1、 列表、元组
2、 字典
3、 集合
4、 字符串的各种姿势
5、 OPEN文件操作
1、 列表、元组
列表
1 names = ['wong','caiyun','dudu','junry','wong','huazai','tudou'] 2 print(names) 3 print(type(names))
###查找
1 # 列表是有序的, 2 3 # 存在位置索引编号,由0开始, 4 5 # 可以倒着取 6 7 print(names[0]) #打印第一个元素 8 9 print(names[-1]) #打印最后一个元素
###切片,取列表中一段元素
1 # 切片用':'分隔, 2 3 # 顺序从左到右, 4 5 # 顾前不顾后, 6 7 # 可以隔着取 8 9 # 0可以忽略 10 11 print(names[0:2]) #取编号为0-1的元素 12 13 print(names[0:-1]) 14 15 print(names[0:]) #取编号大于等于0的元素 16 17 print(names[:]) 18 19 print(names[:-1]) #取编号小于倒数第一个元素编号的元素 20 21 print(names[0::2]) #从编号为0的元素开始,隔着取 22 23 print(names[::2]) 24 25 print(names[1::2])
###追加
1 names.append('我是新来的') 2 3 print(names)
###插入
1 names.insert(2,'强行插入') 2 3 names.insert(5,'猥琐插入') 4 5 print(names)
###修改
1 names[2] = '你不能强行插入' 2 3 print(names)
###删除
1 names.pop() #删除最后一个 2 3 print(names) 4 5 del names[2] #删除第三个 6 7 print(names) 8 9 names.remove('猥琐插入') #删除指定元素 10 11 print(names)
###拷贝
1 # 浅拷贝, 2 3 # 深拷贝,默认一般为浅拷贝,即只拷贝一层(列表里面可能还有列表) 4 5 #法1 6 7 names3 = names.copy() 8 9 print(names3) 10 11 #法2 12 13 import copy 14 15 names3.extend(['猥琐发育,别浪']) #合并列表 16 17 names4 = copy.copy(names3) #浅拷贝 18 19 names5 = copy.deepcopy(names3) #深拷贝 20 21 print(names4)
关于深copy和浅copy
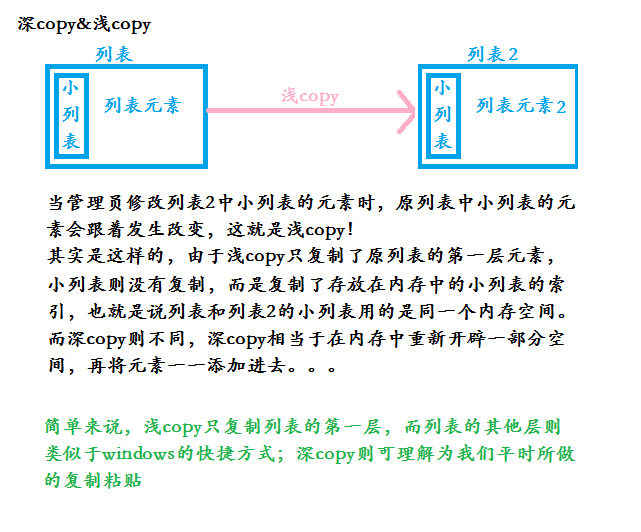
###扩展

1 #合并列表 2 3 names2 = [1,2,3] 4 5 names.extend(names2) 6 7 print(names) 8 9 10 11 #统计 12 13 print(names.count('wong')) 14 15 16 17 #排序&倒转,python3中,int类型和str类型无法比较排序 18 19 #print(names.sort())会报错 20 21 names[7] = '1' 22 23 names[8] = '2' 24 25 names[9] = '3' 26 27 names.sort() #从小到大 28 29 print(names) 30 31 names.reverse() #反转排序 32 33 print(names) 34 35 36 37 #获取元素下标 38 39 print(names.index('caiyun'))
元组
''' 关于元组的简单介绍 * 元组是有序的 * 元组不可变,可理解为不可更改的列表,又叫只读列表 * 工作中通常用它在存放不可变的内容,如id ''' fruit = ('apple','orange','banana','pear','apple','strawberry') print(fruit.index('banana')) print(fruit.count('apple')) print(fruit[2])
2、 字典
字典
1 dict = {'wong':23,'dudu':22,'caiyun':66,'junry':23,'huazai':55,'tudou':29} 2 print(type(dict)) 3 print(dict)
###查找
1 # 查找相应的key对应的value 2 3 print(dict.get('caiyun1')) #用get方法,如key不存在会返回None 4 5 print(dict['caiyun']) #直接key调用,如key不存在会报错 6 7 # 获取字典内所有的key 8 9 dictkey = dict.keys() 10 11 print(dictkey) 12 13 # 获取字典内所有的value 14 15 print(dict.values()) 16
###添加&修改
1 # 如果字典中没有,则添加一项(无修改功能), 2 3 # 以(k,d=None)的格式,默认value为空 4 5 dict.setdefault('Cdong') 6 7 dict.setdefault('Egeng',55) 8 9 print(dict) 10 11 # 添加或修改多个项,如果key已存在,则修改当前key对应的value 12 13 dict.update({'pingan':16,'xiaomi':15,'Cdong':33}) 14 15 print(dict) 16 17 # 单项修改 18 19 dict['caiyun'] = 666 20 21 print(dict.get('caiyun'))
###删除
1 dict.pop('huazai') #指定删除的元素 2 3 print(dict) 4 5 del dict['wong'] #其他删除方式 6 7 print(dict) 8 9 dict.popitem() #随机删除一项 10 11 print(dict)
###扩展
1 # 字典返回一个列表,原字典的key和value分别作为列表内的小元组形式存在 2 3 # for i in dict.items(): 4 5 # for j in i: 6 7 # print(j) 8 9 dict4 = dict.items() 10 11 print(dict4) 12 13 14 15 # 返回一个初始化字典,不同的key相同的value 16 17 dict3 = dict.fromkeys(['dudu','caiyun','tudou'],'23') 18 19 print(dict3) 20 21 22 23 # 字典拷贝 24 25 dict2 = dict.copy() 26 27 print(dict2) 28 29 30 31 # 清空字典内容 32 33 dict.clear() 34 35 print(dict) 36 37 38 39 # 删除字典 40 41 del dict 42 43 print(dict)
3、 集合
集合
1 list1 = ['wong','成都','茂名',1,2,3,'成都'] 2 list2 = ['wong',11,22,33,44,'北京','wong'] 3 set1 = set(list1) 4 set2 = set(list2)
###基本用法
1 #添加 2 3 set1.add('成都2') 4 5 print(set1) 6 7 8 #删除指定元素,如果没有这个元素,则do nothing 9 10 set1.discard('茂名') 11 12 print(set1) 13 14 #删除指定元素,如果没有这个元素,则报错 15 16 set1.remove('成都') 17 18 print(set1) 19 20 #删除任意元素 21 22 set1.pop() 23 24 print(set1) 25 26 27 #清空 28 29 set1.clear() 30 31 print(set1) 32 33 34 #拷贝 35 36 set3 = set1.copy() 37 38 print(set3)
###关系判断
1 s = set([3,6]) 2 3 t = set([3,5,6,77]) 4 5 #交集判断,如没有交集则返回True,否则False 6 7 print(s.isdisjoint(t)) 8 9 10 #set1是否包含在set2内(子集) 11 12 print(s.issubset(t)) 13 14 print(t.issuperset(s))
###集合间操作

1 ##法1 2 3 #取差集,set1有 set2没有 4 5 print(set1.difference(set2)) #返回差集 6 7 set.difference_update(set2) #执行差集修改操作 8 9 print(set1) 10 11 #取交集 12 13 print(set1.intersection(set2)) #返回交集 14 15 set1.intersection_update() #执行交集修改操作 16 17 print(set) 18 19 #取对称差集,你有我没有 我没有你有 20 21 print(set1.symmetric_difference(set2)) #返回对称差集 22 23 set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2) #执行对称差集修改操作 24 25 print(set1) 26 27 #取并集 28 29 print(set1.union(set2)) #返回并集 30 31 set1.update(set2) #执行并集修改操作 32 33 print(set1) 34 35 36 ##法2 37 38 #并集 39 40 print(set1 | set2) 41 42 #交集 43 44 print(set1 & set2) 45 46 #差集 47 48 print(set1 - set2) 49 50 #对称差集 51 52 print(set1 ^ set2)
4、 字符串的各种姿势
1 Introduction = ' my name is {_name}, I am {_age} YEARS OLD. How do you do... ' 2 print(Introduction)
###判断方法

1 #判断是否为数字 2 3 age = '23' 4 5 print(age.isdigit()) 6 7 print(age.isnumeric()) 8 9 10 #判断是否为数字和字母的任意组合 11 12 name = 'wong23dfd' 13 14 print(name.isalnum()) 15 16 17 #判断是否全为字母 18 19 name2 = 'wongdu' 20 21 print(name2.isalpha()) 22 23 24 #判断是否只有十进制字符 25 26 print(age.isdecimal()) 27 28 29 #判断字符串是否是有效的标识符,可简单理解为能成为变量名 30 31 print(name2.isidentifier()) 32 33 34 #判断字符串内字母是否全为小写 35 36 print(name.islower()) 37 38 39 #判断字符串中是否存在制表符 40 41 Introduction2 = 'my name is {_name}, I am {_age} YEARS OLD.How do you do..' 42 43 print(Introduction2.isprintable()) 44 45 46 #判断字符串是否为空白字符串 47 48 space = ' ' 49 50 print(space.isspace()) 51 52 53 #判断字符串是否为标题格式,即单词首字母全部大写 54 55 Introduction3 = 'My Name Is Wong' 56 57 print(Introduction3.istitle()) 58 59 60 #判断字符串中字母自否全为大写 61 62 Introduction4 = ' MY NAME IS WONG... ' 63 64 print(Introduction4.isupper()) 65 66 67 # 判断字符串是否以...(开始)结尾 68 69 print(Introduction.startswith('my')) 70 71 print(Introduction.endswith('...'))
###格式化输出

1 #美观输出? 2 3 print(Introduction.center(66,'*')) #左右补'*' 4 5 print(Introduction.ljust(66,'#')) #右边补'#' 6 7 print(Introduction.rjust(66,'#')) #左边补'#' 8 9 print(Introduction.zfill(66)) #左边补'0' 10 11 12 13 #格式化输出 14 15 print(Introduction.format(_name='Wong',_age=23)) 16 17 print(Introduction.format_map( {'_name':'Wong','_age':23} )) 18
###字符串修改

1 print(Introduction.capitalize()) #字符串首字母变大写,其余变小写 2 3 print(Introduction.casefold()) #字符串变小写(其他字符也有效,如德语) 4 5 print(Introduction.upper()) #字符串变大写 6 7 print(Introduction.lower()) #字符串变小写 8 9 print(Introduction.title()) #字符串变title格式,即单词首字母大写 10 11 print(Introduction.swapcase()) #字符串大写变小写,小写变大写 12 13 14 15 #把制表符转换成空格,默认为8个 16 17 print(Introduction.expandtabs(50)) 18 19 20 21 #组合 22 23 sort = '123' 24 25 print(Introduction.join(sort)) 26 27 28 29 #删除字符串首尾空格或换行符 30 31 Introduction5 = ' MY NAME IS WONG... ' 32 33 print(Introduction5.lstrip()) #左 34 35 print(Introduction5.rstrip()) #右 36 37 print(Introduction5.strip()) #左右 38 39 40 41 #列表单个字符一一替换;a-->1,o-->2 42 43 print(Introduction.maketrans('ao','12')) 44 45 print(Introduction.translate(Introduction.maketrans('ao','12'))) 46 47 48 49 #字符串替换 50 51 print(Introduction.replace('name','123')) 52 53 54 55 #指定分隔符将字符串分成3段组成元组,如分隔符不存在,则在字符串末尾加两个空元素 56 57 print(Introduction.partition('names')) 58 59 print(type(Introduction.partition('a'))) 60 61 62 63 #指定分隔符,将字符串分隔成为列表,默认分隔符为空格 64 65 print(Introduction.rsplit('a',3)) #从右开始 66 67 print(Introduction.split('a',2)) #从左开始 68 69 print(Introduction.splitlines(keepends=False)) #行符分割 70
###其他姿势

1 #统计 2 print(Introduction.count('do')) 3 4 #指定字符串编码格式 5 6 print(Introduction.encode(encoding='utf-8').decode()) 7 8 #从左边开始,查看符合的第一个字符串所在下标,不存在返回-1 9 10 print(Introduction.find('name')) 11 12 #从右边开始,查看符合的第一个字符串所在下标,不存在返回-1 13 14 print(Introduction.rfind('name')) 15 16 #从右边开始,返回符合的第一个字符串所在的下标,不存在则报错 17 18 print(Introduction.index('name')) 19 20 #从右边开始,返回符合的第一个字符串所在的下标,不存在则报错 21 print(Introduction.rindex('name')) 22
5、 OPEN文件操作
文件操作流程
1、打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量
2、通过句柄对文件进行操作
3、关闭文件
文件操作基本格式
1 # f = open('song','r',encoding='utf-8') #打开 2 3 # fread = f.readline() #读取一行 4 5 # print(fread) 6 7 # print('分割线'.center(50,'*')) 8 9 # print(f.read()) #当文件过大时,很耗费内存 10 11 # 12 13 # f.close() #关闭 14
###打开模式
r 以读的方式打开文件,只读
w 以写的方式打开文件,一打开就清空文件,可用来创建文件
a 以追加的方式打开文件,可在文件内容末尾追加内容
+ 可写又可读,如下:
r+ 打开文件,可读写
w+ 打开文件,覆盖文件原本内容,可读写
a+ 和r+差不多
U 表示在读取时,可以将
自动转换成
(与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
比如:rU、r+U
b 表示处理二进制文件
比如:rb、wb、ab
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过with打开文件,当with结束,文件关闭
1 with open('song','r',encoding='utf-8') as f: 2 3 pass
6、小结:
关于文件读取,我们应尽量的少占用内存资源。如下两个例子:
### 字典

1 dict = { 2 'wong':23, 3 'tudou':29, 4 'Egeng':36 5 } 6 #把dict直接一次性读到内存中,再取出来,耗费内存,不建议使用 7 for k,v in dict.items(): 8 print(k,v) 9 #每次循环只读取dict的一个key和value,建议使用 10 for i in dict: 11 print(i,dict[i])
###文件操作

1 #把文件内容全部读取到内存中,再进行调用,耗费内存,不建议使用 2 f = open('song','r',encoding='utf-8') #打开 3 f_read = f.readlines() #读取成列表的形式到内存 4 for f_list in f_read: 5 print(f_list.strip()) 6 f.close() 7 #每次循环只读取f文件的一行,建议使用 8 f = open('song','r',encoding='utf-8') #打开 9 for line in f: 10 print(line.strip()) 11 f.close()
2018-02-24
