n<=50个游戏机有花费,每个游戏机有Gi<=10种游戏,每种游戏有花费有收益,买了游戏机才能玩对应游戏,求最大收益。
这就是一个背包!不过有依存关系,就不会了!
方法一:f[i][j]表示游戏机i用j块钱能得多少收益,这是可以预处理的,而g[i][j]表示前i个游戏机用j块钱最大收益,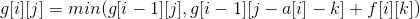
果断tle,究其原因在于g[i][j]的转移,本来一个游戏机没几款游戏,转移10次就够了,被我搞成钱,搞了那么多次。
方法二:与上相同,但k和f[i][k]改成那十个游戏数的值。没了。

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 //#include<iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int n,m; 9 #define maxn 100011 10 struct Start{int v,cnt;}p[maxn]; 11 int v[55][23],w[55][23]; 12 int f[2][maxn],cur; 13 int main() 14 { 15 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 16 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 17 { 18 scanf("%d%d",&p[i].v,&p[i].cnt); 19 for (int j=1;j<=p[i].cnt;j++) scanf("%d%d",&w[i][j],&v[i][j]); 20 } 21 cur=0;memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); 22 for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) 23 { 24 cur^=1; 25 for (int j=0;j<p[i].v;j++) f[cur][j]=0; 26 for (int j=p[i].v;j<=m;j++) f[cur][j]=f[cur^1][j-p[i].v]; 27 for (int j=1;j<=p[i].cnt;j++) 28 for (int k=m;k>=p[i].v+w[i][j];k--) 29 f[cur][k]=max(f[cur][k],f[cur][k-w[i][j]]+v[i][j]); 30 for (int j=0;j<=m;j++) f[cur][j]=max(f[cur^1][j],f[cur][j]); 31 } 32 printf("%d ",f[cur][m]); 33 return 0; 34 }
