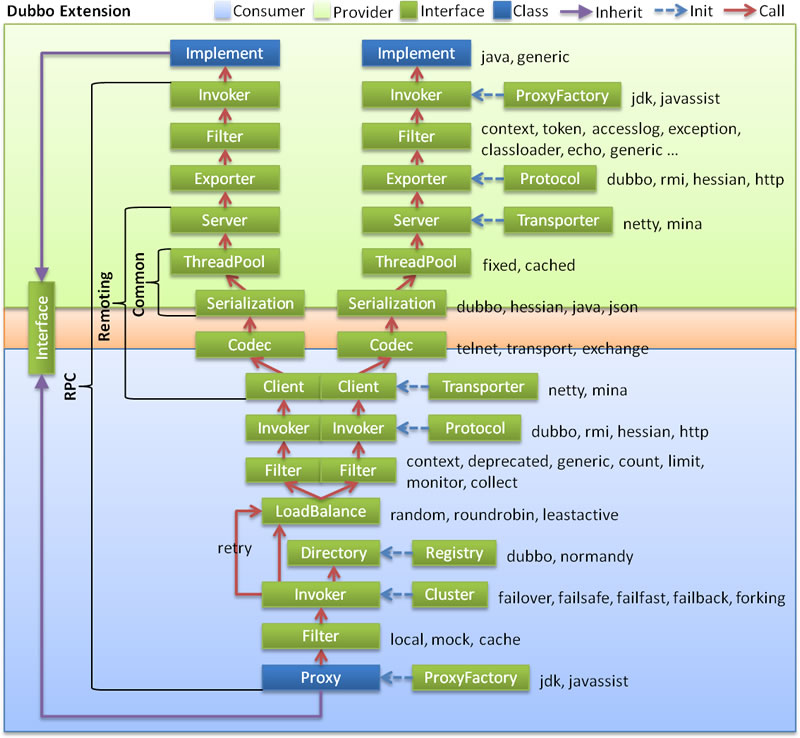
概述
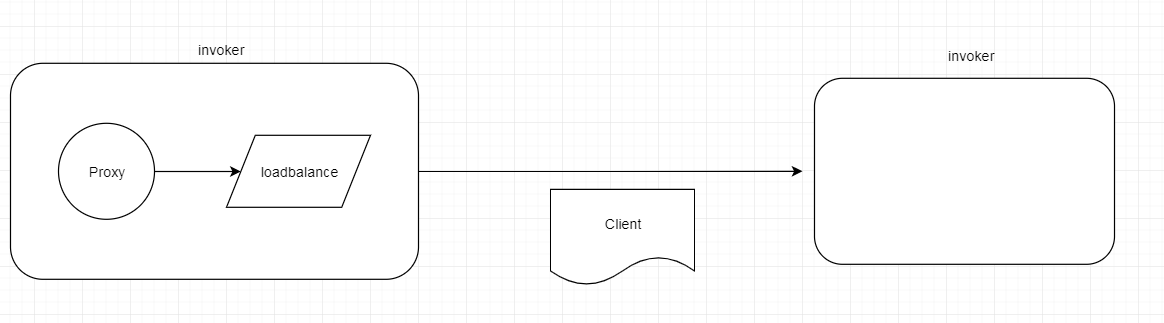
我们从开篇的源码分析就知道了 invoker 是调用目标的抽象,所以从上面也可以看到Proxy 调用的最终到了 invoker 对象,通过了 client 的传输,到了提供端,提供端经过解码等操作,最终到了到达的还是 invoker,最后到达实际的服务。更加详尽的调用过程 :
源码分析
我们先理清一下调用的大概过程,再进行源码分析
proxy --> invoker --> channel --> (封装成一个 RpcInvocation )编码 --> 发送
来源 : dubbo源码中的demo
proxy0#sayHello(String)
—> InvokerInvocationHandler#invoke(Object, Method, Object[])
—> MockClusterInvoker#invoke(Invocation)
—> AbstractClusterInvoker#invoke(Invocation)
—> FailoverClusterInvoker#doInvoke(Invocation, List<Invoker<T>>, LoadBalance)
—> Filter#invoke(Invoker, Invocation) // 包含多个 Filter 调用
—> ListenerInvokerWrapper#invoke(Invocation)
—> AbstractInvoker#invoke(Invocation)
—> DubboInvoker#doInvoke(Invocation)
—> ReferenceCountExchangeClient#request(Object, int)
—> HeaderExchangeClient#request(Object, int)
—> HeaderExchangeChannel#request(Object, int)
—> AbstractPeer#send(Object)
—> AbstractClient#send(Object, boolean)
—> NettyChannel#send(Object, boolean)
—> NioClientSocketChannel#write(Object)
我们上一节在介绍负载均衡的时候就介绍了 FailoverClusterInvoker,还有后面的 DubboInvoker ,那么接下来我们就剩下两部分了 :client类的处理 和 channel 相关的处理,可以看到调用先是经过 client ,而 client 中持有的 channel 再调用 send 方法 ; client类进行的逻辑主要是例如调用数量的统计,请求封装成 request 等等,而 channel 就不用说了,传输的底层。
消费者发出请求
Dubbo 支持同步和异步两种调用方式,其中异步调用还可细分为“有返回值”的异步调用和“无返回值”的异步调用。所谓“无返回值”异步调用是指服务消费方只管调用,但不关心调用结果,此时 Dubbo 会直接返回一个空的 RpcResult。若要使用异步特性,需要服务消费方手动进行配置。默认情况下,Dubbo 使用同步调用方式。
让我们开始源码分析,开始必定是 proxy 代理对象,下面反编译的 proxy 类(代码来自官方文档)
/**
* Arthas 反编译步骤:
* 1. 启动 Arthas
* java -jar arthas-boot.jar
*
* 2. 输入编号选择进程
* Arthas 启动后,会打印 Java 应用进程列表,如下:
* [1]: 11232 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher
* [2]: 22370 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher
* [3]: 22371 com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.consumer.Consumer
* [4]: 22362 com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.Provider
* [5]: 2074 org.apache.zookeeper.server.quorum.QuorumPeerMain
* 这里输入编号 3,让 Arthas 关联到启动类为 com.....Consumer 的 Java 进程上
*
* 3. 由于 Demo 项目中只有一个服务接口,因此此接口的代理类类名为 proxy0,此时使用 sc 命令搜索这个类名。
* $ sc *.proxy0
* com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0
*
* 4. 使用 jad 命令反编译 com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0
* $ jad com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0
*
* 更多使用方法请参考 Arthas 官方文档:
* https://alibaba.github.io/arthas/quick-start.html
*/
public class proxy0 implements ClassGenerator.DC, EchoService, DemoService {
// 方法数组
public static Method[] methods;
private InvocationHandler handler;
public proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) {
this.handler = invocationHandler;
}
public proxy0() {
}
public String sayHello(String string) {
// 将参数存储到 Object 数组中
Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{string};
// 调用 InvocationHandler 实现类的 invoke 方法得到调用结果
Object object = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrobject);
// 返回调用结果
return (String)object;
}
/** 回声测试方法 */
public Object $echo(Object object) {
Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{object};
Object object2 = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[1], arrobject);
return object2;
}
}
首先将运行时参数存储到数组中,然后调用 InvocationHandler 接口实现类的 invoke 方法,得到调用结果,最后将结果转型并返回给调用方。接下来看一下 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 进行什么样的操作。
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InvokerInvocationHandler.class);
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
private ConsumerModel consumerModel;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
String serviceKey = invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey();
if (serviceKey != null) {
this.consumerModel = ApplicationModel.getConsumerModel(serviceKey);
}
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 0) {
if ("toString".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.toString();
} else if ("$destroy".equals(methodName)) {
invoker.destroy();
return null;
} else if ("hashCode".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
} else if (parameterTypes.length == 1 && "equals".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = new RpcInvocation(method, invoker.getInterface().getName(), args);
String serviceKey = invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey();
rpcInvocation.setTargetServiceUniqueName(serviceKey);
if (consumerModel != null) {
rpcInvocation.put(Constants.CONSUMER_MODEL, consumerModel);
rpcInvocation.put(Constants.METHOD_MODEL, consumerModel.getMethodModel(method));
}
//交由另外的 invoker调用 invoker 方法
return invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate();
}
...
}
public class DubboInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
...
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(VERSION_KEY, version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
// oneway : 只管调用不管返回
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodPositiveParameter(methodName, TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
} else {
//异步调用
ExecutorService executor = getCallbackExecutor(getUrl(), inv);
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture =
currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor).thenApply(obj -> (AppResponse) obj);
// save for 2.6.x compatibility, for example, TraceFilter in Zipkin uses com.alibaba.xxx.FutureAdapter
FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture);
AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv);
result.setExecutor(executor);
return result;
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
...
}
ExchangeClient 的调用看一下,ReferenceCountExchangeClient 仅仅是记录调用次数,我们看一下 HeaderExchangeClient
public class HeaderExchangeClient implements ExchangeClient {
public HeaderExchangeClient(Client client, boolean startTimer) {
Assert.notNull(client, "Client can't be null");
this.client = client;
this.channel = new HeaderExchangeChannel(client);
//是否开启一个定时任务,定时心跳服务提供方
if (startTimer) {
URL url = client.getUrl();
startReconnectTask(url);
startHeartBeatTask(url);
}
}
...
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
return channel.request(request, timeout);
}
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
return channel.request(request, executor);
}
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
return channel.request(request, timeout, executor);
}
}
可以看到 HeaderExchangeClient 的作用就是两个 :
- 心跳机制相关
- 将要发送的信息交给 channel
ok,经过了调用链我们看一下dubbo 底层传输 NettyChannel 是如何实现的吧 .
@Override
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
// whether the channel is closed
super.send(message, sent);
boolean success = true;
int timeout = 0;
try {
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(message);
if (sent) {
// wait timeout ms
timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
success = future.await(timeout);
}
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
throw cause;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
removeChannelIfDisconnected(channel);
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + PayloadDropper.getRequestWithoutData(message) + " to " + getRemoteAddress() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (!success) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + PayloadDropper.getRequestWithoutData(message) + " to " + getRemoteAddress()
+ "in timeout(" + timeout + "ms) limit");
}
}
那我们的编码过程呢?下面的方法调用就和 netty 框架的使用有关了,建议大家可以去看看,这里大概讲一下。最后会到了 NettyCodecAdapter ,那么这个类是从哪里被进来的呢 ?nettyclient 中配置的handler
@Override
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
final NettyClientHandler nettyClientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(getUrl(), this);
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
//.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, Math.max(3000, getConnectTimeout()));
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
int heartbeatInterval = UrlUtils.getHeartbeat(getUrl());
if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) {
ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation", SslHandlerInitializer.sslClientHandler(getUrl(), nettyClientHandler));
}
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
.addLast("client-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(heartbeatInterval, 0, 0, MILLISECONDS))
.addLast("handler", nettyClientHandler);
String socksProxyHost = ConfigUtils.getProperty(SOCKS_PROXY_HOST);
if(socksProxyHost != null) {
int socksProxyPort = Integer.parseInt(ConfigUtils.getProperty(SOCKS_PROXY_PORT, DEFAULT_SOCKS_PROXY_PORT));
Socks5ProxyHandler socks5ProxyHandler = new Socks5ProxyHandler(new InetSocketAddress(socksProxyHost, socksProxyPort));
ch.pipeline().addFirst(socks5ProxyHandler);
}
}
});
}
我们看一下 nettyClientHandler 的 write 方法
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
//write 方法内进行编码
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
final NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
final boolean isRequest = msg instanceof Request;
// We add listeners to make sure our out bound event is correct.
// If our out bound event has an error (in most cases the encoder fails),
// we need to have the request return directly instead of blocking the invoke process.
promise.addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
// if our future is success, mark the future to sent.
handler.sent(channel, msg);
return;
}
Throwable t = future.cause();
if (t != null && isRequest) {
Request request = (Request) msg;
Response response = buildErrorResponse(request, t);
handler.received(channel, response);
}
});
}
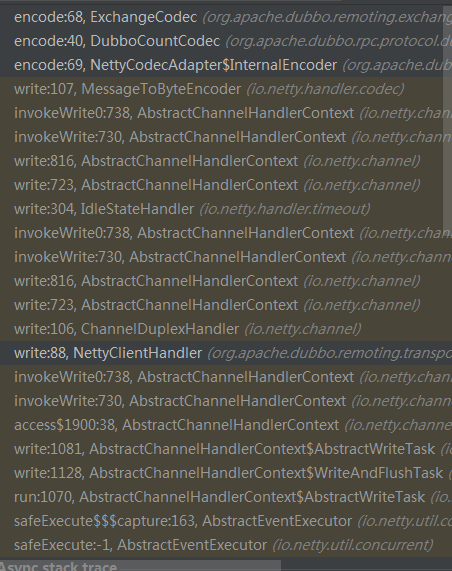
netty 编码的调用栈相关
我们直接看一下最终的调用编码过程吧 ExchangeCodec 类
@Override
public void encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object msg) throws IOException {
if (msg instanceof Request) {
encodeRequest(channel, buffer, (Request) msg);
} else if (msg instanceof Response) {
encodeResponse(channel, buffer, (Response) msg);
} else {
super.encode(channel, buffer, msg);
}
}
protected void encodeRequest(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Request req) throws IOException {
Serialization serialization = getSerialization(channel);
// header.
byte[] header = new byte[HEADER_LENGTH];
// set magic number.
Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header);
// set request and serialization flag.
header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | serialization.getContentTypeId());
if (req.isTwoWay()) {
header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
}
if (req.isEvent()) {
header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
}
// set request id.
Bytes.long2bytes(req.getId(), header, 4);
// encode request data.
int savedWriteIndex = buffer.writerIndex();
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH);
ChannelBufferOutputStream bos = new ChannelBufferOutputStream(buffer);
ObjectOutput out = serialization.serialize(channel.getUrl(), bos);
if (req.isEvent()) {
encodeEventData(channel, out, req.getData());
} else {
encodeRequestData(channel, out, req.getData(), req.getVersion());
}
out.flushBuffer();
if (out instanceof Cleanable) {
((Cleanable) out).cleanup();
}
bos.flush();
bos.close();
int len = bos.writtenBytes();
checkPayload(channel, len);
Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12);
// write
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex);
buffer.writeBytes(header); // write header.
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH + len);
}
提供者接受请求
请求过程概述
dubbo 底层使用netty作为传输层,接受的请求必然是经过解码在进行一系列的操作,这里解码就不详细介绍了,下面讲一下调用服务的过程 :
NettyHandler#messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext, MessageEvent)
—> AbstractPeer#received(Channel, Object)
—> MultiMessageHandler#received(Channel, Object)
—> HeartbeatHandler#received(Channel, Object)
—> AllChannelHandler#received(Channel, Object)
—> ExecutorService#execute(Runnable) // 由线程池执行后续的调用逻辑
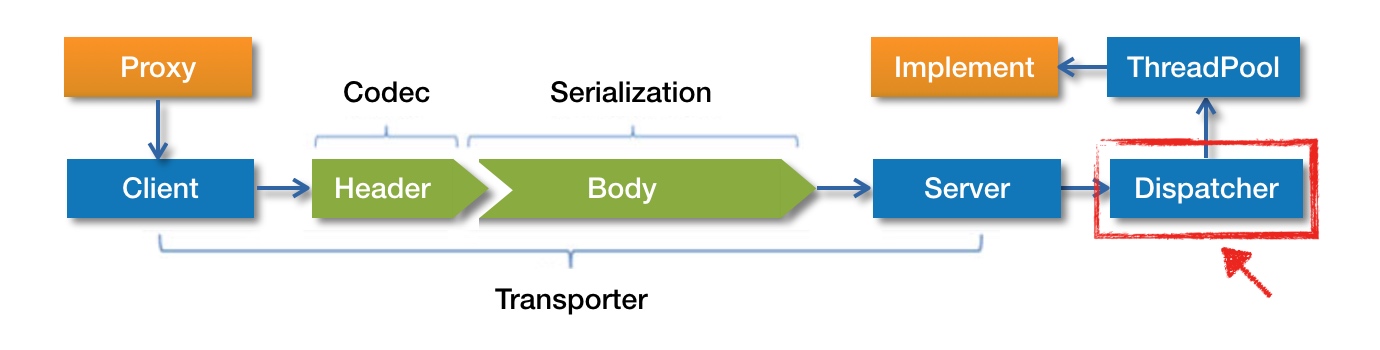
如上图,红框中的 Dispatcher 就是线程派发器。需要说明的是,Dispatcher 真实的职责创建具有线程派发能力的 ChannelHandler,比如 AllChannelHandler、MessageOnlyChannelHandler 和 ExecutionChannelHandler 等,其本身并不具备线程派发能力。Dubbo 支持 5 种不同的线程派发策略.
- all 所有消息都派发到线程池,包括请求,响应,连接事件,断开事件等
- direct 所有消息都不派发到线程池,全部在 IO 线程上直接执行
- message 只有请求和响应消息派发到线程池,其它消息均在 IO 线程上执行
- execution 只有请求消息派发到线程池,不含响应。其它消息均在 IO 线程上执行
- connection 在 IO 线程上,将连接断开事件放入队列,有序逐个执行,其它消息派发到线程池
注意哦,此时分配下去后请求还是未解码的,所以线程派发后再进行解码,调用,形成响应,传输回去。我们看一下默认的 AllChannelHandler
请求过程源码分析
public class AllChannelHandler extends WrappedChannelHandler {
public AllChannelHandler(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
super(handler, url);
}
@Override
public void connected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException {
ExecutorService executor = getExecutorService();
try {
executor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.CONNECTED));
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ExecutionException("connect event", channel, getClass() + " error when process connected event .", t);
}
}
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
ExecutorService executor = getPreferredExecutorService(message);
try {
//可以看到线程池内执行了一个 ChannelEventRunnable 的 Runnable ,我们看一下里面的任务
executor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message));
} catch (Throwable t) {
if(message instanceof Request && t instanceof RejectedExecutionException){
sendFeedback(channel, (Request) message, t);
return;
}
throw new ExecutionException(message, channel, getClass() + " error when process received event .", t);
}
}
....
}
ChannelEventRunnable 的 run 方法
private final ChannelHandler handler;
@Override
public void run() {
if (state == ChannelState.RECEIVED) {
try {
handler.received(channel, message);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel
+ ", message is " + message, e);
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case CONNECTED:
try {
handler.connected(channel);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel, e);
}
break;
case DISCONNECTED:
try {
handler.disconnected(channel);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel, e);
}
break;
case SENT:
try {
handler.sent(channel, message);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel
+ ", message is " + message, e);
}
break;
case CAUGHT:
try {
handler.caught(channel, exception);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel
+ ", message is: " + message + ", exception is " + exception, e);
}
break;
default:
logger.warn("unknown state: " + state + ", message is " + message);
}
}
}
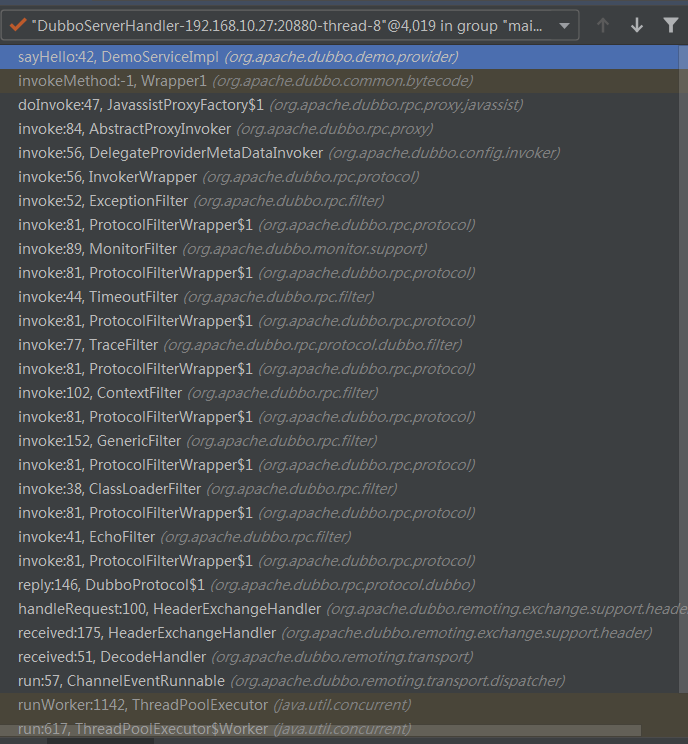
根据状态进行判断分发,里面对用 ChannelHandler 的方法,看一下我们 debug 的情况 。
可以看到经过了 DecodeHandler , HeaderExchangeHandler 到达了 DubboProtocol 的 reply 方法。 DecodeHandler 是解码相关,HeaderExchangeHandler 首先向后进行调用,得到调用结果。然后将调用结果封装到 Response 对象中,最后再将该对象返回给服务消费方。如果请求不合法,或者调用失败,则将错误信息封装到 Response 对象中,并返回给服务消费方,也就是 HeaderExchangeHandler 的逻辑是构建 Response . 解码过程就不介绍了,看一下 HeaderExchangeHandler
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
final ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel);
if (message instanceof Request) {
// handle request.
Request request = (Request) message;
//判断请求的类型
if (request.isEvent()) {
handlerEvent(channel, request);
} else {
// 双向通信
if (request.isTwoWay()) {
handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request);
} else {
handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData());
}
}
} else if (message instanceof Response) {
//响应也会经过这里
handleResponse(channel, (Response) message);
} else if (message instanceof String) {
if (isClientSide(channel)) {
Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl());
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} else {
String echo = handler.telnet(channel, (String) message);
if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) {
channel.send(echo);
}
}
} else {
handler.received(exchangeChannel, message);
}
}
//注意handler 的类型
private final ExchangeHandler handler;
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException {
//这里 res 对象将作为响应返回
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
//判断数据是否损坏
if (req.isBroken()) {
Object data = req.getData();
String msg;
if (data == null) {
msg = null;
} else if (data instanceof Throwable) {
msg = StringUtils.toString((Throwable) data);
} else {
msg = data.toString();
}
res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg);
res.setStatus(Response.BAD_REQUEST);
channel.send(res);
return;
}
// find handler by message class.
Object msg = req.getData();
try {
//这里将会调用到 DubboProtocol 中去
CompletionStage<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg);
future.whenComplete((appResult, t) -> {
try {
if (t == null) {
res.setStatus(Response.OK);
res.setResult(appResult);
} else {
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
}
channel.send(res);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + e);
}
});
} catch (Throwable e) {
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e));
channel.send(res);
}
}
在 debug 图中可以知道 handler.reply 方法将会执行到 DubboProtocol 中,这是如何传递过去的呢? 原来在 DubboProtocol 创建了一个 ExchangeHandler 的内部类,很巧妙地把逻辑调到 DubboProtocol 中执行。
public class DubboProtocol extends AbstractProtocol {
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
if (!(message instanceof Invocation)) {
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: "
+ (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message))
+ ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress());
}
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
// need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback
if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) {
String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods");
boolean hasMethod = false;
if (methodsStr == null || !methodsStr.contains(",")) {
hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr);
} else {
String[] methods = methodsStr.split(",");
for (String method : methods) {
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) {
hasMethod = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!hasMethod) {
logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName()
+ " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored."
+ " please update the api interface. url is:"
+ invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv);
return null;
}
}
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
//继续往下调用,经过过滤器等到达最终的服务
Result result = invoker.invoke(inv);
return result.thenApply(Function.identity());
}
....
}
....
}
参考资料
文章主要从消费者发出请求,到提供者处理请求两个源码分析。
参考资料
- 官网文档