A. Omkar and Password
题意:每次可以将相邻不相等的两项替换成他们的和(原来的两个数变成一个数),问最短能变成多短。
思路:其实会发现,如果这个序列里但凡存在一对a[i]!=a[i+1]的,不管i+1后面有多少相同的,我们都可以产生连锁反应把整个序列变成只有一项。如 3 7 7 7.... ,不管后面7有多少,我一个3就可以把它们全部打乱。所以只需要判断序列是否全相等即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 2e5+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
ll a[maxn];
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll n = read();
rep(i,1,n) a[i] = read();
if(n==1)
{
cout<<1<<endl;
}
else
{
int flag = 1;
rep(i,2,n) if(a[i]!=a[i-1]) flag = 0;
if(flag) cout<<n<<endl;
else cout<<1<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
B. Omkar and Infinity Clock
题意: 有k个操作,每次把所有a[i]变成最大值 - a[i],问最后序列。
思路:随便写几个例子会发现有规律存在,其实就只在两个序列里面来回变动。所以只需要考虑奇偶性就行。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 2e5+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
ll a[maxn];
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll n = read(); ll k = read();
ll ma = -inf, mi = inf;
rep(i,1,n) a[i] = read(), ma = max(ma,a[i]), mi = min(mi, a[i]);
if(k&1)
{
rep(i,1,n) cout<<ma - a[i]<<' '; cout<<'
';
}
else
{
rep(i,1,n) cout<<(ma - mi) - (ma - a[i])<<' '; cout<<'
';
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Omkar and Waterslide
题意:每次可以将序列里面一段非降子串全部+1,问最少多少步可以使得最后整体变为一个非降序列。
思路:贪心+差分。我们先拿一个例子来说,如图
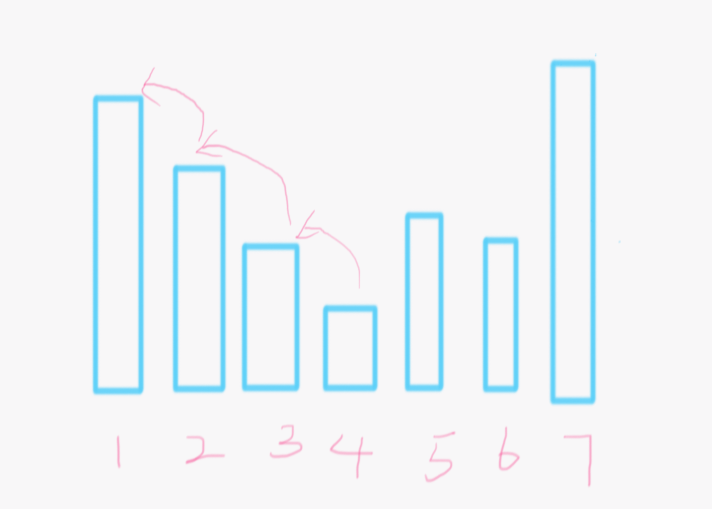
我们发现从下标2->4的元素都是递减的,这一部分是肯定至少要加到a[1]那么大的。我们看看怎么加最少,首先最小的a[4]先自增,等增到a[3]那么大的时候就和a[3]一起增,同理他们俩和a[2]一样大的时候再拉上a[2]一起增,然后一路到a[1]。这样我们发现只需要考虑第一位和第四位的差分就行了。换句话说,我们这个要增加的区间里面只需要考虑最大值和最小值。因为其中间的元素我们都可以搭顺风车一起增。那到a[5]的时候发现比a[4]大了,如果它是直接比a[1]都大,我们就先把前面四个增到a[1]就行了。但是如果像图里这样刚好处于前面的最大最小值之间的话,我们就贪心一下,反正a[5]也要增加到那么大,我们先看看他后面有多少能先增加到它那么大的然后一起搭顺风车。然后发现a[6]就是,所以当a[6]增加到a[5]的时候,就可以和前面几个的一起到a[1]了。em。。。如果还不明白的话就看代码吧,非常简便。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 2e5+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
ll a[maxn];
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll n = read();
rep(i,1,n) a[i] = read();
ll pre = a[1];
ll ans = 0;
ll cur = 0;
rep(i,1,n)
{
if(a[i] < a[i-1]) cur += a[i-1] - a[i];
else
{
ans += cur, cur = 0, pre = a[i];
}
}
ans += cur;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
D. Omkar and Bed Wars
题意:n个人环形坐下,每个人可以给相邻的人扇耳光,如果只有一个人扇了你一耳光,你就扇回去。反之可以扇左右随便一个。现在给你一个可能不按照规则来的,问你最小改变多少个人可以所有人遵循上述规则。
思路:这题看了dalao思路才明白。
1.我们定义一个联通块为一个连续有相同方向的序列。如RRRLRL,前三个R就是一个联通块。然后发现我们操作一个联通块最小只需要len/3次就够了。即隔两位改变一个,如上述RRR变成RLR就满足题意。
2.所以就统计一下这个序列有多少个联通块,每个联通块的贡献就是len/3 。 最后注意如果尾部的联通块和开头的朝向相同,他们其实是一个来的,所以合并一下。
3.如果全局就一个联通块,如RRRRR,就需要(n+2)/3,即向上取整的意思。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include <queue>
#include<sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include<vector>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define abs(a) ((a)>=0?(a):-(a))
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define rep(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
#define per(i,n,a) for(int i=n;i>=a;--i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int maxn = 2e5+200;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-7;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int mod = 1e9+7;
inline int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
void ex_gcd(ll a,ll b,ll &d,ll &x,ll &y){if(!b){d=a,x=1,y=0;}else{ex_gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);}}//x=(x%(b/d)+(b/d))%(b/d);
inline ll qpow(ll a,ll b,ll MOD=mod){ll res=1;a%=MOD;while(b>0){if(b&1)res=res*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b>>=1;}return res;}
inline ll inv(ll x,ll p){return qpow(x,p-2,p);}
inline ll Jos(ll n,ll k,ll s=1){ll res=0;rep(i,1,n+1) res=(res+k)%i;return (res+s)%n;}
inline ll read(){ ll f = 1; ll x = 0;char ch = getchar();while(ch>'9'||ch<'0') {if(ch=='-') f=-1; ch = getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') x = (x<<3) + (x<<1) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();return x*f; }
int dir[4][2] = { {1,0}, {-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} };
int main()
{
int kase;
cin>>kase;
while(kase--)
{
ll n = read();
string s;
cin>>s;
if(n<=2)
{
cout<<0<<endl;
continue;
}
int len = 1;
int ans = 0;
int First = 0;
rep(i,1,s.size()-1)
{
if(s[i] == s[i-1]) len ++;
else
{
if(!First) First = len;
else ans += len/3;
len = 1;
}
}
if(!First) cout<<(n+2)/3<<endl;
else
{
if(s[0] == s[n-1]) cout<<ans + (len + First)/3<<endl;
else cout<<ans + len/3 + First/3 <<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}