Description
现在给出了一个简单无向加权图。你不满足于求出这个图的最小生成树,而希望知道这个图中有多少个不同的最小生成树。(如果两颗最小生成树中至少有一条边不同,则这两个最小生成树就是不同的)。由于不同的最小生成树可能很多,所以你只需要输出方案数对31011的模就可以了。
Input
第 一行包含两个数,n和m,其中1<=n<=100; 1<=m<=1000; 表示该无向图的节点数和边数。每个节点用1~n的整数编号。接下来的m行,每行包含两个整数:a, b, c,表示节点a, b之间的边的权值为c,其中1<=c<=1,000,000,000。数据保证不会出现自回边和重边。注意:具有相同权值的边不会超过10 条。
Output
输出不同的最小生成树有多少个。你只需要输出数量对31011的模就可以了。
Sample Input
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 4 1
2 3 2
2 4 1
3 4 1
Sample Output
分析
先回忆一下求解最小生成树的过程:将边排序,贪心添加进当前生成森林中。由Kruskal算法的性质:【传送门】 ,在算法开始处理权值为val的边前,原图会形成若干个连通块,如图所示:
图中的虚线表示原图中所有权值为val的边。通过与Kruskal算法相似的证明,我们可以知道在处理完边数为val的边后,形成的连通分量是一定的。也就是说,在这一过程中不论我们采取怎样的顺序,图中的点集S1,S2,S3一定连通,且这个新的连通块恰好是新的点集的一个最小生成树。
那么,我们如何计算出这一过程可以有多少种连接方式呢?我们先把三个连通块都缩成点:
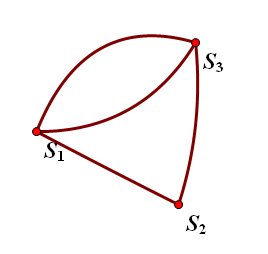
我们的问题就变成了:在图中选取若干条边使得S1,S2,S3构成一棵树有多少种方案?这就转化为了一个数学问题:一般生成树计数,可以用Matrix-Tree定理来计算。
于是我们就得到了本题的解法:1、将所有边升序排列;2、循环处理每一种权值形成的集合;3、对于同一种权值,利用Matrix-Tree定理求出当前处理的所有边可以产生的那些连通块的连接方式总数,乘入答案;4、将当前边可以产生的连通块缩成点。具体实现细节请看代码中的注释:

2 Problem: 1016
3 User: AsmDef
4 Language: C++
5 Result: Accepted
6 Time:0 ms
7 Memory:1292 kb
8 ****************************************************************/
9
10 #include <cctype>
11 #include <cstdio>
12 #include <iostream>
13 #include <cmath>
14 #include <cstdlib>
15 #include <algorithm>
16 #include <assert.h>
17 using namespace std;
18 template<typename T>inline void getd(T &x){
19 char c = getchar(); bool minus = 0;
20 while(!isdigit(c) && c != '-')c = getchar();
21 if(c == '-')minus = 1, c = getchar();
22 x = c - '0';
23 while(isdigit(c = getchar()))x = x * 10 + c - '0';
24 if(minus)x = -x;
25 }
26 /*========================================================*/
27 const int maxn = 103, maxm = 1003, mod = 31011;
28 typedef pair<int, pair<int, int> > Edge;//权值相同的边会按二元组(u,v)排序
29 Edge E[maxm];
30 #define val first
31 #define u second.first
32 #define v second.second
33 int N, M, Ans = 1, *Mat[22], sum;
34
35 inline void watch();
36
37 struct UFS{
38 int pre[maxn];
39 void init(int x){for(int i = 0;i <= x;++i)pre[i] = i;}
40 int find(int x){return pre[x] == x ? x : pre[x] = find(pre[x]);}
41 void link(int a, int b){pre[find(a)] = find(b);}
42 }ufs, tmpS;//ufs用于Kruskal,tmpS在计算Kirchhoff矩阵时判断当前所有边是否已经形成连通图
43 inline void init(){//读入原图
44 getd(N), getd(M);
45 int i;
46 ufs.init(N);
47 for(i = 0;i < M;++i)
48 getd(E[i].u), getd(E[i].v), getd(E[i].val);
49 for(i = 0;i < 21;++i)
50 Mat[i] = new int[22];//使用动态内存,在det中简化“交换两行”的操作
51 sort(E, E + M);
52 sum = N;
53 }
54
55 inline int det(int n){//计算N*N的Mat矩阵的行列式
56 int i, j, k, t, ans = 1;
57 for(i = 1;i < n;++i){
58 for(j = i + 1;j < n;++j){
59 while(Mat[j][i]){
60 t = Mat[i][i] / Mat[j][i];
61 if(t)
62 for(k = i;k < n;++k)
63 Mat[i][k] = (Mat[i][k] - Mat[j][k] * t) % mod;
64
65 swap(Mat[i], Mat[j]), ans = -ans;//交换两行时直接交换两行的内存指针即可
66 }
67 }
68 ans = ans * Mat[i][i] % mod;
69 }
70 return ans;
71 }
72 int tmp[22], block[22], cnt;
73 inline void watch(){//调试用
74 /*int i, j;
75 for(i = 0;i < cnt;++i){
76 for(j = 0;j < cnt;++j)
77 printf("%5d ", Mat[i][j]);
78 printf(" ");
79 }
80 printf(" ");*/
81 }
82 #define index(x) ( lower_bound(block, block + cnt, x) - block )//离散化后将点x映射到它所属的连通块编号
83
84 inline void calc(Edge *A, int len){//A[0]到A[len-1]之间的边权值相等,只需计算所有连接方法数即可
85 int i, j;
86 //int t, adj[22];
87 cnt = 1;
88 for(i = 0,j = 0;i < len;++i){
89 A[i].u = ufs.find(A[i].u);
90 A[i].v = ufs.find(A[i].v);
91 if(A[i].u == A[i].v)continue;
92 tmp[j++] = A[i].u;
93 tmp[j++] = A[i].v;
94 }
95 sort(tmp, tmp + j);//将出现的端点离散化
96 block[0] = tmp[0];
97 for(i = 1;i < j;++i)
98 if(tmp[i] != block[cnt-1])block[cnt++] = tmp[i];//去重后将新的连通块标号
99
100 for(i = 0;i < cnt;++i)for(j = 0;j < cnt;++j)
101 Mat[i][j] = 0;
102
103 tmpS.init(cnt);
104
105 for(i = 0;i < len;++i){
106 if(A[i].u == A[i].v)continue;
107 if(ufs.find(A[i].u) != ufs.find(A[i].v))--sum;//原图中块数减少
108 ufs.link(A[i].u, A[i].v);
109 A[i].u = index(A[i].u);
110 A[i].v = index(A[i].v);//构造缩点后的图
111 ++Mat[A[i].u][A[i].u];
112 ++Mat[A[i].v][A[i].v];
113 //adj[A[i].u] |= (1 << A[i].v);
114 //adj[A[i].v] |= (1 << A[i].u);//理解错了Matrix-Tree定理,以为重边只算一次= =囧……
115 --Mat[A[i].u][A[i].v];
116 --Mat[A[i].v][A[i].u];
117 tmpS.link(A[i].u, A[i].v);
118 }
119 //注意此时整个与当前边相关的图不一定连通,考虑完当前边后原图可能仍是一个森林,为了得到正确答案,我们可以在1以后每个新的连通块与之前的某个连通块之间加一条边。由于加入的每条边都是新图中的桥,这一操作并不会增加整张图的连接方法数。
120 int a, b;
121 for(i = 1;i < cnt;++i)
122 if((a = tmpS.find(i)) != (b = tmpS.find(i-1))){
123 ++Mat[a][a], ++Mat[b][b];
124 //adj[a] |= (1 << b);adj[b] |= (1 << a);
125 --Mat[a][b], --Mat[b][a];
126 tmpS.link(a, b);
127 }
128
129 Ans = Ans * det(cnt) % mod;
130 }
131 inline void work(){
132 int i = 0, j = 1, t;
133 while(i < M){
134 while(j < M && E[i].val == E[j].val)++j;//得到一段权值相等的边
135 if((t = j - i) > 1)calc(E + i, j - i);
136 else if(ufs.find(E[i].u) != ufs.find(E[i].v))//当前权值唯一。直接缩点即可
137 ufs.link(E[i].u, E[i].v), --sum;
138 i = j++;
139 }
140 if(sum > 1)printf("0 ");//最终的图不连通
141 else
142 printf("%d ", Ans);
143 }
144 int main(){
145 #if defined DEBUG
146 freopen("test", "r", stdin);
147 #else
148 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
149 freopen("bzoj_1016.in", "r", stdin);
150 freopen("bzoj_1016.out", "w", stdout);
151 #endif
152 #endif
153 init();
154 work();
155
156 return 0;
157 }
