读取文件
1.建立一个流对象,将已存在的一个文件加载进流。
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File(“Test.txt”));
2.创建一个临时存放数据的数组。
char[] ch = new char[1024];
3.调用流对象的读取方法将流中的数据读入到数组中。
fr.read(ch);
4. 关闭资源。
fr.close();




定义文件路径时,注意:可以用“/”或者“\”。
在写入一个文件时,如果使用构造器FileOutputStream(file),则 目录 下有同名文
件将被 覆盖。
如果使用构造器FileOutputStream(file,true),则目录下的同名文件不会被覆盖,
在文件内容末尾追加内容。
在读取文件时,必须保证该文件已存在,否则报异常。
字节流操作字节,比如:.mp3,.avi,.rmvb,mp4,.jpg,.doc,.ppt
字符流操作字符,只能操作普通文本文件。最常见的文本文
件:.txt,.java,.c,.cpp 等语言的源代码。尤其注意.doc,excel,ppt这些不是文
本文件。

/**
*
* 一、流的分类:
* 1.操作数据单位:字节流、字符流
* 2.数据的流向:输入流、输出流
* 3.流的角色:节点流、处理流
*
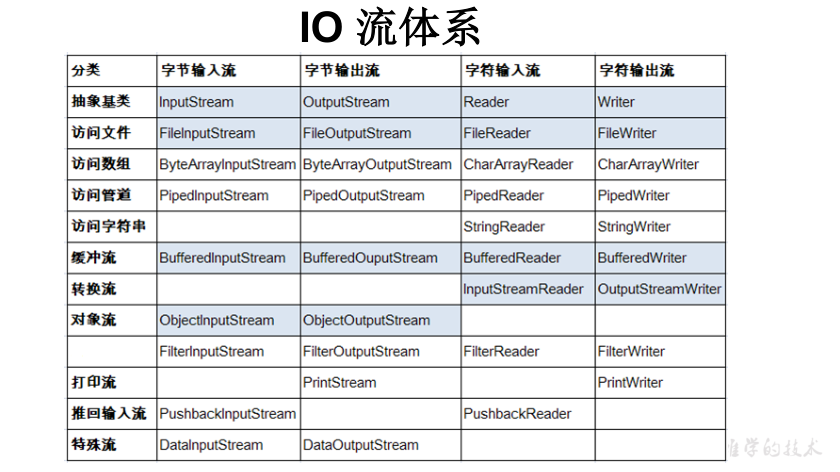
* 二、流的体系结构
* 抽象基类 节点流(或文件流) 缓冲流(处理流的一种)
* InputStream FileInputStream (read(byte[] buffer)) BufferedInputStream (read(byte[] buffer))
* OutputStream FileOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len) BufferedOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len) / flush()
* Reader FileReader (read(char[] cbuf)) BufferedReader (read(char[] cbuf) / readLine())
* Writer FileWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) BufferedWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) / flush()
*
*
*
* @author CH
* @create 2021 上午 10:40
*/
/* 将day09下的hello.txt文件内容读入程序中,并输出到控制台 说明点: 1. read()的理解:返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 2. 异常的处理:为了保证流资源一定可以执行关闭操作。需要使用try-catch-finally处理 3. 读入的文件一定要存在,否则就会报FileNotFoundException。 */ @Test public void testFileReader(){ FileReader fr = null; try { //1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件 File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前Module //2.提供具体的流 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.数据的读入 //read():返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 //方式一: // int data = fr.read(); // while(data != -1){ // System.out.print((char)data); // data = fr.read(); // } //方式二:语法上针对于方式一的修改 int data; while((data = fr.read()) != -1){ System.out.print((char)data); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.流的关闭操作 // try { // if(fr != null) // fr.close(); // } catch (IOException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } //或 if(fr != null){ try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

//对read()操作升级:使用read的重载方法 @Test public void testFileReader1() { FileReader fr = null; try { //1.File类的实例化 File file = new File("hello.txt"); //2.FileReader流的实例化 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.读入的操作 //read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len; while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ //方式一: //错误的写法 // for(int i = 0;i < cbuf.length;i++){ //会输出helloworld123ld,因为5整数倍为一组,【world】--【123ld】 // System.out.print(cbuf[i]); //只覆盖了前三个字符 // } //正确的写法 // for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){ // System.out.print(cbuf[i]); // } //方式二: //错误的写法,对应着方式一的错误的写法 // String str = new String(cbuf);//将数组里的东西全数出来了,原理对应方式一 // System.out.print(str); //正确的写法 String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);//别的构造器ctrl+alt+/调出构造器查看 // String str = new String(cbuf,0,len); System.out.print(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fr != null){ //4.资源的关闭 try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

/* 从内存中写出数据到硬盘的文件里。 说明: 1. 输出操作,对应的File可以不存在的。并不会报异常 2. File对应的硬盘中的文件如果不存在,在输出的过程中,会自动创建此文件。 File对应的硬盘中的文件如果存在: 如果流使用的构造器是:FileWriter(file,false) / FileWriter(file):对原有文件的覆盖 如果流使用的构造器是:FileWriter(file,true):不会对原有文件覆盖,而是在原有文件基础上追加内容 */ @Test public void testFileWriter() { FileWriter fw = null; try { //1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件 File file = new File("hello1.txt"); //2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出 fw = new FileWriter(file,false); //3.写出的操作 fw.write("I have a dream! "); fw.write("you need to have a dream!"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.流资源的关闭 if(fw != null){ try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
@Test public void testFileReaderFileWriter() { FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { //1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件 File srcFile = new File("hello.txt"); File destFile = new File("hello2.txt"); //不能使用字符流来处理图片等字节数据 // File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); // File destFile = new File("爱情与友情1.jpg"); //2.创建输入流和输出流的对象 fr = new FileReader(srcFile); fw = new FileWriter(destFile); //3.数据的读入和写出操作 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len;//记录每次读入到cbuf数组中的字符的个数 while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ //每次写出len个字符 fw.write(cbuf,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.关闭流资源 //方式一: // try { // if(fw != null) // fw.close(); // } catch (IOException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // }finally{ // try { // if(fr != null) // fr.close(); // } catch (IOException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // } //方式二: try { if(fw != null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(fr != null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }