-
为容器中注册Bean
- @Configuration代表该类是一个配置类,配置类起到的作用和xml配置文件一样
- @Bean代表该方法的返回对象作为Bean加入IOC容器,默认Bean的id是方法的名称。可以在@Bean注解里更改value的值来更改名称
@Configuration public class mainConfig { @Bean("person") public Person person01(){ Person person = new Person(); person.setId(1); person.setName("aa"); return person; } }
包扫描
-
ComponentScan配置扫描哪些包,用法和xml配置文件中的包扫描相同,包含可配置的excludeFilter和includeFilter选项。
- excludeFilters是一个Filter类型的数组,所以这里用大括号。每一个Filter元素包含过滤条件的类型以及具体的过滤条件。如下面的Filter类型为注解,过滤条件为Controller。
@Configuration @ComponentScan(value = "comtroller",excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = Controller.class)}) public class mainConfig { @Bean("person") public Person person01(){ Person person = new Person(); person.setId(1); person.setName("aa"); return person; } }
- includeFilters,配置只扫描哪些类型,多用于SpringMVC容器中只扫描controller注解,用法同XML配置,需要禁用默认过滤规则
@Configuration @ComponentScan(value = "comtroller",includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes=Controller.class)},useDefaultFilters = false) public class mainConfig { @Bean("person") public Person person01(){ Person person = new Person(); person.setId(1); person.setName("aa"); return person; } }
其余常用包扫描的过滤方式
类名
只添加或者只过滤某个具体的类
@ComponentScan(value = "comtroller",excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = BookController.class)})
自定义规则
如何查看包扫描是否生效
查看包扫描是否生效就是查看Spring容器里是否有想要的Bean。
方法一:打印出Spring容器中所有Bean。简单粗暴。
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(mainConfig.class); String[] names = context.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String name: names) { System.out.println(name); } } }
方法二:借助idea。每新配置一个Spring容器,无论是通过xml还是配置类方式,最好都配置idea的spring管理插件,这样可以不必运行测试类也可查看容器里的Bean
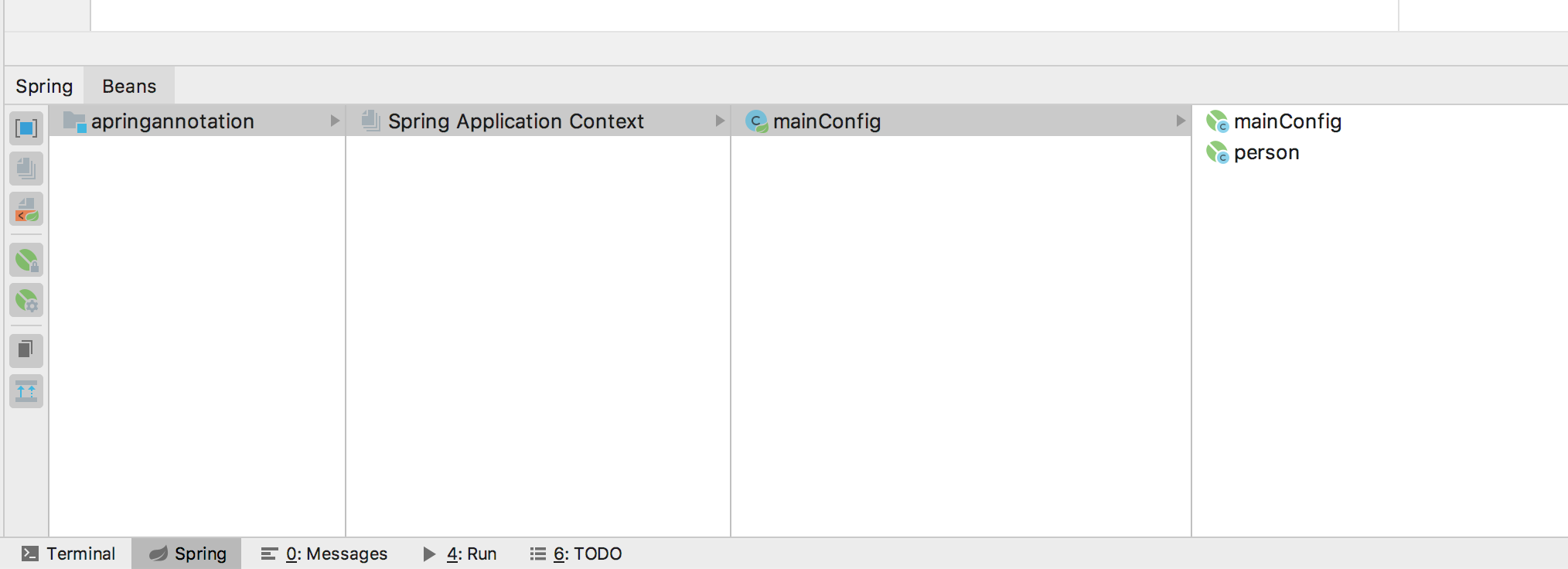
而且在配置生效的情况下@Component注解旁边会多一个符号,点击该符号可以跳转到扫描的包。

改变默认单例
Spring中的Bean默认是单例,且在容器加载的时候就被初始化。使用@Scope改变为多实例,对应的Bean在每次getBean的时候都会初始化一次,所以Bean在容器启动的时候不会初始化。背后的逻辑是单例模式是Spring容器维护了一个缓存HashMap,而多实例下并没有这个缓存。既然没有缓存那么在多实例情况下就无法存储初始化之后的Bean。
@Bean("person")
@Scope("prototype")
public Person person01(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(1);
person.setName("aa");
return person;
懒加载
针对单实例情况下容器创建时Bean就会被创建,使用@Lazy可以实现对单实例Bean在getBean的时候才加载。
按照条件注册Bean
默认情况下被标注了@Configuration的类下所有标注@Bean的方法返回对象都会被加入Spring容器中,使用@Conditional注解可以自定义规则来只把某些Bean加入Spring容器中。
实现Condition接口中的matches方法。conditionContext包含了一个Bean所有的信息
- beanFactory,创建该Bean的工程
- classLoader,该Bean的类加载器
- enviroment,该Bean所处的环境,主要指的是OS的环境
- register,该Bean所处的容器
下面的代码实现两个功能:1、打印该Bean所处容器内所有的Bean 2、判断该Bean所处OS的类型,如果是Win就返回true即把Bean注入到容器中
public class WinCondition implements Condition { /** * * @param conditionContext 环境上下文 * @param annotatedTypeMetadata 注释信息 * @return */ public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = conditionContext.getBeanFactory(); ClassLoader classLoader = conditionContext.getClassLoader(); Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment(); //获得容器对象,进而判断容器中Bean的注册情况 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = conditionContext.getRegistry(); String[] names = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); System.out.println("===="); for (String name : names) { System.out.println(name); } String osName = environment.getProperty("os.name"); if (osName.contains("Win")){ return true; } return false; } }
最后要把注解标注在方法或者配置类上。因为我的系统不是Win系统所以容器里没有zhangsan这个Bean。
@Conditional({WinCondition.class})
@Bean("zhangsan")
public Person person_01(){
return new Person("zhangsan",12);
}
Import
在配置类上方标注@Import注解并声明要导入的类,会自动加到Spring中。
@Import({otherPojo.class, otherPojo2.class})
public class mainConfig {
ImportSelector
使用上和Import类似,通过实现ImportSelector接口可以按照条件批量注册Bean,其中return的String数组中的Bean会被注册到Spring中。
public class importSelect implements ImportSelector { /** * @param annotationMetadata 当前标注Import类的全部注解信息,不仅仅是Import * @return 要导入容器的类的全类名 */ public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { return new String[]{"pojo.otherPojo2"}; } }
@Import(importSelect.class) public class mainConfig
Import注解是标注着配置类上的,ImportSelector中的AnnotationMetadata包含配置类所有注解的信息,通过打断点可以看到如下的结果。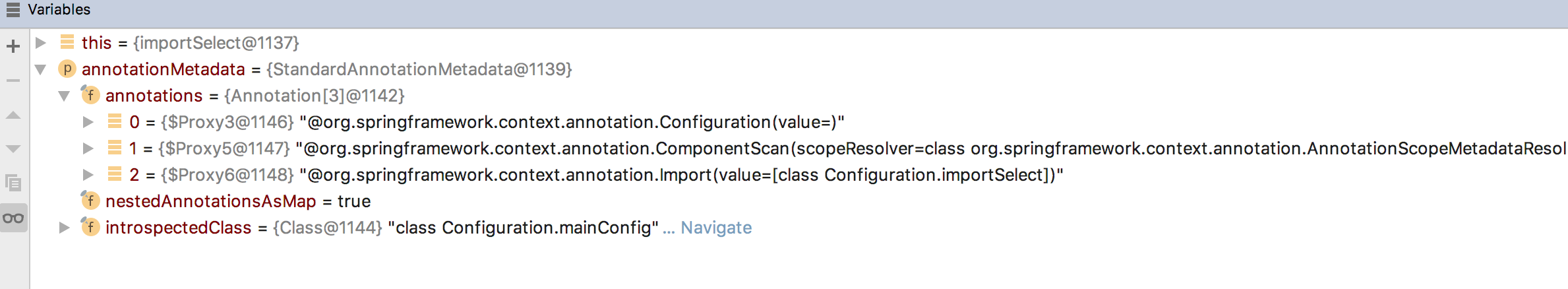
FactoryBean
实现FactoryBean接口重写getObject方法,并用@Bean方式加入Configuration中,则getObject返回的对象会加入Spring容器中