

本题是从1开始计数;n一定是合法的。

能否只遍历一遍链表?
n = 2, 则要删除4和5。使用两个指针来寻找要删除的区间。
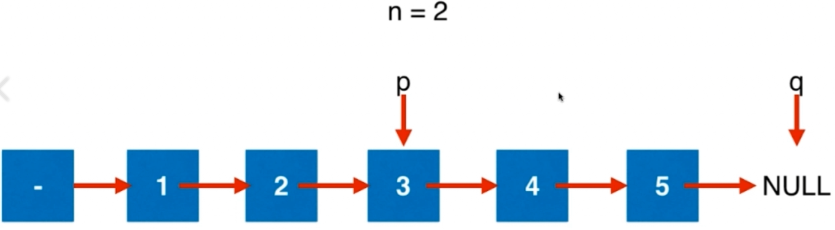

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) { //虚拟头结点 assert(n>=0); ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode* p = dummy; ListNode* q = dummy; for(int i=0; i<n+1;i++){ assert(q); //将q向后移n+1次 q = q->next; } //p和q之间相差n+1步 while(q!=NULL){ p = p->next; q = q->next; } //此时p指向待删除指针的前一个指针 ListNode* delNode = p->next; p->next = delNode->next; delete delNode; ListNode* ret = dummy->next; delete dummy; return ret; } };


思路:快慢指针,一开始让fast和slow指向链表的头结点,然后让fast指向链表旋转k位后的头结点,然后fast和slow同时向后移动,直到fast指向原链表的最后一个元素,此时,slow指向新链表最好一个元素,slow->next指向新链表的head。
注意:需要提前遍历一遍链表,求出其长度n,然后k = k%n
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//1->2->3->4->5->NULL
//k=2
//初始使slow和fast间隔为k
//fast最终指向原链表最后一个元素(即5),slow指向新链表最后一个元素(即3),slow->next指向新链表的head
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* fast = head;
int n = 0; //链表长度
while(fast){
n++;
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
k = k%n;
for(int i=0; i<k; ++i)
fast = fast->next;
while(fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
fast->next = head;
head = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
return head;
}
};
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//1->2->3->4->5->NULL
//k=2
//初始使slow和fast间隔为k
//fast最终指向原链表最后一个元素(即5),slow指向新链表最后一个元素(即3),slow->next指向新链表的head
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* fast = head;
int n = 0; //链表长度
while(fast){
n++;
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
k = k%n;
for(int i=0; i<k; ++i)
fast = fast->next;
while(fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
fast->next = head;
head = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
return head;
}
};
注意:1)如果 k>n 那么在使p, q移动时容易报错产生空指针。所以需要先遍历一遍链表求出其总长度,然后再 k = k % n。
2)在遍历链表时注意n初始值的设立。
3)使用双指针来取得需要旋转的区间。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) { if(head==NULL) return NULL; ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); dummy->next = head; ListNode* p = dummy; ListNode* q = dummy; //遍历一遍链表得到总长度 ListNode* r = head; int n = 0; while(r != NULL){ n += 1; r = r->next; } //取余数,防止k比n大的情况 k = k % n; if(k == 0) return head; for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ assert(q); q = q->next; } while(q->next != NULL){ p = p->next; q = q->next; } //此时p指向需要旋转节点的前一个,q指向最后一个旋转节点 ListNode* ans = p; p = p->next; //p指向第一个旋转节点 ans->next = NULL; dummy->next = p; q->next = head; ListNode* ret = dummy->next; delete dummy; return ret; } };

思路:获得链表中间的元素后将链表分为左右两个链表,把右链表翻转之后,将两个链表分别穿插。
使用中间指针。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode* head) { if(!head || !head->next|| !head->next->next) return; //快慢指针 找到链表中点 ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head; while(fast->next && fast->next->next){ fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } //翻转链表后半段 ListNode* mid = slow->next; //链表中点 slow->next = NULL; ListNode* pre = NULL; while(mid){ ListNode* next = mid->next; mid->next = pre; pre = mid; mid = next; } //合并 while(head && pre){ ListNode* cur = head->next, *pre_next = pre->next; head->next = pre; pre->next = cur; pre = pre_next; head = cur; } } };
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode* head) { if(!head || !head->next || !head->next->next) return; //快慢指针找到链表中点 ListNode* p_fast = head; ListNode* p_slow = head; while(p_fast->next && p_fast->next->next){ p_slow = p_slow->next; p_fast = p_fast->next->next; } //将后一半链表翻转 ListNode* mid = p_slow->next; p_slow->next = NULL; ListNode* last = mid, *pre = NULL; while(last){ ListNode* next = last->next; last->next = pre; pre = last; last = next; } //将两个链表合并 while(pre && head){ ListNode* next = head->next; head->next = pre; pre = pre->next; head->next->next = next; head = next; } } };
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode* head) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); dummy -> next = head; ListNode* fast = dummy; ListNode* slow = dummy; while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL){ slow = slow->next; //slow最终指向链表的中间节点 fast = fast->next->next; } //slow这时指向链表的中间节点 ListNode* ans = slow->next; slow->next = NULL; //翻转第二个链表 ListNode* last = ans, *pre = NULL; while(last) { ListNode* next = last->next; last->next = pre; //将后一个节点赋值给前一个节点 pre = last; last = next; } while(pre!=NULL && head!=NULL){ ListNode* next = head->next; head->next = pre; pre = pre->next; head->next->next = next; head = next; } } };
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void reorderList(ListNode* head) { if(!head || !head->next ||!head->next->next) return; ListNode* fast= head, *slow = head; while(fast->next && fast->next->next){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } ListNode* mid = slow->next, *pre = NULL, *next = NULL; slow->next = NULL; //令前半段链表最后一个元素的后继为空 while(mid){ next = mid->next; mid->next = pre; pre = mid; mid = next; } ListNode *h_n = NULL, *pre_n = NULL; while(head && pre){ h_n = head->next; pre_n = pre->next; head->next = pre; pre->next = h_n; head = h_n; pre = pre_n; } } };
注意: slow->next = NULL; //令前半段链表最后一个元素的后继为空
这句一定要记得写,不然会 time limit !!!!

回文:正着看和反着看是一样的。
若是数组实现:则用两个指针,一个从前向后移,一个从后向前移,来分别判断是否对应的元素相同。
思路1:使用快慢指针找中点的原理,在每次慢指针走一步时都把值存入栈中,然后等到达中点了,链表的前半段都存入栈中了,由于栈先进后出的性质,可以和后半段链表按照回文对应的顺序比较了。
思路2:若是要采用O(1)的时间复杂度,那就不能使用stack了。可以在找到中点后,将后半段的链表翻转一下,这样就可以按照回文的顺序比较了。
注意边界条件的判断!
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) { if(head==NULL || head->next == NULL) return true; //分为两个链表 ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head; while(fast->next && fast->next->next){ slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } //翻转后一个链表 ListNode* last = slow->next, *pre = NULL; while(last){ ListNode* next = last->next; last->next = pre; pre = last; last = next; } //最终pre指向第二个链表的头结点 while(pre){ if(pre->val != head->val) return false; pre=pre->next; head = head->next; } return true; } };