
思路:给我们一堆糖,每种糖的个数不定,分给两个人,让我们求其中一个人能拿到的最大的糖的种类数。那么我们想,如果总共有n个糖,平均分给两个人,每人得到n/2块糖,那么能拿到的最大的糖的种类数也就是n/2种,不可能再多,只可能再少。那么我们要做的就是统计出总共的糖的种类数,如果糖的种类数小于n/2,说明拿不到n/2种糖,最多能拿到的种类数数就是当前糖的总种类数,明白了这点就很容易了,利用集合set的自动去重复特性来求出糖的种类数,然后跟n/2比较,取二者之中的较小值返回即可。
class Solution { public: int distributeCandies(vector<int>& candies) { unordered_set<int> s; for(int candy : candies) s.insert(candy); return min(s.size(), candies.size()/2); } };

这道题让我们判断一个字符串的全排列有没有是回文字符串的,那么根据题目中的提示,我们分字符串的个数是奇偶的情况来讨论,如果是偶数的话,由于回文字符串的特性,每个字母出现的次数一定是偶数次,当字符串是奇数长度时,只有一个字母出现的次数是奇数,其余均为偶数,那么利用这个特性我们可以使用 unordered_map 建立每个字母和其出现次数的映射,然后我们遍历 HashMap,统计出现次数为奇数的字母的个数,那么只有两种情况是回文数,第一种是没有出现次数为奇数的字母,再一个就是字符串长度为奇数,且只有一个出现次数为奇数的字母。
class Solution { public: bool canPermutePalindrome(string s) { unordered_map<char, int> m; int cnt = 0; for (auto a : s) ++m[a]; for (auto a : m) { if (a.second % 2 == 1) ++cnt; } return cnt == 0 || (s.size() % 2 == 1 && cnt == 1); } };
解法一:使用C++中的 next_permutation() 函数,头文件是#include<algorithm>
注意:要先对数组进行从小到大排序。
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); //使用next_permutation()之前需要排序 do{ vector<int> out(nums); res.push_back(out); }while(next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end())); return res; } };
解法二:递归+回溯(backtracking)
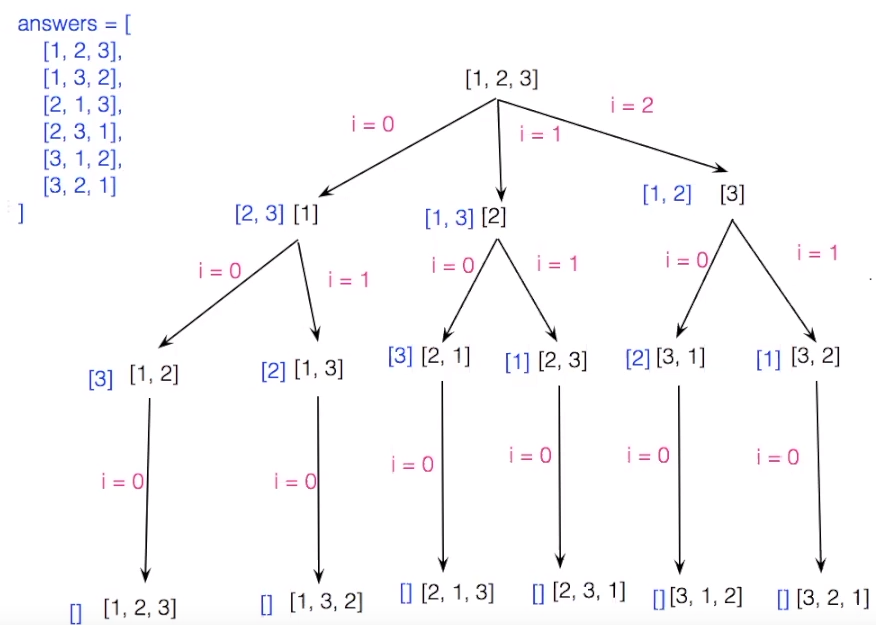
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> out; vector<int> visit(nums.size(), 0); search(nums, visit, out, res); return res; } void search(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& visit, vector<int>& out, vector<vector<int>>& res){ if(out.size()== nums.size()){ res.push_back(out); return; } for(int i=0; i<nums.size();i++){ if(visit[i]==0){ visit[i] = 1; out.push_back(nums[i]); search(nums, visit, out, res); out.pop_back(); visit[i] = 0; } } } };
Palindrome Permutation II 回文全排列之二
Given a string s, return all the palindromic permutations (without duplicates) of it. Return an empty list if no palindromic permutation could be form.
For example:
Given s = "aabb", return ["abba", "baab"].
Given s = "abc", return [].
Hint:
- If a palindromic permutation exists, we just need to generate the first half of the string.
- To generate all distinct permutations of a (half of) string, use a similar approach from: Permutations II or Next Permutation.
注意:string(n,char) 表示n个连续的char类型字符构成的string。
class Solution { public: vector<string> generatePalindromes(string s) { vector<string> res; unordered_map<char, int> m; string t = "", mid = ""; for (auto a : s) ++m[a]; for (auto &it : m) { if (it.second % 2 == 1) mid += it.first; it.second /= 2; t += string(it.second, it.first); if (mid.size() > 1) return {}; } permute(t, m, mid, "", res); return res; } void permute(string &t, unordered_map<char, int> &m, string mid, string out, vector<string> &res) { if (out.size() >= t.size()) { res.push_back(out + mid + string(out.rbegin(), out.rend())); return; } for (auto &it : m) { if (it.second > 0) { --it.second; permute(t, m, mid, out + it.first, res); ++it.second; } } } };
class Solution { public: vector<string> generatePalindromes(string s) { vector<string> res; unordered_map<char, int> m; string t = "", mid = ""; for (auto a : s) ++m[a]; for (auto it : m) { if (it.second % 2 == 1) mid += it.first; t += string(it.second / 2, it.first); if (mid.size() > 1) return {}; } sort(t.begin(), t.end()); do { res.push_back(t + mid + string(t.rbegin(), t.rend())); } while (next_permutation(t.begin(), t.end())); return res; } };