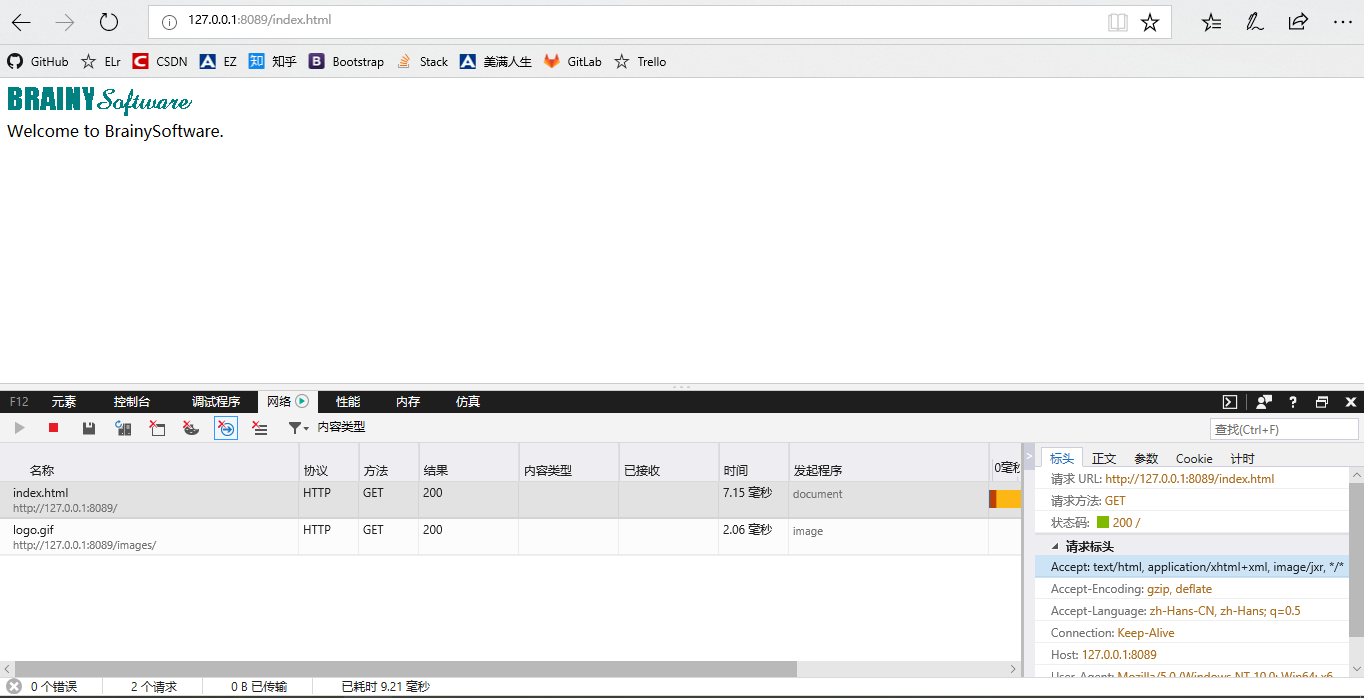
一个简单的Web服务器
- Web服务器也称为超文本传输协议(HyperText Transfer Protocol)服务器,因为它使用HTTP和客户端(通常是Web浏览器)进行通信
- 基于JavaWeb服务器会使用到两个重要的类:java.net.Socket类和java.net.ServerSocket类,并通过发送HTTP消息进行通信。
1.1 HTTP
- HTTP允许Web服务器和浏览器通过Internet发送并接受数据,是一种基于“请求--响应”的协议。
- HTTP使用可靠地TCP连接,TCP协议默认使用TCP 80端口。
- HTTP中总是有客户端通过建立连接并发送HTTP请求来初始化一个事务的。客户端或服务器可提前关闭连接
- 1.1.1 HTTP请求
- HTTP请求包含三部分:
- 请求方法--统一资源标识符URI--协议/版本
- 请求头
- 实体
- 每个HTTP请求可以使用HTTP标准中指定方法中的一种。HTTP1.1支持的方法:GET,POST,HEAD,OPTIONS,PUT,DELETE,TRACE
- URI 指定Internet资源的完整路径。URI通常为服务器根目录的相对路径
- 请求头包含客户端环境和请求实体之间的相关信息
- 请求头和实体之间包含一个空行,该空行只有CRLF字符,CRLF告诉HTTP服务器请求实体正文从哪里开始
- HTTP请求包含三部分:
- 1.1.2 HTTP响应
- HTTP响应包含三部分:
- 协议--状态码--描述
- 响应头
- 响应实体
- HTTP响应包含三部分:
-
1.2 Socket类
- 套接字是网络连接的断电。套接字使应用程序可以从网络中读写数据。
- 应用程序之间发送或接收消息,需要知道另一个应用程序中套接字的IP地址和端口号。Java中套接字由java.net.Socket表示
- 创建一个套接字:
-
public Socket(java.net.String host,int port)
-
- 创建成功Socket实例,就可以使用该实例发送或接受字节流。要发送字节流需要调用Socket类的getOutputStream方法获取一个OutputStream对象。接收字节流使用getInputStream方法获得输入流InputStream对象
- ServerSocket类
- Socket表示客户端套接字,即想要连接到远程服务器应用程序时创建的套接字。
- 如果要实现一个服务器向客户端发送响应,则需要另一种套接字ServerSocket。因为服务器需要时刻待命,等待客户端发起连接。
- ServerSocket类和Socket类并不相同。服务器套接字需要等待来自客户端的连接。当服务器套接字收到了连接请求后,会创建一个Socket实例处理与客户端的通信。
- 要创建服务器套接字,可以使用ServerSocket类提供的4个构造函数中的任意一个:需要指明IP地址和服务器套接字侦听的端口号。
-
//如果主机只有一个IP 地址, 那么默认情况下, 服务器程序就与该IP 地址绑定. ServerSocket 的第 4 个构造方法 ServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress bingAddr) 有一个 bindAddr 参数, 它显式指定服务器要绑定的IP 地址, 该构造方法适用于具有多个IP 地址的主机. 假定一个主机有两个网卡, 一个网卡用于连接到 Internet, IP为 222.67.5.94, 还有一个网卡用于连接到本地局域网, IP 地址为 192.168.3.4. 如果服务器仅仅被本地局域网中的客户访问, 那么可以按如下方式创建 ServerSocket: ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8000, 10, InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.4"));
-
1.3应用程序
- Web服务器应用程序包含三个类:
- HTTPServer
- Request
- Response
- 应用程序入口点(静态main方法)在HTTPServer类中,main方法创建一个HTTPServer实例,然后调用其await方法。该方法会在指定端口上等待HTTP请求,对其进行处理,然后发送响应信息会客户端。
- 1.3.1 HTTPServer类
-
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.File; public class HttpServer { /** WEB_ROOT is the directory where our HTML and other files reside. * For this package, WEB_ROOT is the "webroot" directory under the working * directory. * The working directory is the location in the file system * from where the java command was invoked. */ public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "webroot"; // shutdown command private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN"; // the shutdown command received private boolean shutdown = false; public static void main(String[] args) { HttpServer server = new HttpServer(); server.await(); } public void await() { ServerSocket serverSocket = null; int port = 8080; try { serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); } // Loop waiting for a request while (!shutdown) { Socket socket = null; InputStream input = null; OutputStream output = null; try { socket = serverSocket.accept(); input = socket.getInputStream(); output = socket.getOutputStream(); // create Request object and parse Request request = new Request(input); request.parse(); // create Response object Response response = new Response(output); response.setRequest(request); response.sendStaticResource(); // Close the socket socket.close(); //check if the previous URI is a shutdown command shutdown = request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } }
-
- 1.3.2 Request类
- Request类表示一个HTTP请求。可以传递InputStream对象,来创建Request对象。使用read方法读取HTTP中的数据:
-
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Request { private InputStream input; private String uri; public Request(InputStream input) { this.input = input; } public void parse() {//解析HTTP请求中原始数据 // Read a set of characters from the socket StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048); int i; byte[] buffer = new byte[2048]; try { i = input.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); i = -1; } for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { request.append((char) buffer[j]); } System.out.print(request.toString()); uri = parseUri(request.toString()); } private String parseUri(String requestString) { int index1, index2; index1 = requestString.indexOf(' '); if (index1 != -1) { index2 = requestString.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1); if (index2 > index1) return requestString.substring(index1 + 1, index2); } return null; } public String getUri() { return uri; } }
-
1.3.3 Response类
-
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.File; /* HTTP Response = Status-Line *(( general-header | response-header | entity-header ) CRLF) CRLF [ message-body ] Status-Line = HTTP-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF */ public class Response { private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; Request request; OutputStream output; public Response(OutputStream output) { this.output = output; } public void setRequest(Request request) { this.request = request; } public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException { byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; FileInputStream fis = null; try { File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri()); if (file.exists()) { fis = new FileInputStream(file); int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); while (ch!=-1) { output.write(bytes, 0, ch); ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); } } else { // file not found String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found " + "Content-Type: text/html " + "Content-Length: 23 " + " " + "<h1>File Not Found</h1>"; output.write(errorMessage.getBytes()); } } catch (Exception e) { // thrown if cannot instantiate a File object System.out.println(e.toString() ); } finally { if (fis!=null) fis.close(); } } }
运行结果