You are given an array a with n distinct integers. Construct an array b by permuting a such that for every non-empty subset of indices S = {x1, x2, ..., xk} (1 ≤ xi ≤ n, 0 < k < n) the sums of elements on that positions in a and b are different, i. e.
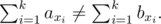
The first line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 22) — the size of the array.
The second line contains n space-separated distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 10^9) — the elements of the array.
If there is no such array b, print -1.
Otherwise in the only line print n space-separated integers b1, b2, ..., bn. Note that b must be a permutation of a.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
| input |
|
2 1 2 |
| output |
| 2 1 |
| input |
|
4 1000 100 10 1 |
| output |
| 100 1 1000 10 |
An array x is a permutation of y, if we can shuffle elements of y such that it will coincide with x.
Note that the empty subset and the subset containing all indices are not counted.
题解
考虑一个元素互异且升序的数列A,则易知满足题目条件的数列B = {A[n],A[1],...,A[n-1]},即将A数列循环右移一个单位。为什么可以这样做?
由于A是升序的数列且元素互异,故对于任意的S = {x1, x2, ..., xk} (1 ≤ xi ≤ n, 0 < k < n):
- 若1 不在S内,则对于任意位置xi (xi ≠ 1) ,都有A[xi] > B[xi],故∑ki=1A[xi] > ∑ki=1B[xi],满足不相等条件;
- 若1在S内,由于A[1]是A中最小的数,而B[1]是A中最大的数,且对于其他的位置xi ≠ 1仍有A[xi] > B[xi]。又因为∑nj=1A[j] = ∑nj=1B[j],除了位置1是A[1] < B[1]以外,其余位置j都是A[j] > B[j],这就是说A[1]-B[1]的值需要其后n-1个位置的A[j]-B[j]的值来共同抵消,且1位置的A[1]-B[1]为负,其余n-1个位置的A[j]-B[j]均为正。也就是说,一旦S包含1,则要想∑ki=1A[xi] = ∑ki=1B[xi]必须有|S| = n,然而|s| < n,故有∑ki=1A[xi] < ∑ki=1B[xi],仍然满足题意。
可见,如此获得的数列B即是A满足题意得一个排列,但题目中得数列a并不一定升序排列,所以我们可以记录原数列a中每一个数的下标后,对其进行升序排列,此时下标跟随着值的升序而打乱。然后将升序后的a数列的值(注意记录的数的下标不动)循环右移一个单位得到b,此时的b相对升序后的a满足题意。再将b和升序后的a数列按照记录的下标重新升序排列,a数列还原,此时得到新的b数列即为满足题意的数列。(因为排序过程并没有改变同一位置数列a和b数列相对应的值(即若ai与bj相对应于同一下标位置,排序后二者仍然是对应的),故原来的b数列是升序a数列的满足题意的数列,则排列后新的b数列则是升序a数列排列后(即原a数列)满足题意得数列)。也就是说对于满足题意得任意a数列,都有满足题意得b数列存在,故输出-1是不存在的。


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #define re register 8 #define il inline 9 #define ll long long 10 #define ld long double 11 const ll MAXN = 1e6+5; 12 const ll INF = 1e8; 13 14 //快读 15 il ll read() 16 { 17 char ch = getchar(); 18 ll res = 0, f = 1; 19 while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') 20 { 21 if(ch == '-') f = -1; 22 ch = getchar(); 23 } 24 while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') 25 { 26 res = (res<<1) + (res<<3) + (ch-'0'); 27 ch = getchar(); 28 } 29 return res*f; 30 } 31 32 //数列节点 33 struct A 34 { 35 ll v, p; //v为值,p为下标位置 36 }; 37 38 //按值排序 39 bool cmpv(const A a1, const A a2) 40 { 41 return a1.v < a2.v; 42 } 43 44 //按下标排序 45 bool cmpp(const A a1, const A a2) 46 { 47 return a1.p < a2.p; 48 } 49 50 A a[MAXN], b[MAXN]; 51 52 int main() 53 { 54 ll n = read(); 55 for(re ll i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 56 { 57 a[i].v = read(); 58 a[i].p = i; 59 } 60 std::sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmpv); 61 //将值整体循环右移一位 62 b[1].v = a[n].v, b[1].p = a[1].p; 63 for(re ll i = 2; i <= n; ++i) 64 { 65 b[i].v = a[i-1].v; 66 b[i].p = a[i].p; 67 } 68 std::sort(b+1,b+n+1,cmpp); 69 printf("%lld", b[1].v); 70 for(re ll i = 2; i <= n; ++i) 71 { 72 printf(" %lld", b[i].v); 73 } 74 printf("\n"); 75 return 0; 76 }