1.ord函数
>>> ord('a') 97 >>> chr(97) 'a'
就是上面这个样子,返回ASCII值,有值就输出对应的字符。
2.GPU不是用来计算的吗?为什么还可以存储数据呢?
https://www.cnblogs.com/hellobb/p/11023873.html
是可以存储数据的,不然进行高速计算中间结果之类的存储在什么地方呢?。。
CPU的内存一般称之为主存(main memory),GPU自己的存储则称为local memory,即GPU的本地存储,有时候也称为video memory。
就像显卡集显和2G独显之类的,这都是它们的本地存储容量.
3.GRU了解
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32481747
内部结构像LSTM,但是门和参数都少了,有重置门和更新门,计算能力和时间成本需求较小。
4.

尝试运行这个:
import torch a=torch.tensor([1,2,3]) out=a.data.view(-1).div(0.1).exp() #运行不起来,会自动结束。。
就会直接RESTART: Shell。。。
终于找到了一些:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31170525
# 这里是将输出转化为一个多项式分布 output_dist = output.data.view(-1).div(temperature).exp() # 从而可以根据混乱度 temperature 来选择下一个字符 # 混乱度低,则趋向于选择网络预测最大概率的那个字符 # 混乱度高,则趋向于随机选择字符 top_i = torch.multinomial(output_dist, 1)[0]
torch.multinomial 学习

意思是,从每一行中根据多项式分布采样,每行都采nums_samples个样,然后返回这个tensor。
>>> weights = torch.tensor([0, 10, 3, 0], dtype=torch.float) >>> torch.multinomial(weights, 2) tensor([1, 2]) >>> torch.multinomial(weights, 3) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#78>", line 1, in <module> torch.multinomial(weights, 3) RuntimeError: invalid argument 2: invalid multinomial distribution (with replacement=False, not enough non-negative category to sample) at c:aw1swindowspytorchatensrc hgeneric/THTensorRandom.cpp:320 >>> torch.multinomial(weights, 4, replacement=True) tensor([1, 1, 1, 1])
经过以上的实验,首先它是根据input中数据值的大小来采样的,然后默认是不采0的,只采正数.下面可以看出它不采负数的。
>>> w=torch.tensor([0, 10, -3, 0], dtype=torch.float) >>> torch.multinomial(w, 2) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#81>", line 1, in <module> torch.multinomial(w, 2) RuntimeError: invalid argument 2: invalid multinomial distribution (encountering proba
5.指数加权平均
https://www.jianshu.com/p/41218cb5e099?utm_source=oschina-app
它能够模拟点的趋势,并且将过去给考虑进来,能够平滑曲线;应用到SGD的时候,能够加快收敛速度,减少震荡。
还能将长期趋势显现出来,通常设置β为0.9。
2-26——————————————
3.距离和相似度度量方法
https://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/45651315
5.GEO到底哪些表示真实数据呢?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi
2-27——————————
1.JS散度:
https://www.cnblogs.com/smuxiaolei/p/7400923.html


JS是对称的而且值是有界的[0,1]. 当P1和P2完全相同时,JS=0;当不同时为1.
分别用P1和P2来和第三个分布,相当于一个中间分布来计算KL散度,相比于直接KL就会有一个折中?
2.itertools.chain.from_iterable(l)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50775024/itertools-chain-from-iterable
展平一个嵌套的列表。仅仅是展平,不去重。
import itertools country_and_countrycodes = [('United States', 'US'), ('China', 'CH')] all_countries = ['United States', 'Mongolia', 'Togo'] print(list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(country_and_countrycodes))) print(list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(all_countries))) #输出: ['United States', 'US', 'China', 'CH'] ['U', 'n', 'i', 't', 'e', 'd', ' ', 'S', 't', 'a', 't', 'e', 's', 'M', 'o', 'n', 'g', 'o', 'l', 'i', 'a', 'T', 'o', 'g', 'o']
从这里就能看出来它的作用了吧,就是解决嵌套一层的列表。往里走一层。
2-28————————————————————————————————
1.python常用函数
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1140244 字符串函数、集合函数、列表函数和字典函数。
https://www.cnblogs.com/ljhdo/p/10664286.html
1.filter函数,可以代替循环的if判断,很厉害
>>> ret = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, range(10)) >>> ret <filter object at 0x000002191AEF7DD8> >>> list(ret) [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
第一个参数为需要满足的条件(一个函数),第二个为一个可迭代循环的对象吧,比如list,然后就可以每个元素去判断是否符合function的条件。
2.list的sort和内置的sort
list的sort是直接对list操作修改,不返回任何内容;内置sort是会返回一个新的排好序的list,不在原list上修改。
有一点特殊讲解是,针对按关键字排序的方法:
>>> list = [('d',3),('a',5),('d',1),('c',2),('d',2)] >>> sorted(list,key=lambda x:x[1]) [('d', 1), ('c', 2), ('d', 2), ('d', 3), ('a', 5)]
也就是当按固定键排序的时候,用key关键字,然后lambda匿名函数。
3.print的格式化输出,这个需要学习
print(format % args)
格式就是这个样子,前面是format字符串,然后由%分隔,args为参数;
>>> name='hh' >>> age=20 >>> print('my name is %s, %d years old'%(name,age)) my name is hh, 20 years old
就挺有用的。其中%d表示整数,%s字符串,%发表示浮点数。
还有不使用%号,而对所有输出格式一视同仁的{}peihe.format(变量1,变量2.。。)
name = 'langxm' age = '28' corp = "NetEase" print("hello my name is {} i am {} i worked at {}".format(name, age, corp))
4.非常常见的map函数
将function应用到每个可迭代对象上:
map(func, seq1[, seq2,…])
>>> map(lambda x: x*x , [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) <map object at 0x000002191AF0ED68> >>> list(map(lambda x: x*x , [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]))#这里居然不能用list,难道只能用 #for循环访问吗? Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#19>", line 1, in <module> list(map(lambda x: x*x , [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) TypeError: 'list' object is not callable >>> m=map(lambda x: x*x , [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])#输出只有一个seq可迭代对象时 >>> for i in m: print(i) 1 4 9 16 25 >>> t=map(lambda x,y:(x**y,x+y),[1,2,3],[1,2,4])#当有两个seqs时,也可以操作。 >>> for i in t: print(i) (1, 2) (4, 4) (81, 7)
2.nlp小项目
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/51279338
3.关于CEL计算损失时
https://blog.csdn.net/ccbrid/article/details/79844005
如果时出现,Dimension specified as 0 but tensor has no dimensions,就
loss += criterion(output, target_var[c].unsqueeze(0))
就插入一个维度;
如果是不能有 RuntimeError: multi-target not supported (newbie)的错误,那么就squeeze(0)即可,就是维度的调整,因为CEL交叉熵损失要求target是一个一维的向量吧。
4.torch.bmm(input, mat2, out=None) → Tensor
将存储在input和mat2中的多个矩阵进行批次矩阵乘法操作,两个输入中所含的矩阵数目必须是一样的。
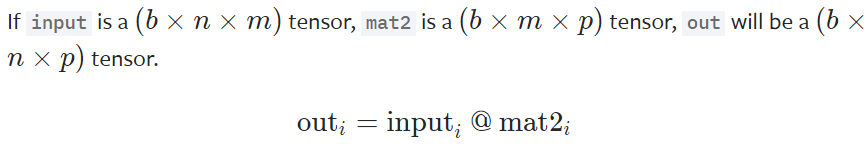
下面的代码就很容易能够看出来它的功能。
>>> input = torch.randn(10, 3, 4) >>> mat2 = torch.randn(10, 4, 5) >>> res = torch.bmm(input, mat2) >>> res.size() torch.Size([10, 3, 5])