建的就是个10个大小的数组,只不过这个数组是Object数组罢了!
2.4 获取单链表的长度
public int getLength(Node node){
if(head == null){
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
Node current = head;
while(current != null){
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
2.5 如何在不使用递归的情况下逆转单链表? 小米/美团/快手
迭代实现
public class LinkReverse{
static class Node{
int Node;
Node next;
public Node(int data, Node next){
this.node = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
private static Node reverseLinkByIterate(Node node){
Node prev = null;
Node now = node;
while(now != null){
Node next = now.next;
now.next = prev;
prev = now;
now = next;
}
return prev
}
}
private static Node reverseLink(Node node, Node prev) {
if(node.next == null) {
node.next = prev;
return node;
} else {
//该处比较难理解,这个是始终返回的第一个节点,一层层的向上传递
Node head = reverseLink(node.next, node);
node.next = prev;
return head;
}
}
2.6 如何在一次遍历中找到单个链表的中值?
基本思想:设置两个指针p,q,初始时,分别指向头结点,循环使p后移两位,q后移一位,当单链表遍历完毕时,q的位置就是中间位置。
iNode * GetMiddleNode ( iNode *head )
{
iNode *p1 = head;
iNode *p2 = p1;
while( p2 )
{
p2 = p2->next;
if(p2!=NULL)
{
p2 = p2->next;
p1=p1->next;
}
}
return p1;
}
2.7 如何证明给定的链表是否包含循环?如何找到循环的头节点? 优酷 腾讯 滴滴
思路:
设置一个快指针fast,一个慢指针slow,二者初始都指向链表头,fast一次走两步,slow一次走一步,两个指针同时向前移动,每移动一次,两个指针都要进行比较,如果快指针等于慢指针,则证明这是个有环的单链表,否则如果fast先行到达链表尾部或为NULL,则证明这是个不带环的单链表。
public static boolean isLoop(Node head){
boolean flag = false;
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (fast == null || fast.next == null){
flag = falst;
}
return falg;
}
综上可得:从链表头到环入口点等于(n - 1)循环内环 + 相遇点到环入口点,于是在链表头和环入口点分别设置一个指针,同时出发,每次各走一步,它们必定会相遇,且第一次相遇的点就是环入口点。
public static Node findLoopPort(Node node){
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
//先判断该链表是否有环
while(falst != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;
}
//如果链表有环,则将slow设置指向链表头,此时fast指向相遇点,然后同时开始移动,直到两个指针相遇
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;//环入口
}
2.8 两个有交叉的单链表,求交叉点
方案描述
第一种情况:两个链表均不含环

思路
- 直接法
采用暴力的方法,遍历两个链表,判断第一个链表的每个结点是否在第二个链表中,时间复杂度为O(len1*len2),耗时很大。
- hash计数法
如 果 两个链表相交,则两个链表就会有共同的结点;而结点地址又是结点唯一标识。因而判断两个链表中是否存在地址一致的节点,就可以知道是否相交了。可以对第一 个链表的节点地址进行hash排序,建立hash表,然后针对第二个链表的每个节点的地址查询hash表,如果它在hash表中出现,则说明两个链表有共 同的结点。这个方法的时间复杂度为:O(max(len1+len2);但同时还得增加O(len1)的存储空间存储哈希表。这样减少了时间复杂度,增加 了存储空间。
以链表节点地址为值,遍历第一个链表,使用Hash保存所有节点地址值,结束条件为到最后一个节点(无环)或Hash中该地址值已经存在(有环)。
再遍历第二个链表,判断节点地址值是否已经存在于上面创建的Hash表中。
这个方面可以解决题目中的所有情况,时间复杂度为O(m+n),m和n分别是两个链表中节点数量。由于节点地址指针就是一个整型,假设链表都是在堆中动态创建的,可以使用堆的起始地址作为偏移量,以地址减去这个偏移量作为Hash函数
- 有没有环
第三种思路是比较奇特的,在编程之美上看到的。先遍历第一个链表到他的尾部,然后将尾部的next指针指向第二个链表(尾部指针的next本来指向的是null)。这样两个链表就合成了一个链表,判断原来的两个链表是否相交也就转变成了判断新的链表是否有环的问题了:即判断单链表是否有环?
- 仔细研究两个链表,如果他们相交的话,那么他们最后的一个节点一定是相同的,否则是不相交的。
typedef struct node_t{
int data;
struct node_t *next;
}node;
node* find_node(node *head1,node *head2)
{
if (NULL = head1 || NULL = head2){
return NULL;
}
node *p1,*p2;
p1 = head1;
p2 = head2;
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
int diff = 0;
while(NULL != p1->next)
{
p1 = p1->next;
len1++;
}
while(NULL != p2->next)
{
p2 = p2->next;
len2++;
}
if(p1 != p2)//判断最后一个节点是否相等
{
return NULL;
}
diff = abs(len1 - len2);//该函数返回 x 的绝对值。
for(int i = 0;i<diff;i++){//使得p1;和p2 从一个起点出发
if(len1>len2){
p1 = p1->next;
}else if(len2>len1){
p2 = p2->next;
}else{
break;
}
}
while(p1 != p2){
p1 = p1 -> next;
p2 = p2 -> next;
}
return p1;
}
第二种情况: 链表中有环时
情况一:
(1)当两个链表中有环时,相交的判断:
如果链表有环且相交,那么这两个链表都是有环的。
找到第一个链表的环点,然后将环断开(当然不要忘记了保存它的下一个节点),然后再来遍历第二个链表,如果发现第二个链表从有环变成了无环,那么他们就是相交的嘛,否则就是不相交的了。
当两个有环的链表相交时,有以下两种情况:

在这种情况下,两个链表的交点在环点之前,可以将环点切断,这样就变成了两个无环的链表求相交点。可使用以上方法。
另一种情况为:

在这种情况下,不存在所谓的相交点。
(2)当一个链表中有环,一个链表中没有环时,两个链表必不相交。
2.9 合并单链表
思路:首先用尾插法建立两个链表LA,LB(头插法建立的链表顺序为倒序),遍历LA直到至LA的尾部即LA->next为空,让LA->指向LB的头部然后free(LB)
#include<iostream>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace id;
typedef struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}LinkNode,*Linklist;
//初始化
Linklist Initlist()
{
Linklist L;
L=(Linklist)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
L->next=NULL;
return L;
}
//尾插法建立链表
void CreatFromTail(Linklist L)
{
int data=-1;
Linklist s,tail;
tail=L;
cin>>data;//cin是C++编程语言中的标准输入流对象,即istream类的对象。cin主要用于从标准输入读取数据,这里的标准输入,指的是终端的键盘
while(data!=-1)
{
s=(Linklist)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s->data=data;
tail->next=s;
tail=s;
cin>>data;
}
tail->next=NULL;
}
// 输出链表
void PrintList(Linklist L)
{
Linklist p=L->next;
while(p)
{
cout<<p->data;
p=p->next;
}
}
/*
合并链表
*/
void merge(Linklist LA,Linklist LB)
{
Linklist p=LA->next;
while(p->next)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next=LB->next;
free(LB);
//PrintList(LA);
}
int main()
{
Linklist LA,LB;
LA=Initlist();
LB=Initlist();
CreatFromTail(LA);
PrintList(LA);
CreatFromTail(LB);
PrintList(LB);
cout<<endl;
merge(LA,LB);
PrintList(LA);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
扩展:
-
头插法建立单链表
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std
typedef struct Node{
int value;
struct Node *next;
}node,*linkedlist;
linkedlist linkedlistcreath()//返回的是该链表的地址
{
node *l=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));//该函数返回一个指针 ,指向已分配大小的内存。如果请求失败,则返回 NULL。
l->next = NULL;
int number;
while(scanf("%d",&number) != EOF){//,EOF是文件结尾标志,所以意思是没有到文件结尾 EOF是一个计算机术语,为End Of File的缩写
node *p = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));//新建一个node结构并为其申请空间
p->value = number;//给新建的node结构赋值
p->next = l -> next;//赋值p所指的节点(就是l所指的节点,即链表的第2个节点)
l->next = p;//将l所指的节点更新为p点
}
return l;
}
- 尾插法建立单链表
linkedlist linkedlistcreatt()//返回的是该链表的地址
{
node *l=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
l->next=NULL;
node *r;//r指向的始终是该链表的最后一个node结构
r=l;//这个地方是地址之间的赋值,所以对r操作就相当于对l操作,即对链表最后一个node结构操作
int number;
while (scanf("%d",&number)!=EOF)
{
node *p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));//新建一个node结构并为其申请空间
p->value=number;//给新建的node结构赋值
r->next=p;//将p插入到链表的最后一个node结构的后面
p->next=NULL;//此时p已经是链表的最后一个了,给p的next赋值
r=p;//让r等于链表的最后一个node结构,即p节点
}
return l;//返回头节点的地址
}
2.10 找到链表中倒数第k个节点腾讯
方法一
- 先遍历统计链表长度,记为 n*n ;
- 设置一个指针走 (n-k)步,即可找到链表倒数第 kk 个节点。
方法二
双指针
- 初始化: 前指针 former 、后指针 latter ,双指针都指向头节点 head 。
- 构建双指针距离: 前指针 former 先向前走 k 步(结束后,双指针 former 和 latter 间相距 k 步)。
- 双指针共同移动: 循环中,双指针 former 和 latter 每轮都向前走一步,直至 former 走过链表 尾节点 时跳出(跳出后, latter 与尾节点距离为 k-1k−1,即 latter 指向倒数第 k 个节点)。
- 返回值: 返回 latter 即可。
class Solution{
public ListNode getKthFormEnd(ListNode head,int k){
ListNode former = head, latter = head;
for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){
if(former == null) return null;
former = former.next;//检测k是否越界
}
while(former != null){
former = former.next;
latter = latter.next;
}
return latter;
}
}
方法三
- 使用栈保存链表,再按照k依次pop,最后返回栈头即为答案。要注意k=1时的特殊情况。
//C++
class Solution{
public: listNode* getKthFormEnd(ListNode* head,int k){
stack<listNode*> temp;
while(head){
temp.push(head);
head = head->next;
}
while(k>1){
tem.pop();
k--;
}
return temp.pop;
}
};
2.11 求矩阵中连续1的个数 Number of Islands 三星
关于图的算法问题 可以看这个文章
class Solution{
public int closedIsland(int[][] grid){
int rows = grid.length;
int cols = grid[0].length;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < rows; i++){
for(int j = 1; j< cols;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 0){
if(dfs(grid,i,j)){
res++;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
private boolean dfs(int[][] grid, int i,int j){
int rows = grid.length;
int cols = grid[0].length;
if(i<0 || j<0 || i >= rows || j>= cols){
return false;
}
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
return true;
}
grid[i][j] = 1;
boolean up = dfs(grid,i-1,j);
boolean down = dfs(grid,i+1,j);
boolean left = dfs(grid,i,j-1);
boolean right = dfs(grid,i,j+1);
if(up && down && left&& right){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2.12 大数相加(今日头条,美团)
方法一:栈
思路与算法
本题的主要难点在于链表中数位的顺序与我们做加法的顺序是相反的,为了逆序处理所有数位,我们可以使用栈:把所有数字压入栈中,再依次取出相加。计算过程中需要注意进位的情况。
class Solution{
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1,ListNode L2){
Deque<Integer> stack1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Deque<Integer> stack2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while(l1 != null){
stack1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
stack2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode ans = null;
while (!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int a = stack1.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack1.pop();
int b = stack2.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack2.pop();
int cur = a + b + carry;
carry = cur / 10;
cur %= 10;
ListNode curnode = new ListNode(cur);
curnode.next = ans;
ans = curnode;
}
return ans;
}
}
队列&堆栈
3.1 对比一下队列和栈,以及它们底部实现 腾讯
队列是一个有序的列表,原则:先入先出
首先:
1.自定义实现链表
public class NodeClass<T> {
private T Date;// 数据
private NodeClass<T> next //指针
public T getData(){
return Date;
}
public void setData(T Date){
Data = date;
}
public NodeClass<T> getNext(){
return next;
}
public void setNext(NodeClass<T> next){
Next = next;
}
@overide
public String toString(){
return "NodeClass{" +
"data=" + Date +
", next=" + Next +
'}';
}
}
自我理解:
栈就是采用 头插法的 链表,后插入的指向head 后进先出
队列 是尾插发,在新的节点后面插入节点,后进来的指向最后一个节点
3.2 一个送礼的场景, 礼物有权重属性,怎么根据权重进行对礼物进行处理,然后再排队纷发,每次取一个礼物, 怎么设计数据结构。喜马拉雅
用有序队列,权重大的排在队列前,每次取礼物只拿个就行。细节还有数据重排,队列维护,数据同步等
3.3 如何使用栈实现队列的功能?(广州荔枝FM)
栈实现队列
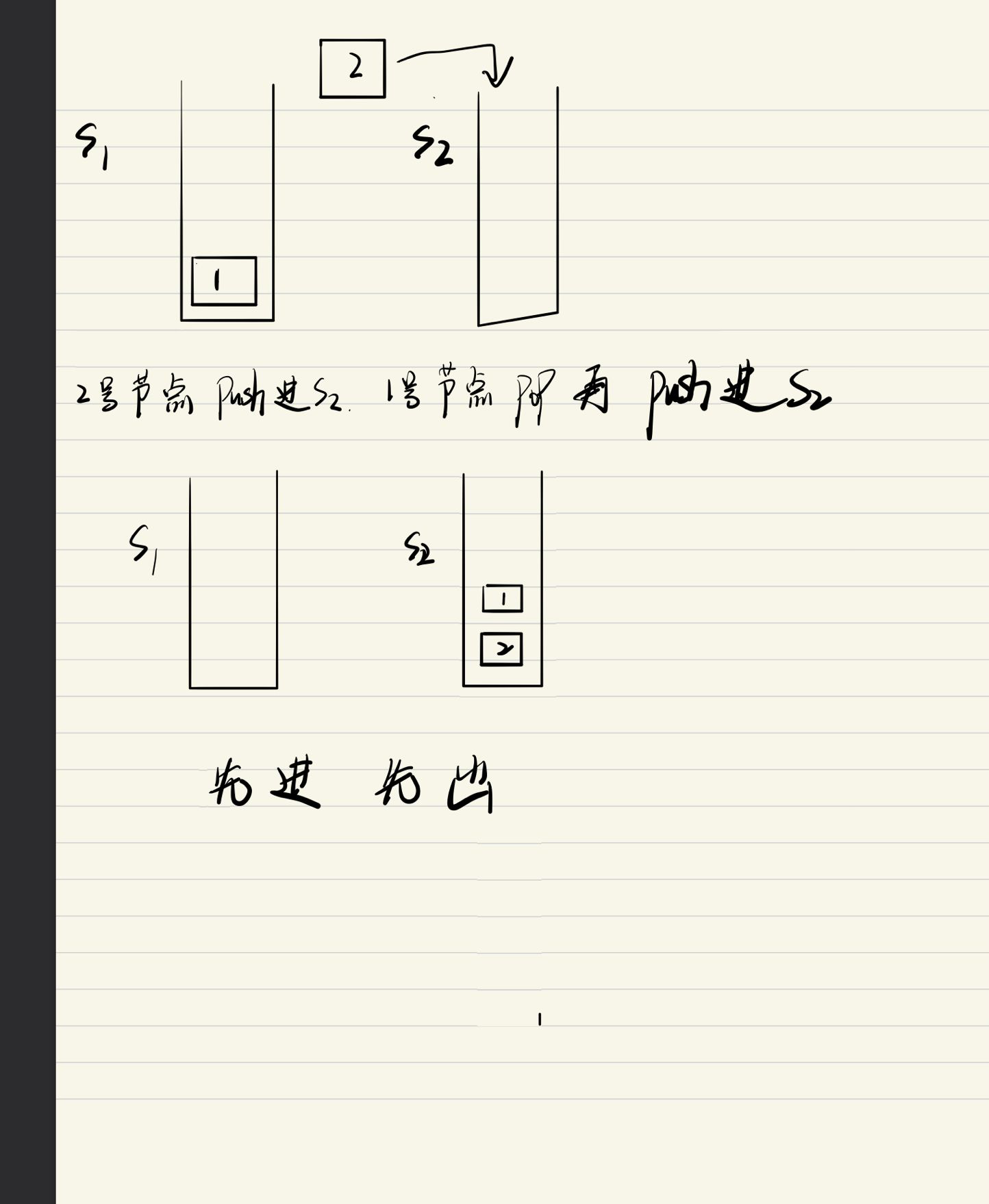
栈实现队列的基本思路:构造两个栈,其中一个用来存放存进来的数据,另外一个用来倒置其中的数据实现输出。
public static class twoStacksQueue{
private Stack<Integer> stackPop;
private Stack<Integer> stackPuch;
public twoStacksQueue(){
stackPop = new Stack<>();
stackPush = new Stack<>();
}
public void add(int pushInt){
stackPush.push(pushInt);
}
public int poll(){
if(stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
}else if(stackPop.empty()){
while(!stackPush.isEmpty()){
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.pop();
}
public int peek(){
if(stackPop.isEmpty() && stackPush.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is Empty!");
}else if(stackPop.isEmpty()){
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
stackPop.push(stachPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.peek();
}
}
3.5. 用队列实现栈
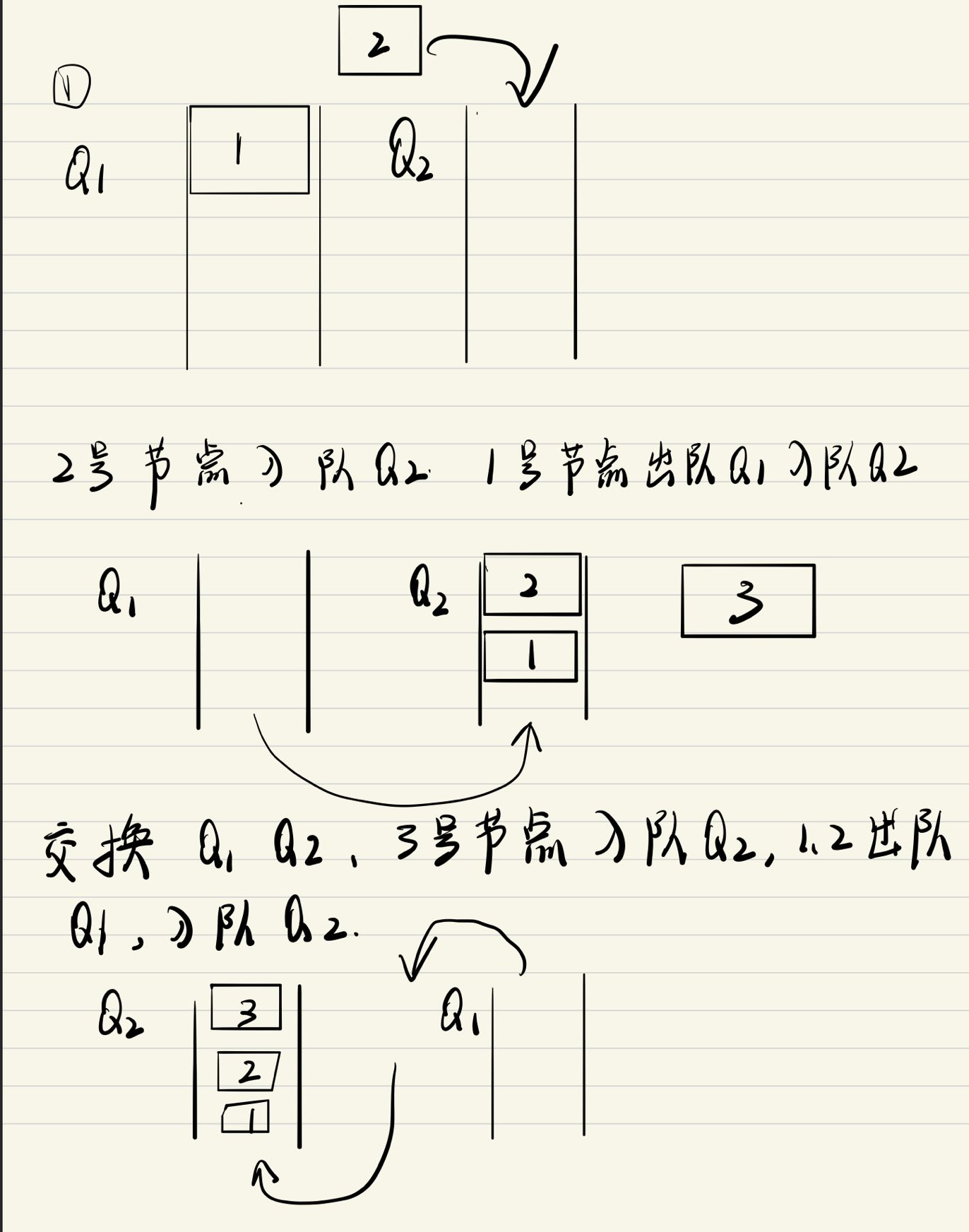
以使用两个队列实现栈的操作,其中 queue1用于存储栈内的元素,queue 2
作为入栈操作的辅助队列。
class MyStack{
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x){
queue2.offer(x);
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
4. 二叉树
4.1 知前序遍历为{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8},中序遍历为{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},它的二叉树是怎么样的? 58

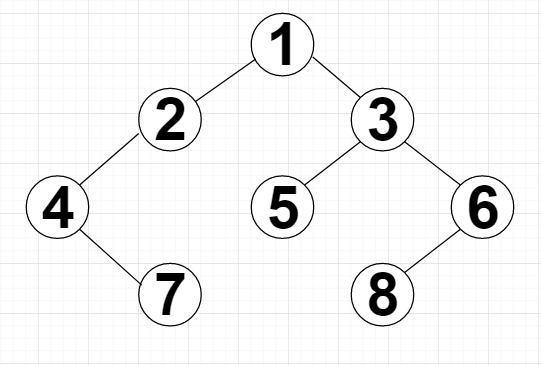
解题:
-
当前序遍历序列(pre)和中序遍历序列(in)为空时,返回一个空二叉树;
-
采用递归的思想,前序遍历序列(pre)的第一个结点为二叉树的根结点,先找出该根节点,定义为root根结点,并赋值给val,然后遍历中序遍历序列(in),找出val的位置,将其索引赋值给index;根据index对中序遍历序列(in)进行划分,将0-index(不包含index)的子序列划分为LeftIn,将index+1-in.length的子序列划分为RightIn; 根据LeftIn子序列和RightIn子序列的长度对前序遍历序列(pre)进行划分,将1-LeftIn.length+1的子序列划分为LeftPre,将index+1-pre.length的子序列划分为RightPre; 然后根据LeftPre子序列和LeftIn子序列构造二叉树左子树,根据RightPre子序列和RightIn子序列构造二叉树右子树;依次往下,直到整个二叉树构造完成;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] str1 = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
String[] str2 = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
// 先序遍历序列
int[] pre = new int[str1.length];
// 中序遍历序列
int[] in = new int[str2.length];
for(int i=0 ; i<str1.length ; i++) {
pre[i] = Integer.parseInt(str1[i]);
in[i] = Integer.parseInt(str2[i]);
}
TreeNode root = null;
root = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, in);
posttraverse(root);
System.out.println();
}
public static TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre, int [] in) {
if(pre.length == 0 && in.length == 0)
return null;
int val = pre[0];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(val);
int index = 0;
for(int i=0 ; i<in.length ; i++){
if(in[i]==val)
index = i;
}
int[] LeftIn = Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0, index);
int[] RightIn = Arrays.copyOfRange(in, index+1, in.length);
int[] LeftPre = Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, LeftIn.length+1);
int[] RightPre = Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, index+1, pre.length);
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(LeftPre, LeftIn);
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(RightPre, RightIn);
return root;
}
// 后序遍历输出
public static void posttraverse(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return;
posttraverse(root.left);
posttraverse(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
}
4.2什么是平衡二叉树,它有什么特征 美团
平衡二叉树特点:
(1)非叶子节点最多拥有两个子节点;
(2)非叶子节值大于左边子节点、小于右边子节点;
(3)树的左右两边的层级数相差不会大于1;
(4)没有值相等重复的节点;
平衡二叉树概念
平衡二叉树是基于二分法的策略提高数据的查找速度的二叉树的数据结构;
特点:
平衡二叉树是采用二分法思维把数据按规则组装成一个树形结构的数据,用这个树形结构的数据减少无关数据的检索,大大的提升了数据检索的速度;平衡二叉树的数据结构组装过程有以下规则:
(1)非叶子节点只能允许最多两个子节点存在。
(2)每一个非叶子节点数据分布规则为左边的子节点小当前节点的值,右边的子节点大于当前节点的值(这里值是基于自己的算法规则而定的,比如hash值);
平衡树的层级结构:因为平衡二叉树查询性能和树的层级(h高度)成反比,h值越小查询越快、为了保证树的结构左右两端数据大致平衡降低二叉树的查询难度一般会采用一种算法机制实现节点数据结构的平衡,实现了这种算法的有比如Treap、红黑树,使用平衡二叉树能保证数据的左右两边的节点层级相差不会大于1.,通过这样避免树形结构由于删除增加变成线性链表影响查询效率,保证数据平衡的情况下查找数据的速度近于二分法查找;
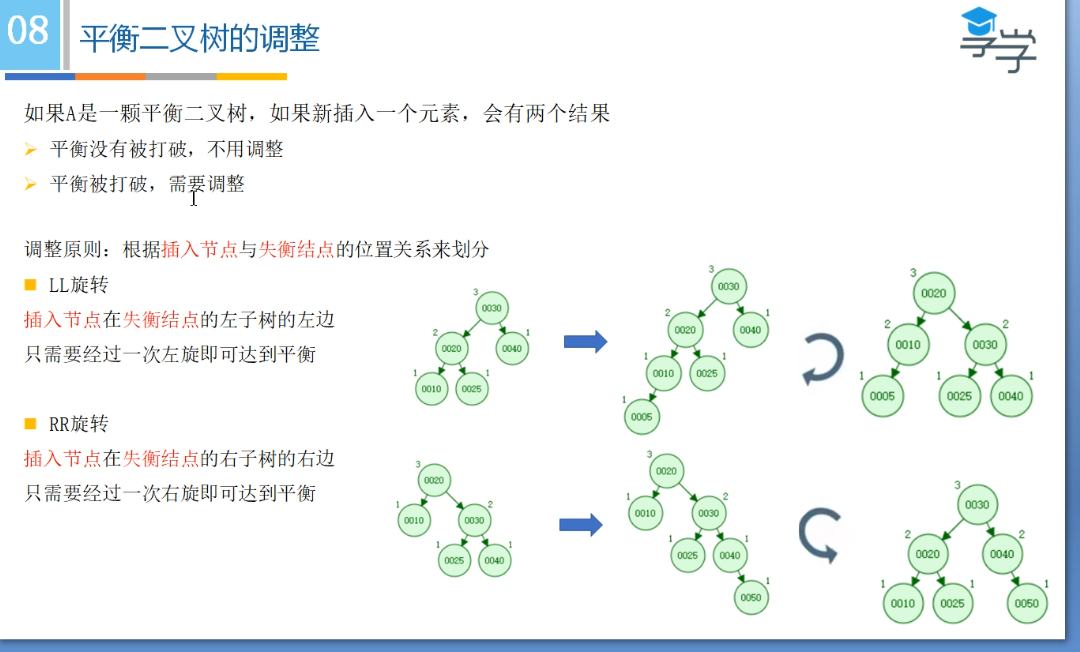
4.3 平衡二叉树和红黑树的区别?字节跳动
1、红黑树放弃了追求完全平衡,追求大致平衡,在与平衡二叉树的时间复杂度相差不大的情况下,保证每次插入最多只需要三次旋转就能达到平衡,实现起来也更为简单。
2、平衡二叉树追求绝对平衡,条件比较苛刻,实现起来比较麻烦,每次插入新节点之后需要旋转的次数不能预知。
红黑树
- 特殊的二叉查找树
- 根节点是黑色
- 所有NULL节点称为叶子节点,且认为颜色为黑
- 所有红色节点的子节点都为黑色
- 从任一节点到其叶子节点的所有路径都包含相同的黑节点
查找的时候 最坏的路径也就比最短的长一倍
4.4 B 树,B+树 是什么区别? 字节跳动
B树:二叉树,每个结点只存储一个关键字,等于则命中,小于走左结点,大于
走右结点;
B-树:多路搜索树,每个结点存储M/2到M个关键字,非叶子结点存储指向关键
字范围的子结点;
所有关键字在整颗树中出现,且只出现一次,非叶子结点可以命中;
B+树:在B-树基础上,为叶子结点增加链表指针,所有关键字都在叶子结点
中出现,非叶子结点作为叶子结点的索引;B+树总是到叶子结点才命中;
B*树:在B+树基础上,为非叶子结点也增加链表指针,将结点的最低利用率
4.5 如何在给定的二叉树中执行先序遍历?百度
首先我们需要了解什么是二叉树的前序遍历:按照访问根节点——左子树——右子树的方式遍历这棵树,而在访问左子树或者右子树的时候,我们按照同样的方式遍历,直到遍历完整棵树。因此整个遍历过程天然具有递归的性质,我们可以直接用递归函数来模拟这一过程。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, res);
preorder(root.right, res);
}
}
后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, res);
postorder(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
}
}
4.6 检查子树
class Solution {
public:
bool checkSubTree(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2) {
if (t2 == NULL) return true;
if (t1 == NULL) return false;
if (t1->val == t2->val) {
return checkSubTree(t1->left, t2->left) && checkSubTree(t1->right, t2->right);
} else {
return checkSubTree(t1->left, t2) || checkSubTree(t1->right, t2);
}
}
};
4.7 请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化二叉树和反序列化二叉树。 YY
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return "[]";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }};
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node != null) {
res.append(node.val + ",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
else res.append("null,");
}
res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1);
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data.equals("[]")) return null;
String[] vals = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }};
int i = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
queue.add(node.left);
}
i++;
if(!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
queue.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
4.9 任意一颗二叉树,求最大节点距离 字节跳动 百度
题目:如果我们把二叉树看做图,父子节点之间的连线看成是双向的,我们姑且定义“距离”为两个节点之间边的个数。写一个程序求一棵二叉树中相距最远的两个节点之间的距离。来自(这里)[https://blog.csdn.net/liuyi1207164339/article/details/50898902]
书上对这个问题的分析是很清楚的,计算一个二叉树的最大距离有两个情况:
情况A: 路径经过左子树的最深节点,通过根节点,再到右子树的最深节点。
情况B: 路径不穿过根节点,而是左子树或右子树的最大距离路径,取其大者
对于情况A来说,只需要知道左右子树的深度,然后加起来即可。
对于情况B来说,需要知道左子树的最远距离,右子树的最远距离。
//改进的版本
int HeightOfBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode*pNode, int&nMaxDistance){
if (pNode == NULL)
return -1; //空节点的高度为-1
//递归
int nHeightOfLeftTree = HeightOfBinaryTree(pNode->m_pLeft, nMaxDistance) + 1; //左子树的的高度加1
int nHeightOfRightTree = HeightOfBinaryTree(pNode->m_pRight, nMaxDistance) + 1; //右子树的高度加1
int nDistance = nHeightOfLeftTree + nHeightOfRightTree; //距离等于左子树的高度加上右子树的高度+2
nMaxDistance = nMaxDistance > nDistance ? nMaxDistance : nDistance; //得到距离的最大值
return nHeightOfLeftTree > nHeightOfRightTree ? nHeightOfLeftTree : nHeightOfRightTree;
}
5 HashMap
参考此链接
5.1 HashMap的底层原理是什么?线程安全么? 百度 美团
HashMap底层是用的哈希表,哈希表是由数组+链表组成。
思考:哈希表有什么优势呢?
数组
数组存储区间是连续的,占用内存严重,故空间复杂度很大。但数组的二分查找时间复杂度小,为O(1);数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;
链表
链表存储区间离散,占用内存比较宽松,故空间复杂度很小,但时间复杂度很大,达O(N)。链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。
哈希表((Hash table)既满足了数据的查找方便,同时不占用太多的内容空间,使用也十分方便。
1、HashMap的线程不安全场景
- 多线程的put
- put和get并发时,可能导致get为null
- 3)JDK7中HashMap并发put会造成循环链表,导致get时出现死循环
- 线程安全的HashMap==>ConcurrentHashMap
5.2. HashMap中put是如何实现的? 滴滴
-
HashMap添加的元素是一个Entry(Key-Value对),因此首先需要有一个的元素类型的Hash表
-
添加元素时,HashMap会根据Key的值,计算hash值,进一步计算出该元素在Hash表中对应的索引
-
从源码中可以看出,HashMap对于一个Key的索引计算是通过tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]进行的,也就是说该元素的索引是i = (n - 1) & hash,其中n为hash表长度,传递进putVal()中的hash值是在put()方法中的hash(key)得到,hash()方法的源码如下:
static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); } -
其返回值是一个int类型的整型数,32位
-
因此若添加的一个元素中Key通过Object类hashCode()方法得到的hash值为h,则该元素在HashMap中的hash表索引为:i = (n - 1) & (h^(h>>>16)),其中n为hash表长度
-
如果hash数组中,该元素的索引位置没有元素,就把该元素放在hash数组中,如果存在元素,则把已存在的元素作为链表的头节点,添加元素依次往后放,这么一条链表上的元素,其hash值是相同的
4)当一个链表长度过长,其检索性能也会降低,新的版本中会把链表长度大于8的链表转换为红黑树,除此之外也会通过将hash数组扩容的方法来提高效率5.3. 谈一下hashMap中什么时候需要进行扩容,扩容resize()又是如何实现的?
-
hash数组会有一个初始容量,及一个系数(默认是0.75),当hash数组容量超过初始容量的0.75时,会将hash数组扩大两倍(resize()),然后将之前存的元素rehash()到新的hash数组中,这个过程中会改变索引,会把以往较长的链表重新打散存储在新的hash数组中
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//扩容前的参数复制
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//如果旧表不为空
if (oldCap > 0) {
//旧表长度超出最大容量
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//新表赋值长度是旧表的两倍(newCap = oldCap << 1)
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // 容量阈值也同步放大两倍
}
//如果旧表为空,就开始第一次初始化表
else if (oldThr > 0)
newCap = oldThr;
else {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);//初始化表赋值
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;//新表长度乘以加载因子
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
//构造新表,并把旧表中的所有元素rehash
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
//hash数组的遍历
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;//旧表中删去元素
//如果旧表中该索引只有一个元素,即链表长度为1
if (e.next == null)
//在新表中重新计算该元素的hash索引
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//如果该hash索引下是否包含多个元素
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)//判断是否是红黑树结构
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // 如果是正常的链表结构,则需要将链表遍历,重新放置
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
//遍历整个链表
do {
next = e.next;
//新表是旧表的两倍,实例上就把单链表拆成两队
//(e.hash & oldCap) == 0为一队,!=0为一队
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
//将两个单链表的头节点放到对应索引处
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
5.4 什么是哈希碰撞?怎么解决? 滴滴 美团
两个不同的元素得到了同一个存储地址
hash冲突的解决方法
开放定址法
当冲突发生时,使用某种探查技术在散列表中形成一个探查序列。沿此序列逐个单元地查找,直到找到给定的关键字,或者碰到一个开放的地址(即该地址单元为空)为止(若要插入,在探查到开放的地址,则可将待插入的新结点存入该地址单元)。
哈希表越来越满时数据插入非常耗时,因此设计Hash表确保元素数不超过容量的一半,最多不超过2/3
开放定址方法按照寻址方法可以分为:
- 1)线性探测:在原来值的基础上往后加一个单位,直至不发生哈希冲突
- 2)在平方探测:在原来的值上先加1的平方个单位,若仍然冲突则减1平方个单位,随之是2的平法,3的平方
- 3)伪随机探测:在原来值基础上加上一个随机函数生成的数,直至不发生哈希冲突
链地址法(拉链法),也是目前HashMap使用的方法
将具有相同HashCode的值根据插入顺序,形成链表,链表的头节点地址放Hash表中
生成链表需要额外的空间,需要花费精力和时间维护链表,扩容的时候需reHash
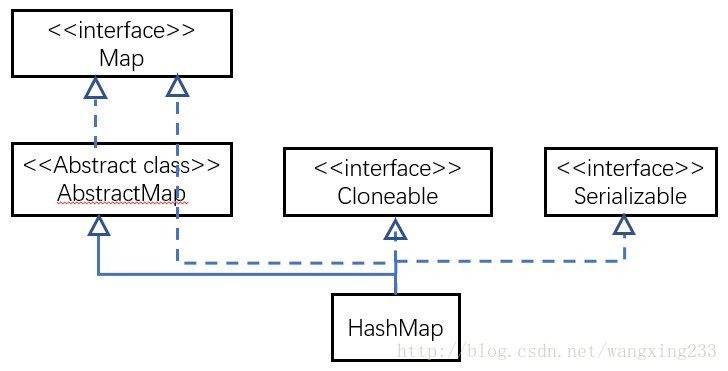
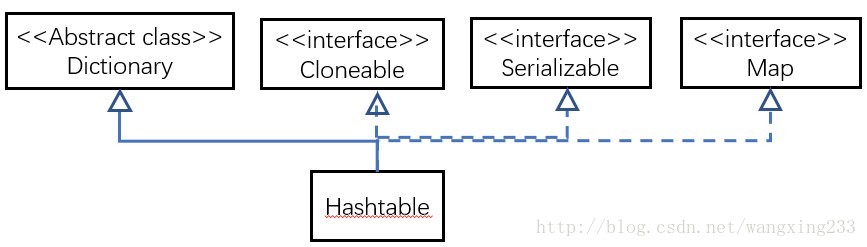
5.5 HashMap和HashTable的区别 小米
HashMap和Hashtable都实现了Map接口,但是具体用哪个,还要看他们两个的区别:
参考链接
Hashtable是线程安全的,它的每个方法中都加入了Synchronize(vt. 使……合拍;使……同步)方法。在多线程并发的环境下,可以直接使用Hashtable,不需要自己为它的方法实现同步(可以多个线程可以共享一个Hashtable)
HashMap不是线程安全的,在多线程并发的环境下,可能会产生死锁等问题。使用HashMap时就必须要自己增加同步处理.
附加链接
Dictionary类是一个已经被废弃的类(见其源码中的注释)。父类都被废弃,自然而然也没人用它的子类Hashtable了。
5.6 hashmap concurrenthashmap原理
参考链接
HashMap 在高并发下会出现链表环,从而导致程序出现死循环,高并发下避免 HashMap 出问题的方法有两种,一是使用 HashTable,二是使用 Collections.syncronizedMap。但是这两种方法的性能都能差。因为这两个在执行读写操作时都是将整个集合加锁,导致多个线程无法同时读写集合。高并发下的 HashMap 出现的问题就需要 ConcurrentHashMap 来解决了。

可以说,ConcurrentHashMap 是一个二级哈希表。在一个总的哈希表下面,有若干个子哈希表。这样的二级结构,和数据库的水平拆分有些相似。
5.7 arraylist和hashmap的区别,为什么取数快?字节跳动
可以直接根据下标取数
6. 图
6.1. 旋转输出矩阵 美团
借助辅助
第一行的第 xx 个元素在旋转后恰好是倒数第一列的第 xx 个元素。
我们将其翻译成代码。由于矩阵中的行列从 00 开始计数,因此对于矩阵中的元素 matrix[i] [j],在旋转后,它的新位置为 maxtrix[j] [n-i-1]
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
int[][] matrix_new = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix_new[j][n - i - 1] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
matrix[i][j] = matrix_new[i][j];
}
}
}
}
6. 2 给定一个矩阵 int matrixA[[m]][][n],每行每列都是增序的,实现一个算法去寻找矩阵中的某个元素 element. 搜 狗
https://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7085669
7 排序算法
7.1 top-k排序(堆排序,位图法) 美团
五、总结
TopK,不难;其思路优化过程,不简单:
- 全局排序,O(n*lg(n))
- 局部排序,只排序TopK个数,O(n*k)
- 堆,TopK个数也不排序了,O(n*lg(k))
- 分治法,每个分支“都要”递归,例如:快速排序,O(n*lg(n))
- 减治法,“只要”递归一个分支,例如:二分查找O(lg(n)),随机选择O(n)
- TopK的另一个解法:随机选择+partition
7.2. 冒泡排序的手写 华捷艾米
public class Bubblsort{
public static int[] sort{int[] array}{
if (array.length == 0 || array.length == 1){
return array;
}
for(int i = 0;i < array.length; i++){
for (int j = 0;j = array.length - 0 - i;j++){
if(array[j+1] < array[j]){
int temp = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
7.3 堆排序算法的手写 华捷艾米
public class HeapSort{
//声明全局遍历。用于记录 array的长度
private static int len;
private static int[] sort(int[] array){
len = array.length;
if (len<1) return array;
//构建最大堆
buildMaxHeap(array);
//取出堆顶元素和尾元素交换
while(len>0){
swap(array,0,len-1);
len--;// len-- 数组不变
adjustHeap(array,i);
}
return array;
}
}
// 构建一个最大堆
private static void bulidMaxHeap(int[] array){
for(int i = (len/2 -1);i>=0;i++){
adjustHeap(array,i);
}
}
// 调整堆
private static void adjustHeap(int[] array, int i){
int manIndex = i;//保存最大的元素
int left = 2*i + 1;//左节点
int right = 2*(i - 1);//右节点
if (right < len && array[left] > array[MaxIndex]){
maxIndex = left;
}
if (right < len && array[right] > array[MaxIndex]){
maxIndex = right;
}
if(maxIndex != i){
swap(array,maxIndex,i);
adjustHeap(array,maxIndex);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
7.4 椭圆形场地有两个赛道,可以同时提供两匹马比赛,两匹马比赛后,可以获知两匹马中跑的快的那匹马,但是 没有计时工具。问题,如何最优的算法(比赛次数最少),获知10匹马中速度最快的三匹马 阿里
堆排序
平衡二叉树
7.5. 输入一个整型无序数组,对堆排序的方法使得数组有序 阿里
public class HeapSort{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};
heapSort(arr);
}
//堆排序函数
public static void heapSort(int[] arr){
int len = arr.length;
bulidHeap(arr,len);
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++){
swap(arr,0,len-1-i)
adjustHeap(arr,len-1-i,0);
}
}
// 搭建堆
public static void buildHeap(int[] arr,int maxlen){
int len = maxlen/2 -1;
for (int i = len; i >= 0; i--){
adjustHeap(arr, maxlen, i);
}
}
// 调整堆
private static void adjustHeap(int[] array, int i){
int manIndex = i;//保存最大的元素
int left = 2*i + 1;//左节点
int right = 2*(i + 1);//右节点
if (right < len && array[left] > array[MaxIndex]){
maxIndex = left;
}
if (right < len && array[right] > array[MaxIndex]){
maxIndex = right;
}
if(maxIndex != i){
swap(array,maxIndex,i);
adjustHeap(array,maxIndex);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
7.6. 快速排序 手写实现 小米 CVTE
public class QuickSort{
public static int[] sort(int[] array,int start,int end){
if(array.length<1 || start < 0 || end >= array.length || start > end)
return null;
// 分区(割)指示器 = 一趟快速排序之后的返回值下标
int zoneIndex = partition(array,start,end);
//对左右两个部分递归调用 sort方法
if(zoneIndex > start){
sort(array,start,zoneIndex -1);
}
if(zoneIndex < end){
sort(array,zoneIndex+1,end);
}
return array;
}
private static int partition(int[] array,int start, int end){
//基准数
int pivot = (int)(start + Math.random() + (end - start+1));
int zoneIndex = start -1;
swap(array,pivot,end);// 交换基准数和尾元素
for(int i = start;i < end;i ++){
if(array[i] < array[end]){
zoneIndex +=;
if(i>zoneIndex){
swap(array,i,zoneIndex);
}
}
}
return zoneIndex;
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
7.7 直接插入排序手写实现 小米
public class InsertionSort{
public static int[] sort(int[] array){
if(array.length == 0){
return array;
}
int currentValue;//待排序数组
for(int i =0;i<array.length-1;i++){
//默认第一个元素已经排序
int preIndex = i;//已排序数据的索引
currentValue = array[preIndex+1];
while(preIndex >= 0&& currentValue < array[preIndex]){
array[preIndex + 1] = array[preIndex];
preIndex--;//遍历已排序的数组
}
array[preIndex+1] = currentValue;
}
}
}
8. 查找算法
8.1. 有序数组的二分查找算法 百度 苏宁
public int search(int[] nums,int target){
int pivot,left = 0,right = nums.length -1;
while(left<= right){
pivot = left +(right - left) /2;
if(nums[pivot] == target) return pivot;
if(target < nums[pivot])
right = pivot -1;
else left = pivot +1;
}
return -1;
}
8. 2 如何在给定数组中执行二分法搜索? 苏宁
int Binary_Search(SeqList L,int n,ElemType k){
int low=0,high=n-1,mid;
while(low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(L[mid].key==k)
return mid+1;
if(L[mid].key>k)
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
}
return 0;
}
8.3 设计一个算法,已知某年某月某日是星期几,求另外年月日对应的星期几 华为
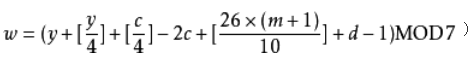
int Calculate_Week( int year , int month, int day )
{
int c,y,week;
if (month == 1 || month == 2)
year--, month += 12;
c = year / 100;
y = year - c * 100;
week = y + y / 4 + c / 4 - 2 * c + 26 * (month + 1) / 10 + day - 1;
while (week < 0)
week += 7;
week %= 7;
return week;
}
9 串
9.1 给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串的长度。 字节跳动
public int lengthOfLongertSubstring(String s){
// 哈希集合,记录每一个字符是否出现过
Set<Character> occ = new HashSet<Character>();
int n = s.length();
// 右指针,初始值为 -1, 相当于 我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动。
int rk = -1,ans = 0;
for(int i =0;i<n;++i){
if(i!=0){
// 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符
occ.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
}
while (rk + 1 < n && !occ.contains(s.charAt(rk + 1))) {
// 不断地移动右指针
occ.add(s.charAt(rk + 1));
++rk;
}
// 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串
ans = Math.max(ans, rk - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}