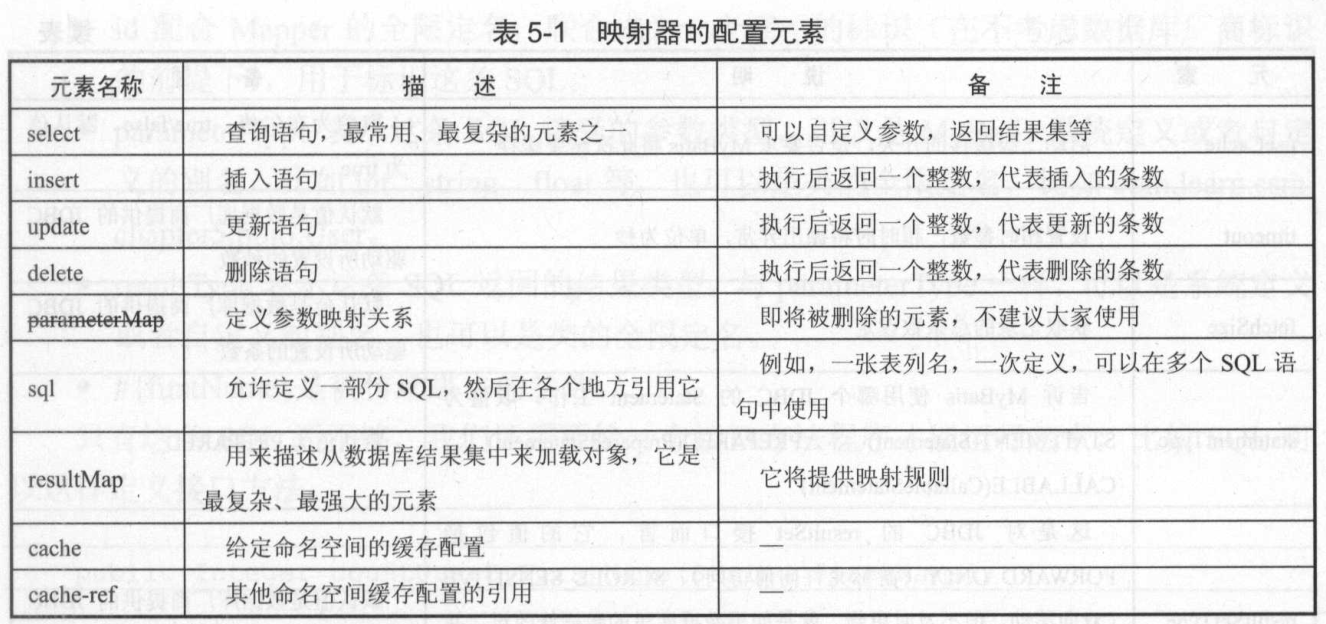
一、select元素
1.select元素的应用
id为Mapper的全限定名,联合称为一个唯一的标识
paremeterType标识这条SQL接收的参数类型
resultType标识这条SQL返回的结果类型
<select id="getRole" parameterType="long" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where id = #{id} </select>
只有这条SQL还不够,还需要给一个接口方法程序才能运行起来,即与之对应的是
public Role getRole(Long id);
2.自动映射和驼峰映射
MyBatis提供了自动映射功能,在默认的情况下自动映射是开启的,使用它的好处是能有效地较少大量的映射配置,从而减少工作量。
例如:原来的列名role_name被别名roleName代替了,这样就和POJO属性名称private String roleName;保持一致了。此时MyBatis就会将这个结果集映射到POJO的属性roleName上,自动完成映射,而无须再进行任何配置,明显减少了工作量。
<select id="getRole" parameterType="long" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where id = #{id} </select>
如果将mapUnderscoreToCamelCase设置为true,那么将按照驼峰映射(即数据库字段为role_name,则POJO属性名为roleName;数据库字段为user_name,则POJO属性名为userName),即上面的例子中的select语句将改成:
select id, role_name, note from t_role where id = #{id}
3.传递多个参数
(1)使用map接口传递多个参数
声明接口方法:
public List<Role> findRolesByMap(Map<String, Object> parameterMap);
在XML中设置使用map传递多个参数:
<select id="findRolesByMap" parameterType="map" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%') and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%') </select>
使用findRolesByMap方法:
public static void testFindRolesByMap() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlSession(); RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); Map<String, Object> parameterMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); parameterMap.put("roleName", "1"); parameterMap.put("note", "1"); List<Role> roles = roleMapper.findRolesByMap(parameterMap); System.out.println(roles.size()); } catch(Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
不推荐这种方式,是因为:1.map是一个键值对应的集合,使用者要通过阅读它的键,才能明白其作用;2.使用map不能限定其传输的数据类型,因此业务性不强,可读性差。
(2)使用注释传递多个参数
接口方法定义为:
public List<Role> findRolesByAnnotation(@Param("roleName") String rolename, @Param("note") String note);
xml配置文件修改为:
<select id="findRolesByAnnotation" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%') and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%') </select>
使用findRolesByAnnotation方法:
public static void testFindRolesByAnnotation() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlSession(); RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); List<Role> roles = roleMapper.findRolesByAnnotation("1", "1"); System.out.println(roles.size()); } catch(Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
通过改写使可读性大大提高,使用者也方便了,但是这会带来一个麻烦,如果SQL很复杂,拥有大于10个参数,那么接口方法的参数个数就多了,使用起来就很不容易。
(3)使用Java Bean传递多个参数
先定义一个参数的POJO-RoleParams
package com.ssm.chapter5.param; public class RoleParams { private String roleName; private String note; public String getRoleName() { return roleName; } public void setRoleName(String roleName) { this.roleName = roleName; } public String getNote() { return note; } public void setNote(String note) { this.note = note; } }
将接口方法定义为:
public List<Role> findRolesByBean(RoleParams roleParam);
在xml中使用下面的配置:
<select id="findRolesByBean" parameterType="com.ssm.chapter5.param.RoleParams" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where role_name like concat('%', #{roleName}, '%') and note like concat('%', #{note}, '%') </select>
使用findRolesByBean方法时:
public static void testFindRolesByBean() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlSession(); RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); RoleParams roleParam = new RoleParams(); roleParam.setNote("1"); roleParam.setRoleName("1"); List<Role> roles = roleMapper.findRolesByBean(roleParam); System.out.println(roles.size()); } catch(Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
Java Bean的属性roleName代表角色名称,而note代表备注。
首先引入Java Bean定义的属性作为参数,然后进行查询。
(4)混合使用
如果,查询一个角色,可以通过角色名称和备注进行查询,与此同时还需要支持分页,而分页的POJO的实现如下:
package com.ssm.chapter5.param; public class PageParams { private int start; private int limit; public int getStart() { return start; } public void setStart(int start) { this.start = start; } public int getLimit() { return limit; } public void setLimit(int limit) { this.limit = limit; } }
接口设计如下:
public List<Role> findByMix(@Param("params") RoleParams roleParams, @Param("page") PageParams PageParam);
xml配置如下:
<select id="findByMix" resultType="role"> select id, role_name as roleName, note from t_role where role_name like concat('%', #{params.roleName}, '%') and note like concat('%', #{params.note}, '%') limit #{page.start}, #{page.limit} </select>
使用findByMix方法:
public static void testFindByMix() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlSession(); RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); RoleParams roleParam = new RoleParams(); roleParam.setNote("1"); roleParam.setRoleName("1"); PageParams pageParams = new PageParams(); pageParams.setStart(0); pageParams.setLimit(100); List<Role> roles = roleMapper.findByMix(roleParam, pageParams); System.out.println(roles.size()); } catch(Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
4.使用resultMap映射结果集
自动映射和驼峰映射规则比较简单,无法定义多的属性。为了支持复杂的映射,select元素提供了resultMap属性。
先定义resultMap属性,然后再在select中使用resultMap属性:
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="role"> <id property="id" column="id" /> <result property="roleName" column="role_name" /> <result property="note" column="note" /> </resultMap> <select id="getRoleUseResultMap" parameterType="long" resultMap="roleMap"> select id, role_name, note from t_role where id = #{id} </select>
resultMap元素顶一个roleMap,type代表的是作为映射的POJO类,意思也就是,POJO类的id名对应数据库的id,POJO类的roleName名对应数据库的role_name,POJO类的note名对应数据库的note。然后在select元素中的水性resultMap中制定了采用哪个resultMap作为其映射规则。
5.分页参数RowBounds
二、insert元素
三、update元素和delete元素
四、sql元素
五、参数
六、resultMap元素
七、级联
八、缓存
九、存储过程