1 并集
一谈到并集就会用到union以及union all,两者的区别如下:
union:对两个表的并集操作,不包含重复行,相当于distinct,同时进行默认规则的排序。
默认规则即:按照select后面的查询字段出现的顺序进行排序。
union all:对两个表的并集操作,包含重复行,且不排序。
具体实例如下:
1 --创建一张表 2 create table test 3 ( 4 id int primary key, 5 name varchar2(30) not null, 6 score number not null 7 ); 8 --插入数据 9 insert into test values(1,'Aaron',78); 10 insert into test values(2,'Bill',76); 11 insert into test values(3,'Cindy',89); 12 insert into test values(4,'Damon',90); 13 insert into test values(5,'Ella',73); 14 insert into test values(6,'Frado',61); 15 insert into test values(7,'Gill',99); 16 insert into test values(8,'Hellen',56); 17 insert into test values(9,'Ivan',93); 18 insert into test values(10,'Jay',90); 19 commit;
利用union和union all进行查询
1.1 union all
1 -- union all 2 select id,name,score from test where id < 4 3 union all 4 select id,name,score from test where id > 2 and id < 6 ; 5 --第一个结果集应为1,2,3;第二个结果集应为3,4,5. 6 --最终结果为1,2,3,3,4,5,6.共6行.
结果显示: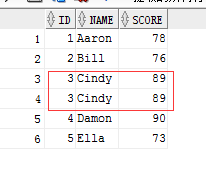
1 -- union all 2 select id,name,score from test where id > 2 and id < 6 3 union all 4 select id,name,score from test where id < 4
结果显示:
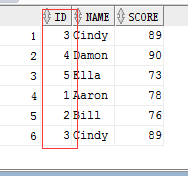
未排序,使用union all显示的结果集顺序即为两条select出现查询的顺序。
1.2 union
1 -- union 2 select id,name,score from test where id > 2 and id < 6 3 union 4 select id,name,score from test where id < 4; 5 --第一个结果集应为1,2,3;第二个结果集应为3,4,5. 6 --最终结果为1,2,3,4,5,6.共5行.
结果显示:
1 -- union 2 select score,id,name from test where id > 2 and id < 6 3 union 4 select score,id,name from test where id < 4;
结果显示:
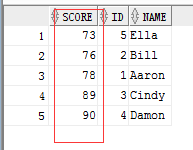
验证union的结果集排序方式为select后面字段出现的顺序。
备注:union前后关联的列数必须一样多,前面查询n个字段,后面也要查询n个字段。一般情况下查询结果列名按照关联前面的命名。
2 交集 intersect
---对两个结果集进行交集操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序.
实例:
1 --intersect 2 select EMPNO,ENAME,SAL from EMP 3 intersect 4 select EMPNO,ENAME,SAL from EMP where SAL>'2500'; 5 --前面是对EMP的全表查询的结果集,后面是对sal字段>2500的查询结果集 6 --求两个结果集的并集
结果显示: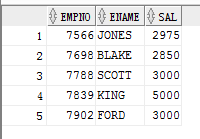
3 差集 Minus
---对两个结果集进行差操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序。
实例:
1 --minus 2 select EMPNO,ENAME,SAL from EMP 3 minus 4 select EMPNO,ENAME,SAL from EMP where SAL>'2500'; 5 --前面是对EMP的全表查询的结果集,后面是对sal字段>2500的查询结果集 6 --求两个结果集的差集
结果显示:
以上这几种操作均可在最后进行人为的排序。把order by 字段放在最后一个结果集后面即可。