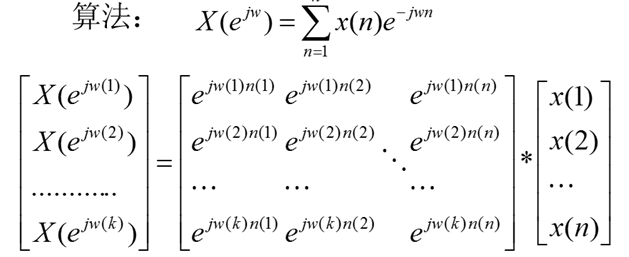一、离散序列傅里叶变化——DTFT
1、DTFT公式
2、Matlab算法实现
function[X]=dtft(x,n,w,flag) %计算离散时间付里叶变换 %[X]=dtft(x,n,w) %X=在w频率点上的DTFT数组 %x=n点有限长度序列 %n=样本位置向量 %w=频率点位置向量 X = x * (exp(-j).^(n' * w));
3、DTFT一些画图代码
function [] = signal_write(X,w,flag) % X:数据 % w:频率向量 magX=abs(X);angX=angle(X); realX=real(X);imagX=imag(X); if(flag == 1) figure(); magX=abs(X);angX=angle(X); realX=real(X);imagX=imag(X); subplot(2,2,1);plot(w/pi,magX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('幅度部分');ylabel('幅度') subplot(2,2,3);plot(w/pi,angX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('相角部分');ylabel('弧度') subplot(2,2,2);plot(w/pi,realX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('实部');ylabel('实部') subplot(2,2,4);plot(w/pi,imagX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('虚部');ylabel('虚部') end if(flag == 2) plot(w/pi,magX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('幅度部分');ylabel('幅度') end if(flag == 3) plot(w/pi,angX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('相角部分');ylabel('弧度') end if(flag == 4) plot(w/pi,realX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('实部');ylabel('实部') end if(flag == 5) plot(w/pi,imagX);grid xlabel('以pi为单位的频率');title('虚部');ylabel('虚部') end
二、求LTI系统的频率响应H
%example2.4 clear all;close all; b=[1]; a=[1 -0.8]; m=0;length(b)-1; l=0:length(a)-1; %频率分点 K=500; k=-2*K:1:2*K; w=pi*k/K; %构建分子和分母的傅里叶变换 num=b*exp(-j*m'*w); %分母 den=a*exp(-j*l'*w); %分子 h=num./den; magH=abs(h); angH=angle(h); figure(1) subplot(2,1,1);plot(w/pi,magH),grid,title('幅度部分') subplot(2,1,2);plot(w/pi,angH),grid,title('相角部分') n=0:100; x=cos(0.05*pi*n); y=filter(b,a,x); figure(2) subplot(2,1,1);plot(n,x),grid,title('输入信号') subplot(2,1,2);plot(n,y),grid,title('输出信号')
三、采样与重构
Matlab代码
function [ ] = caiyang(Fs,N,jt,flag) %UNTITLED3 此处显示有关此函数的摘要 % 此处显示详细说明 % Dt 模拟时间间隔:在特定精度下信号为模拟的 % t 模拟时刻序列 % n 离散时间索引 % Ts 采样周期 % Fs 采样频率 % xa 在特定精度下,由离散信号逼近模拟信号 % jt 是否需要重构 % flag 5 第五题 % 6 第六题 Dt=0.00005; % 模拟时间间隔:在特定精度下信号为模拟的 Ts=1/Fs; % 采样周期 n=-N:1:N; % 离散时间索引 nTs=n*Ts; % 序列时刻索引 t=-N*Ts:Dt:N*Ts; % 模拟时刻序列 %% 只是对应相应的作业、、 if flag == 5 xa=exp(-1000*abs(t)); % 在特定精度下,由离散信号逼近模拟信号 x1=exp(-1000*abs(nTs)); % Fs=5000 样本/s:x1为采样后的离散时间序列 end if flag == 6 xa=sin(1000*pi*t); % 在特定精度下,由离散信号逼近模拟信号 x1=sin(1000*pi*nTs); % Fs=5000 样本/s:x1为采样后的离散时间序列 end if flag == 7 xa = sin(20*pi*t + pi/4); x1 = sin(20*pi*nTs + pi/4); end %% K = 500; % 对pi进行K等分:相当于对单位园2pi进行1000等分 dk = pi/K; % pi 的等分步进索引 w = 0 : dk : pi; % 角度步进索引 X = x1 * exp(-j* n'*w);% 对x1序列做离散傅立叶变换 Xr = real(X); w = [-fliplr(w),w(2:end)]; % 定义w负半轴 Xr = [fliplr(Xr),Xr(2:end)]; % 由于实部偶对称,得到Xr的负半轴 %% 决定是否重构 if jt == 1 figure(); % 绘出xa subplot(3,1,1) plot(t*1000,xa);hold on % 绘出x(jw) stem(n*Ts*1000,x1,'r.'),hold off,title('时域波形') % 绘出以pi归一化的数字频率对应的频域实部波形 subplot(3,1,2);plot(w/pi,Xr);title('频域波形') subplot(3,1,3) chonggou(x1,Fs,N); end if jt == 0 figure(); % 绘出xa subplot(2,1,1); plot(t*1000,xa);hold on % 绘出x(jw) stem(n*Ts*1000,x1,'r.'),hold off,title('时域波形') % 绘出以pi归一化的数字频率对应的频域实部波形 subplot(2,1,2);plot(w/pi,Xr);title('频域波形') end if jt == 2 % 绘出以pi归一化的数字频率对应的频域实部波形 plot(w/pi,Xr);title('频域波形') end if jt == 3 figure(); subplot(2,1,1); % 绘出xa plot(t*1000,xa);hold on % 绘出x(jw) plot(n*Ts*1000,x1,'r.'),hold off,title('时域波形') xa = x1 * sinc(Fs*(ones(length(nTs),1) * t-nTs'*ones(1,length(t)))); % 内插重构 subplot(2,1,2); plot(t*1000,xa, 'k' ),hold on plot(n*Ts*1000,x1,'r.'),hold off ,title('重构波形' ) axis([-N/Fs*1000,N/Fs*1000,min(x1),max(x1)]); end
重构代码:
function [ ] = chonggou(x1,Fs,N) %UNTITLED4 此处显示有关此函数的摘要 % 此处显示详细说明 % x1 抽样序列 % Fs 采样率 % t 时间轴 % Dt 离散间隔,模拟信号 Dt = 0.00005; % 模拟时间间隔:在特定精度下信号为模拟的 n = -N:N; nTs = n/Fs; t = -N/Fs:Dt:N/Fs; % 模拟时刻序列 xa = x1 * sinc(Fs*(ones(length(nTs),1) * t-nTs'*ones(1,length(t)))); % 内插重构 plot(t*1000,xa, 'k' ),hold on stem(nTs*1000,x1, 'r.' ),hold off ,title('重构波形' ) axis([-N/Fs*1000,N/Fs*1000,min(x1),max(x1)]); end