3个整数数组进行整体排序,根据输入的三个数组的元素,输出排序后的结果(从大到小)
输入格式:
第1个数组的长度
第1个数组的各个元素
第2个数组的长度
第2个数组的各个元素
第3个数组的长度
第3个数组的各个元素
输出格式:
所有数组的整体排序
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3
79 80 61
3
88 66 77
2
23 90输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
90 88 80 79 77 66 61 23
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n1 = s.nextInt(); int []a1 = new int [n1]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n1 ;i++) { a1[i] = s.nextInt(); } int n2 = s.nextInt(); int []a2 = new int [n2]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n2 ;i++) { a2[i] = s.nextInt(); } int n3 = s.nextInt(); int []a3 = new int [n3]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n3 ;i++) { a3[i] = s.nextInt(); } int []a = new int [n1+n2+n3]; System.arraycopy(a1, 0, a, 0, n1); System.arraycopy(a2, 0, a, n1, n2); System.arraycopy(a3, 0, a, n1+n2, n3); Arrays.sort(a); for(int i = a.length-1 ; i > 0 ;i--) { System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } System.out.print(a[0]); s.close(); } }
注意:不用去重
A、B两队进行比赛,每队各有多名队员及其分数(分数不重复),使用A、B队所有队员得分的TOP 3来判断两队输赢,在TOP 3中拥有更多人数的队获胜。写程序实现该过程。
输入格式:
A队人数
A队每人得分
B队人数
B队每人得分
输出格式:
前三甲分数
赢的队
输入样例:
5
22 33 44 55 11
4
12 32 42 52输出样例:
55 52 44 A
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n1 = s.nextInt(); Integer [] a = new Integer [n1]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n1 ; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder()); int n2 = s.nextInt(); Integer [] b = new Integer [n2]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n2 ; i++) { b[i] = s.nextInt(); } Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder()); Sort_Judge(a,b); s.close(); } public static void Sort_Judge(Integer a[],Integer b[]) { Integer [] c = new Integer [a.length+b.length]; System.arraycopy(a, 0, c, 0, a.length); System.arraycopy(b, 0, c, a.length, b.length); Arrays.sort(c, Collections.reverseOrder()); System.out.print(c[0]); for(int i = 1 ; i < 3 ; i++) { System.out.print(" "+c[i]); } System.out.println(); int flag1 = 0; int flag2 = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { if(c[i] == a[i]) { flag1++; } if(c[i] == b[i]) { flag2++; } } if(flag1 > flag2) { System.out.println("A"); } if(flag1 < flag2) { System.out.println("B"); } } }
年底了,某公司要做销售统计,请输入各月份的销售额(单位:万元),请分别统计每季度的以及全年度的公司销售总额。 要求:
1.用一个四行3列数组记录销售额
2.在Main类中写一个方法统计并输出季度以及全年度的销售总额,并输出。方法声明定义为:
public static void showTotal(int [][]sale)
3.在main方法中顶一个二维数组并通过键盘输入各月份的销售总额,然后调用showTotal方法,输出统计结果。
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出12个月份的销售额,中间用空格隔开。
输出格式:
每一行分别输出各季度的销售额总和,最后一行输出年度销售额。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
22 33 44 33 44 66 77 45 64 43 34 23 45输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1季度的销售额为:99 2季度的销售额为:143 3季度的销售额为:186 4季度的销售额为:100 全年销售额为:528
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int [][]sale = new int [4][3]; for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { for(int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; j++) { sale[i][j] = s.nextInt(); } } showTotal(sale); s.close(); } public static void showTotal(int [][]sale) { int all = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int sum = 0; for(int j = 0 ; j < 3 ;j++) { sum += sale[i][j]; } System.out.print((i+1)+"季度的销售额为:"+sum); System.out.println(); all+=sum; } System.out.println("全年销售额为:"+all); } }
完成数组元素的移动功能:假设数组有n个元素,输入一个数x,把数组的第x个位置的元素删除了,后面的元素依次前进一个位置。 重复若干次这样的删除,得到最后的结果。
输入格式:
第一行包括一个整数n(1<=n<=100),表示数组元素的个数。 第二行输入n个数组元素,均为整数,用空格隔开。 第三行输入一个数k(1<=k<=100),表示要进行k次删除。 接下来k行,每行一个数x,表示要删除第x个元素。
输出格式:
输出经过k次删除后的数组,每两个元素之间用空格隔开。
输入样例:
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
4
3
2
4
6输出样例:
1 4 5 7 8 10
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); int [] a = new int [n]; for(int i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } int k = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < k ; i++) { int x = s.nextInt(); for(int j = x-1 ; j < a.length-1 ; j++) { a[j] = a[j+1]; } } System.out.print(a[0]); for(int i = 1 ; i < a.length - k; i++) { System.out.print(" "+a[i]); } System.out.println(); s.close(); } }
369寝室是比较特殊的寝室,因为别的寝室都住了四个人,而369寝室只有三个人。也因为这个原因,寝室里的三位同学感情特别好。但是,毕业在即,三位小伙伴马上要分别。为了在未来的某个日子可以见面,三位小伙伴有了一个约定,假设在未来的某一年,三位小伙伴的年龄的末尾正好出现3、6、9三个数,那么他们会再次相聚。
现在问题来了,假设今年三位小伙伴的年龄分别是x,y,z,那么,他们三人最早几年后可以相聚呢?
输入格式:
输入数据包括三个整数x,y,z,分别表示三位伙伴的年龄。
输出格式:
如果小伙伴最早在n年后可以相见(不包括当前这一年),那么请输出这个n;如果100年内都不存在这样的情况,输出:so sad!
输入样例:
25 22 28 输出样例:
1
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int x = s.nextInt(); int y = s.nextInt(); int z = s.nextInt(); boolean sad = false; for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { boolean flag1 = false; boolean flag2 = false; boolean flag3 = false; if(i == 100) { sad = true; break; } if((x+i)%10 ==3 ||(y+i)%10 == 3 || (z+i)%10 == 3) { flag1 = true; } if((x+i)%10 ==6 ||(y+i)%10 == 6 || (z+i)%10 == 6) { flag2 = true; } if((x+i)%10 ==9 ||(y+i)%10 == 9 || (z+i)%10 == 9) { flag3 = true; } if(flag1 && flag2 && flag3) { System.out.print(i); break; } } if(sad) { System.out.print("so sad!"); } s.close(); } }
从键盘输入N个整数,并输出指定的某个整数在这N个整数中的按照由小到大的顺序排列的位次(最小的位次是1,最大的位次是N,指定的整数如果不在这N个数中,则其位次是-1)
输入格式:
整数个数,指定的整数值
输出格式:
指定的整数的位次
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3
12 4 7
4输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); int[] a = new int [n+1]; for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } Arrays.sort(a); int x = s.nextInt(); boolean flag = true; for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) { if(a[i] == x) { System.out.print(i); flag = false; } } if(flag) { System.out.print(-1); } s.close(); } }
给定两个整型数组A和B,将A的元素复制到B中,使得两个数组完全相同。再将B数组从小到大排列,将两数组的同一位置上对应的元素进行比较,统计出A中大于B的元素个数,等于B中元素的个数,小于B中的元素的个数。 提示:可用Arrays.sort排序
输入格式:
数组A的个数 数组A元素
输出格式:
A大于B的个数 A等于B的个数 A小于B的个数
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
10
23 1 32 87 65 12 21 9 76 45输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4 1 5
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); int[] a = new int [n]; int[] b = new int [n]; for(int i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, a.length); Arrays.sort(b); int n1 = 0; int n2 = 0; int n3 = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { if(a[i] > b[i]) { n1++; } else if(a[i] < b[i]) { n2++; } else if(a[i] == b[i]) { n3++; } } System.out.print(n1+" " + n3+" " + n2 +" "); s.close(); } }
小熊买东西,太便宜的怕质量不好,太贵的买不起。每种东西N个商品(价格可能相同),小熊决定都买第三便宜的东西,输出价格。编写程序,要求:首先输入一个正整数N(N <= 50),接下来输入N个数表示每个商品的价格(价格均是正整数,且小于等于10000)。如果存在第3便宜的商品,则输出这个价格是多少,否则输出-1。
输入格式:
商品的个数N,每个商品的价格
输出格式:
第3便宜的商品的价格
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
10 40 10 10 10 10 20 20 30 30 40输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
30
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { set.add(s.nextInt()); } ArrayList l = new ArrayList(set); if(l.size() >= 3) { System.out.print(l.get(2)); } else { System.out.print(-1); } s.close(); } }
从键盘录入1行包含6个整数(整数可以重复)的字符串,前3个整数和后3个整数分别构成2个集合。编写程序,输出这两个集合的交集中的元素个数。
输入格式:
键盘录入的1行包含6个整数(整数可以重复)的字符串
输出格式:
前3个整数和后3个整数构成的2个集合的交集中的元素个数
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
12 14 22 12 16 22输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); TreeSet<Integer> set1 = new TreeSet<>(); TreeSet<Integer> set2 = new TreeSet<>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { set1.add(s.nextInt()); } for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { set2.add(s.nextInt()); } TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet(set1); set.addAll(set2); // System.out.print(set1); // System.out.print(set2); // System.out.print(set); System.out.print(set1.size()+set2.size()-set.size()); s.close(); } }
读入一个字符串,该字符串表示一个整型二维数组d,数组中的元素通过解析字符串参数获得。例如,字符串参数:“1,2;3,4,5;6,7,8”,对应的数组为: d[0,0] = 1 d[0,1] = 2
d[1,0] = 3 d[1,1] = 4 d[1,2] = 5 d[2,0] = 6 d[2,1] = 7 d[2,2] = 8 打印这个数组各元素的内容
输入格式:
字符串
输出格式:
二维数组各元素
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1,2;3,4,5;6,7,8输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
d[0,0] = 1 d[0,1] = 2 d[1,0] = 3 d[1,1] = 4 d[1,2] = 5 d[2,0] = 6 d[2,1] = 7 d[2,2] = 8
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String S = s.nextLine(); String[] s1 = S.split(";"); int[][] arr = new int [s1.length][]; for(int i = 0 ; i < s1.length ; i++) { String[] s2 = s1[i].split(","); arr[i] = new int [s2.length]; for(int j = 0 ; j < arr[i].length ; j++) { arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(s2[j]); } } for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++) { for(int j = 0 ; j < arr[i].length ; j++) { if(j == 0) { System.out.print("d["+i+","+j+"] = "+arr[i][j]); } else { System.out.print(" "+"d["+i+","+j+"] = "+arr[i][j]); } } System.out.println(); } s.close(); } }
利用二维数组(int[])实现一个矩阵类:Matrix。要求提供以下方法:(1)set(int row, int col, int value):将第row行第col列的元素赋值为value;(2)get(int row,int col):取第row行第col列的元素;(3)width():返回矩阵的列数;(4)height():返回矩阵的行数;(5)Matrix add(Matrix b):返回当前矩阵与矩阵b相加后的矩阵;(6)Matrix multiply(Matrix b):返回当前矩阵与矩阵b相乘后的矩阵。(7)Matrix transpose():返回当前矩阵的转置矩阵;(8)toString():以行和列的形式打印出当前矩阵。
输入格式:
矩阵的行列数 矩阵的数据 设置矩阵值的行、列和值 获取矩阵值的行、列 待相加矩阵的行列数 待相加矩阵的值 待相乘矩阵的行列数 待相乘矩阵的值
输出格式:
矩阵的行、列数 设置矩阵值后的矩阵 某行某列的矩阵值 矩阵相加结果 矩阵相乘结果 矩阵转置结果
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
2 3 8
1 3
3 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
3 2
1 2
1 2
1 2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
row:3 column:3 after set value: 1 2 3 4 5 8 7 8 9 value on (1,3):3 after add: 2 4 6 8 10 14 14 16 18 after multiply: 6 12 17 34 24 48 after transpose: 1 4 7 2 5 8 3 8 9
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Matrix m = new Matrix(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); m.cin(s); System.out.println("row:"+m.height()+" column:"+m.width()); m.set(s.nextInt(), s.nextInt(), s.nextInt()); System.out.println("after set value:"); m.print(); int x = s.nextInt(); int y = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("value on ("+x+","+y+"):"+m.get(x, y)); Matrix m_add = new Matrix(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); m_add.cin(s); System.out.println("after add:"); m.add(m_add).print(); Matrix m_mul = new Matrix(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); m_mul.cin(s); System.out.println("after multiply:"); m.multiply(m_mul).print(); System.out.println("after transpose:"); m.transpose().print(); s.close(); } } class Matrix { public int row; public int col; public int[][] m = new int [row+1][col+1]; public Matrix(int row, int col) { this.row = row; this.col = col; m = new int [row+1][col+1]; } public void cin(Scanner s) { for(int i = 1 ; i <= row ; i++) { for(int j = 1 ; j <= col ; j++) { m[i][j] = s.nextInt(); } } } public void print() { for(int i = 1 ; i <= row ; i++) { for(int j = 1 ; j <= col ; j++) { if(j == 1) { System.out.print(m[i][j]); } else { System.out.print(" "+m[i][j]); } } System.out.println(); } } public void set(int row, int col, int value) { m[row][col] = value; } public int get(int row,int col) { return m[row][col]; } public int width() { return col; } public int height() { return row; } public Matrix add(Matrix b) { Matrix t = new Matrix(this.row , this.col); for(int i = 1 ; i <= row ; i++) { for(int j = 1 ; j <= col ; j++) { t.set(i, j, this.get(i, j)+b.get(i, j)); } } return t; } public Matrix multiply(Matrix b) { Matrix t = new Matrix(this.row , b.col); for(int i = 1 ; i <= this.row ; i++) { for(int j = 1 ; j <= b.col ; j++) { int v = 0; for(int k = 0 ; k <= this.col ; k++) { v += this.get(i, k)*b.get(k, j); } t.set(i, j, v); } } return t; } public Matrix transpose() { Matrix t = new Matrix(this.col , this.row); for(int i = 1 ; i <= row ; i++) { for(int j = 1 ; j <= col ; j++) { t.set(j, i, this.get(i, j)); } } return t; } }
设计一个BankAccount类,这个类包括:
(1)一个int型的balance表时账户余额。
(2)一个无参构造方法,将账户余额初始化为0。
(3)一个带一个参数的构造方法,将账户余额初始化为该输入的参数。
(4)一个getBlance()方法,返回账户余额。
(5)一个withdraw()方法:带一个amount参数,并从账户余额中提取amount指定的款额。
(6)一个deposit()方法:带一个amount参数,并将amount指定的款额存储到该银行账户上。
提供main函数,构造一个账户对象,并对其进行存取款操作。
其中操作类型类型为1表示存款,2表示取款,每次操作后都打印余额
输入格式:
账户余额 操作个数 操作类型 操作金额
输出格式:
每次操作后的余额
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0
4
1 100
1 200
2 100
2 100输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
100 300 200 100
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); BankAccount ba = new BankAccount(s.nextInt()); int n = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int type = s.nextInt(); if(type == 1) { ba.deposit(s.nextInt()); } if(type ==2) { ba.withdraw(s.nextInt()); } System.out.println(ba.getBlance()); } s.close(); } } class BankAccount { public int balance; public BankAccount() { balance = 0; } public BankAccount(int balance) { this.balance = balance; } public int getBlance() { return balance; } public void withdraw(int amount) { if(balance >= amount) { balance -=amount; } } public void deposit(int amount) { balance += amount; } }
构造日期类MyDate类,包含年月日,提供相应的get和set函数,提供void print()函数打印日期,提供int compare(MyDate d)测试当前对象和参数对象d的早晚,如果早则返回-1,晚则返回1,相等则返回0 在main函数中,读入两个日期对象,输出第一个日期对象的信息,输出两个对象的比较结果
输入格式:
两个日期对象,第一个为当前日期对象的年月日,第二个为待比较日期对象的年月日
输出格式:
当前日期对象的信息,当前对象和待比较日期对象的比较结果
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2008 6 12 2009 6 22输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
6/12/2008 -1
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); MyDate md1 = new MyDate(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); MyDate md2 = new MyDate(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); md1.print(); System.out.print(md1.compare(md2)); s.close(); } } class MyDate { public int year; public int month; public int day; public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) { this.year = year; this.month = month; this.day = day; } public void print() { System.out.print(month+"/"+day+"/"+year+" "); } public int compare(MyDate d) { if(this.year < d.year) { return -1; } else if(this.year > d.year) { return 1; } else { if(this.month < d.month) { return -1; } else if(this.month > d.month) { return 1; } else { if(this.day < d.day) { return -1; } else if(this.day > d.day) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } } } }
在Person类的基础上,添加一个静态变量avgAge表示所有Person对象的平均年龄(整数),提供方法getAvgAge能够读取该静态变量。 main函数中,构造三个Person类的对象,读入他们的信息,并输出他们的平均年龄
输入格式:
多个用户信息
输出格式:
平均年龄
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
a male 23
b female 21
c male 22输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
22
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Person[] p = new Person[3]; int aveage = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { p[i] = new Person(s.next(),s.next(),s.nextInt()); aveage = p[i].getAvgAge(); } System.out.print(aveage); s.close(); } } class Person { public String name; public String sex; public int age; public static int sumAge; public Person(String name, String sex, int age) { this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = age; sumAge += this.age; } public static int getAvgAge() { return sumAge/3; } }
给定一个整数N,编写程序求1!+2!+……+N!(0<N<100)
输入格式:
输入一个整数N
输出格式:
输出1!+2!+……+N!
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
873
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); System.out.print(getAddN(n)); s.close(); } public static int getN(int n) { if(n == 1) { return 1; } else { return n*getN(n-1); } } public static int getAddN(int n) { if(n == 1) { return 1; } else { return getN(n)+getAddN(n-1); } } }
一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为"完数"。 例如,6的因子为1、2、3,而6=1+2+3,因此6是"完数"。 编程序找出N之内的所有完数。
输入格式:
整数N
输出格式:
N之内的所有完数,每个完数之间用逗号(英文半角)分隔开。注意:1不作为完数
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
30输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
6,28
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ;i++) { int sum = 0; for(int j = 1 ; j < i ; j++) { if(i%j == 0) { sum += j; } } if(sum == i) { if(sum == 6) { System.out.print(6); } else { System.out.print(","+sum); } } } s.close(); } }
求Sn=a+aa+aaa+…+aa…aaa(有n个a)之值,其中a是一个数字(1<=a<=9)。例如:2+22+222+2222+22222(a=2,n=5),a和n由键盘输入。
输入格式:
a,n(说明:a是出现在各个数字每一位的数字,n是最大数的位数)
输出格式:
Sn=a+aa+aaa+…+aa…aaa的值
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 3输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
246
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int a = s.nextInt(); int n = s.nextInt(); int sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int aa = 0; for(int j = 0 ; j <= i ; j++) { aa += a*Math.pow(10, j); } sum += aa; } System.out.print(sum); s.close(); } }
输入一个长整型的数,统计其中0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9各个数字的个数,并将结果合成一个整数。(前面的0不输出)
输入格式:
长整型数
输出格式:
合成后的整数
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
234353632
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String n = s.next(); int[] a = new int [10]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n.length() ; i++) { int x = n.charAt(i)-'0' ; a[x]++; } boolean flag = false; for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { if(a[i] != 0) flag = true; if(flag) { System.out.print(a[i]); } } s.close(); } }
编写一个类的方法,其输入参数为一个整数,输出为该整数各个位上的最大数字。
输入格式:
输入一个整数N
输出格式:
输出该整数N各个位上的最大数字
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
59274输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
9
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); MaxNum m = new MaxNum(s.nextLong()); System.out.print(m.FoundMax()); s.close(); } } class MaxNum { public long n; public MaxNum(long n) { this.n = n; } public int FoundMax() { int max = 0; while(n != 0) { int x = (int)n%10; n = n/10; if(x > max) { max = x; } } return max; } }
编写代码,要求:输入参数是一个正整数,输出该整数所对应的二进制数对应的字符串。
输入格式:
正整数
输出格式:
输入的正整数对应的二进制字符串“1001”
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
9输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1001
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); System.out.print(Integer.toBinaryString(n)); s.close(); } }
编码实现:输入一个字符串,判断该字符串是否是回文(回文是指将该字符串含有的字符逆序排列后得到的字符串和原字符串相同的字符串)如果是回文,则输出“Yes”;否则输出“No”。
输入格式:
判定是否是回文的字符串
输出格式:
“Yes”或者“No”
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
TooooT输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Yes
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String str = s.next(); boolean flag = true; for(int i = 0,j = str.length()-1 ; i < str.length()&&j >= 0 ; i++,j--) { if(str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(j)) { flag = false; } } if(flag) { System.out.print("Yes"); } else { System.out.print("No"); } s.close(); } }
小白学习了一些复利投资知识,想比较一下复利能多赚多少钱(所谓复利投资,是指每年投资的本金是上一年的本金加收益。而非复利投资是指每年投资金额不包含上一年的收益,即固定投资额)。假设他每年固定投资M元(整数),每年的年收益达到P(0<P<1,double),那么经过N(整数)年后,复利投资比非复利投资多收入多赚多少钱呢?计算过程使用双精度浮点数,最后结果四舍五入输出整数(Math的round函数)。
输入格式:
M P N
输出格式:
复利收入(含本金),非复利收入(含本金),复利比非复利收入多的部分(全部取整,四舍五入)
输入样例:
10000 0.2 3输出样例:
17280 16000 1280
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int m = s.nextInt(); double p = s.nextDouble(); int n = s.nextInt(); double fu = 0; double feifu = 0; fu = m*Math.pow(1+p, n); feifu = m*n*p+m; System.out.print(Math.round(fu)+" "+Math.round(feifu)+" "+Math.round(fu-feifu)); s.close(); } }
编写程序打印出所有的水仙花数。所谓"水仙花数"是指一个三位数,其各位数字立方和等于该本身。例如:153是一个水仙花数,因为153=1^3+5^3+3^3。 输出的数之间用“,”(英文半角的逗号)分割。
输入格式:
无
输出格式:
153,370,371,407
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
153,370,371,407
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print(153); for(int i = 154 ; i < 1000 ; i++) { int a = i%10; int b = i/10%10; int c = i/100%10; if(Math.pow(a, 3) + Math.pow(b, 3) + Math.pow(c, 3) == i) { System.out.print(","+i); } } s.close(); } }
编写程序将整数逆序输出。如输入为9876输出为6789 Main函数中读入n个整数,输出n个整数的逆序数
输入格式:
整数个数n n个整数
输出格式:
n个整数的逆序数
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3
1234
2323
1112输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4321 3232 2111
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { String str = s.next(); for(int j = str.length()-1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { System.out.print(str.charAt(j)); } System.out.println(); } s.close(); } }
假定要为某个公司编写雇员工资支付程序,这个公司有各种类型的雇员(Employee),不同类型的雇员按不同的方式支付工资(都是整数): (1)经理(Manager)——每月获得一份固定的工资 (2)销售人员(Salesman)——在基本工资的基础上每月还有销售提成 (3)一般工人(Worker)——则按他每月工作的天数计算工资 在Employee中提供函数getSalary()计算每个雇员一个月的工资,并在子类中重写。
在main函数中构造Employee的三个变量,分别指向Manager、Salesman、Worker的对象,调用getSalary函数,输出三个对象的工资
输入格式:
经理的月工资 销售人员的基本工资 销售人员的提成 工人的工作天数 工人每天的工资
输出格式:
经理的工资 销售人员的工资 工人的工资
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
12000
3000 5000
22 200输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12000 8000 4400
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Employee e = null; e = new Manager(s.nextInt(),1); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); e = new Salesman(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); e = new Worker(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); s.close(); } } class Employee { int sal; int td; public Employee(int sal, int td) { super(); this.sal = sal; this.td = td; } public int getSalary() { return sal; } } class Manager extends Employee { public Manager(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } } class Salesman extends Employee { public Salesman(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public int getSalary() { return sal+td; } } class Worker extends Employee { public Worker(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public int getSalary() { return sal*td; } }
修改题目7-35的员工类,使得Employee类为抽象类,getSalary()方法是抽象方法
输入格式:
经理的月工资 销售人员的基本工资 销售人员的提成 工人的工作天数 工人每天的工资
输出格式:
经理的工资 销售人员的工资 工人的工资
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
12000
3000 5000
22 200输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12000
8000
4400import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Employee e = null; e = new Manager(s.nextInt(),1); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); e = new Salesman(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); e = new Worker(s.nextInt(),s.nextInt()); System.out.println(e.getSalary()); s.close(); } } abstract class Employee { int sal; int td; public Employee(int sal, int td) { super(); this.sal = sal; this.td = td; } abstract public int getSalary(); } class Manager extends Employee { public Manager(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public int getSalary() { return sal; } } class Salesman extends Employee { public Salesman(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); } @Override public int getSalary() { return sal+td; } } class Worker extends Employee { public Worker(int sal, int td) { super(sal, td); } @Override public int getSalary() { return sal*td; } }
定义一个形状类Shape,提供计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea()的函数 定义一个子类正方形类Square继承自Shape类,拥有边长属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea() 定义一个子类长方形类Rectangle继承自Square类,拥有长、宽属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea() 定义一个子类圆形类Circle继承自Shape,拥有半径属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea()
在main函数中,分别构造三个Shape类的变量,分别指向一个Square、Rectangle、Circle对象,并输出他们的周长、面积.
输入格式:
正方形类的边长 长方形类的长宽 圆类的半径
输出格式:
正方形的周长、面积 长方形的周长、面积 圆形的周长、面积
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
1 2
2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4.00 1.00
6.00 2.00
12.57 12.57import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Shape shape = null; shape = new Square(s.nextDouble(),1); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); shape = new Rectangle(s.nextDouble(),s.nextDouble()); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); shape = new Circle(s.nextDouble(),1); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); s.close(); } } class Shape { public double a; public double b; public Shape(double a, double b) { super(); this.a = a; this.b = b; } public double getPerimeter() { return a*4; } public double getArea() { return a*a; } } class Square extends Shape { public Square(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } } class Rectangle extends Square { public Rectangle(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*a+2*b; } public double getArea() { return a*b; } } class Circle extends Shape { public Circle(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*3.14259*a; } public double getArea() { return 3.14159*a*a; } }
修改题目133,将Shape类改为抽象类
输入格式:
正方形类的边长 长方形类的长宽 圆类的半径
输出格式:
正方形的周长、面积 长方形的周长、面积 圆形的周长、面积
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
1 2
2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4.00 1.00
6.00 2.00
12.57 12.57import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Shape shape = null; shape = new Square(s.nextDouble(),1); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); shape = new Rectangle(s.nextDouble(),s.nextDouble()); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); shape = new Circle(s.nextDouble(),1); System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", shape.getPerimeter())+" "+String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea())); s.close(); } } abstract class Shape { public double a; public double b; public Shape(double a, double b) { super(); this.a = a; this.b = b; } public double getPerimeter() { return a*4; } public double getArea() { return a*a; } } class Square extends Shape { public Square(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } } class Rectangle extends Square { public Rectangle(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*a+2*b; } public double getArea() { return a*b; } } class Circle extends Shape { public Circle(double a, double b) { super(a, b); } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*3.14259*a; } public double getArea() { return 3.14159*a*a; } }
修改函数题6-33(学生类-本科生类-研究生类) 为学生类添加属性成绩,添加相应的get和set函数,添加函数getGrade()表示获得等级,该函数应当为抽象函数。 本科生和研究生的等级计算方式不同,如下所示
本科生标准 研究生标准 [80--100) A [90--100) A [70--80) B [80--90) B [60--70) C [70--80) C [50--60) D [60--70) D 50 以下 E 60 以下 E
main函数中构造两个学生Student变量,分别指向本科生和研究生对象,调用getGrade()方法输出等级
输入格式:
本科生类信息,学号、姓名、性别、专业、成绩 研究生类信息,学号、姓名、性别、专业、导师、成绩
输出格式:
本科生等级 研究生等级
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 chen female cs 90
3 li male sc wang 80输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
A
Bimport java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Student st = null; int no = s.nextInt(); String name = s.next(); String sex = s.next(); String major = s.next(); int grade = s.nextInt(); String supervisor = null; st = new CollegeStudent(no,name,sex,grade,major); System.out.println(st.getGrade()); no = s.nextInt(); name = s.next(); sex = s.next(); major = s.next(); supervisor = s.next(); grade = s.nextInt(); st = new GraduateStudent(no,name,sex,grade,major,supervisor); System.out.println(st.getGrade()); s.close(); } } /* 你的代码被嵌在这里*/ class Student { public int no; public String name; public String sex; public int grade; public Student(int no, String name, String sex, int grade) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.grade = grade; } public void setGrade(int grade) { this.grade = grade; } public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public void attendClass(String className) { } public void print() { System.out.println("no: "+this.no+" "+ "name: "+this.name+" "+ "sex: "+this.sex); } // ben // [80--100) A // [70--80) B // [60--70) C // [50--60) D // 50 以下 E public String getGrade() { int x = this.grade; if(x>= 80 ) return "A"; if(x >= 70 && x < 80) return "B"; if(x >= 60 && x < 70) return "C"; if(x >= 50 && x < 60) return "D"; else return "E"; } } class CollegeStudent extends Student { public String major; public CollegeStudent(int no, String name, String sex, int grade, String major) { super(no, name, sex, grade); this.major = major; } public String getMajor() { return major; } public void setMajor(String major) { this.major = major; } @Override public void print() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.print(); System.out.println("major: "+this.major); } @Override public String getGrade() { return super.getGrade(); } } class GraduateStudent extends CollegeStudent { public String supervisor; public GraduateStudent(int no, String name, String sex, int grade, String major, String supervisor) { super(no, name, sex, grade, major); this.supervisor = supervisor; } public String getSupervisor() { return supervisor; } public void setSupervisor(String supervisor) { this.supervisor = supervisor; } public void doResearch() { System.out.println(this.name + " is doing research"); } @Override public void print() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.print(); System.out.println("supervisor: "+this.supervisor); } // yanjiu // [90--100) A // [80--90) B // [70--80) C // [60--70) D // 60 以下 E public String getGrade() { int x = this.grade; if(x>= 90 ) return "A"; if(x >= 80 && x < 90) return "B"; if(x >= 70 && x < 80) return "C"; if(x >= 60 && x < 70) return "D"; else return "E"; } }
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Student stu1 = new CollegeStudent(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.next(),s.next(),s.nextInt()); Student stu2 = new GraduateStudent(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.next(),s.next(),s.next(),s.nextInt()); System.out.println(stu1.getGrade()); System.out.println(stu2.getGrade()); s.close(); } } abstract /* 你的代码被嵌在这里*/ class Student { public int no; public String name; public String sex; public Student(int no, String name, String sex) { this.no = no; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } abstract public String getGrade(); } class CollegeStudent extends Student { public String major; public int score; public CollegeStudent(int no, String name, String sex, String major,int score) { super(no, name, sex); this.major = major; this.score = score; } @Override public String getGrade() { if(score >= 80) { return "A"; } else if(score >= 70) { return "B"; } else if(score >= 60) { return "C"; } else if(score >= 50) { return "D"; } else { return "E"; } } } class GraduateStudent extends Student { public String major; public String supervisor ; public int score; public GraduateStudent(int no, String name, String sex, String major, String supervisor,int score) { super(no, name, sex); this.major = major; this.supervisor = supervisor; this.score = score; } public String getGrade() { if(score >= 90) { return "A"; } else if(score >= 80) { return "B"; } else if(score >= 70) { return "C"; } else if(score >= 60) { return "D"; } else { return "E"; } } }
电动汽车的电池必须周期性地进行充电,每次充电若干小时,充电过程不能被中断。充电费用基于充电的起止时间决定,费用表列出了一天内各个小时(0-23)的充电费率。每天使用的充电费率表相同,每小时费率是正整数。一个充电费率表示例如下图所示
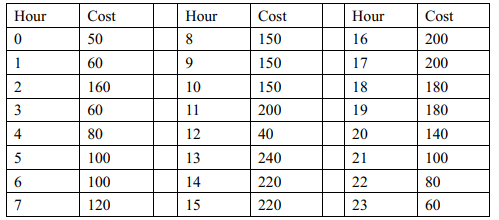
类BatteryCharger使用费率表来决定最经济的充电方式。该类包含如下两个公有方法:
int getChargeCost(int startHour, int chargeTime) 该方法返回从开始时间经过一定的充电时长的全部充电费用。
int getChargeStartTime(int chargeTime),该函数返回给定充电时长后能使充电费用最小的起始时间。如果存在多个可能的起始时间能产生最少的费用,返回较早(较小)的一个时间。
请写出BatteryCharge类。
在main函数中首先读入24个整数代表每个小时的费用,而后调用getChargeCost,读入两个参数startHour和chargeTime,输出总的费用;而后调用getChargeStartTime,读入充电时间chargeTime,输出费用最少的起始时间。
输入格式:
每小时费用 开始时间和充电时间 充电时间
输出格式:
总的费用 最小费用的起始时间
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
50 60 160 60 80 100 100 120 150 150 150 200 40 240 220 220 200 200 180 180 140 100 80 60
0 2
7输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
110
22import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int[] a = new int [24]; for(int i = 0 ; i < 24 ; i++) { a[i] = s.nextInt(); } BatteryCharger bc = new BatteryCharger(a); System.out.println(bc.getChargeCost(s.nextInt(), s.nextInt())); System.out.print(bc.getChargeStartTime(s.nextInt())); s.close(); } } class BatteryCharger { int [] a = new int [24]; public BatteryCharger(int[] a) { this.a = a; } public int getChargeCost(int startHour, int chargeTime) { int fee = 0; for(int i = startHour ; i < startHour+chargeTime ; i++) { fee += a[i%24]; } return fee; } public int getChargeStartTime(int chargeTime) { int flag = 0; int fee = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < chargeTime ; i++) { fee += a[i%24]; } for(int i = 0 ; i < 24 ; i++) { int fee1 = 0; for(int j = i ; j < i + chargeTime ; j++) { fee1 += a[j%24]; } if(fee1 < fee) { fee = fee1; flag = i; } } return flag; } }
Arrays.sort可以对所有实现Comparable的对象进行排序。但如果有多种排序需求,如有时候需对name进行降序排序,有时候只需要对年龄进行排序。使用Comparable无法满足这样的需求。可以编写不同的Comparator来满足多样的排序需求。
#1.编写PersonSortable2类 属性:private name(String)、private age(int)
有参构造函数:参数为name,age
toString方法:返回格式name-age
#2 编写Comparator类
- 编写
NameComparator类,实现对name进行升序排序 - 编写
AgeComparator类,对age进行升序排序
#3.main方法中
- 输入n
- 输入n行name age,并创建n个对象放入数组
- 对数组按照name进行升序排序后输出。
- 在3的基础上对数组按照age进行升序排序后输出。
- 最后最后两行使用如下代码输出NameComparator与AgeComparator所实现的所有接口。
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(NameComparator.class.getInterfaces()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(AgeComparator.class.getInterfaces()));
输入样例:
5
zhang 15
zhang 12
wang 14
Wang 17
li 17
输出样例:
NameComparator:sort
Wang-17
li-17
wang-14
zhang-15
zhang-12
AgeComparator:sort
zhang-12
wang-14
zhang-15
Wang-17
li-17
//最后两行是标识信息import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); PersonSortable2 p [] = new PersonSortable2[n]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { p[i] = new PersonSortable2(s.next(),s.nextInt()); } System.out.println("NameComparator:sort"); Arrays.sort(p,new NameComparator()); for(int i = 0 ; i < p.length ; i++) { System.out.println(p[i]); } System.out.println("AgeComparator:sort"); Arrays.sort(p,new AgeComparator()); for(int i = 0 ; i < p.length ; i++) { System.out.println(p[i]); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(NameComparator.class.getInterfaces())); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(AgeComparator.class.getInterfaces())); s.close(); } } class PersonSortable2 { private String name; private int age; public PersonSortable2() { super(); } public PersonSortable2(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return name+"-"+age; } } class NameComparator implements Comparator<PersonSortable2> { @Override public int compare(PersonSortable2 o1, PersonSortable2 o2) { if(o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName())>0) { return 1; } else if(o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName())<0) { return -1; } else { return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()); } } } class AgeComparator implements Comparator<PersonSortable2> { @Override public int compare(PersonSortable2 o1, PersonSortable2 o2) { if(o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()) { return 1; } else if(o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()) { return -1; } else { return 1; } } }
从键盘录入表示矩形个数的数字n,然后录入n个矩形的长和宽,然后对这n个矩形按照面积从大到小排序,并输出排序后的每个矩形的面积。要求:请设计Rectangle类,包含相应的构造函数和成员函数,实现Comparable接口
输入描述:
矩形个数,每个矩形的长和宽
输出描述:
由大到小排序的每个矩形的面积
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*你的代码被嵌在这里*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//输入矩形个数
int num_rectangle = scan.nextInt();
Rectangle[] recs = new Rectangle[num_rectangle];
//输入每个矩形的长和宽
for(int i=0;i<num_rectangle;i++){
int length = scan.nextInt();
int width = scan.nextInt();
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(length,width);
recs[i] = rec;
}
//按照面积由大到小排序
Arrays.sort(recs);
//打印前n-1个矩形的面积
for(int i=0;i<recs.length-1;i++){
System.out.print(recs[i].getArea()+",");
}
//打印最后一个矩形的面积
System.out.print(recs[recs.length-1].getArea());
scan.close();
}
}输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 1 2 3 4 2 3输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12,6,2import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; class Rectangle implements Comparable<Rectangle> { public int length; public int width; public Rectangle(int length, int width) { this.length = length; this.width = width; } public int getArea() { return length*width; } @Override public int compareTo(Rectangle o) { if(this.getArea() > o.getArea()) { return -1; } else if(this.getArea() < o.getArea()) { return 1; } return 0; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); //输入矩形个数 int num_rectangle = scan.nextInt(); Rectangle[] recs = new Rectangle[num_rectangle]; //输入每个矩形的长和宽 for(int i=0;i<num_rectangle;i++){ int length = scan.nextInt(); int width = scan.nextInt(); Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(length,width); recs[i] = rec; } //按照面积由大到小排序 Arrays.sort(recs); //打印前n-1个矩形的面积 for(int i=0;i<recs.length-1;i++){ System.out.print(recs[i].getArea()+","); } //打印最后一个矩形的面积 System.out.print(recs[recs.length-1].getArea()); scan.close(); } }
Comparator 对应 public int compare(Type o1, Type o2) {}是给专门用来比较的类AgeComparator用的,main函数中用Arrays.sort(对象数组名,new 比较器类名())
Comparable对应 public int compareTo(Type o) {} 是在非比较器类中把this对象和另一个对象比较,main函数中用Arrays.sort(对象数组名)排序
某大型家电企业拥有一批送货卡车,运送电视机、洗衣机、空调等家电。编程计算每个卡车所装载货物的总重量。要求有一个Appliance(家电)接口和有三个实现类TV、WashMachine和AirConditioner,这些类能够提供自重。有一个Truck类,包含了该货车上的所有家电,用一个集合(数组或集合类)表示。 Main函数中程序能够输出Truck类所装载货物的总重量。
输入格式:
家电数量 家电种类编号 家电重量
注意:各个家电的编号为:TV:1 WashMachine:2 AirConditioner:3
输出格式:
总重量
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
1 20
2 30
3 25
3 30
2 40输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
145import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); // TV:1 // WashMachine:2 // AirConditioner:3 int n = s.nextInt(); Truck[] a = new Truck[n]; int sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int type = s.nextInt(); if(type == 1) { a[i] = new TV(s.nextInt()); } if(type == 2) { a[i] = new WashMachine(s.nextInt()); } if(type == 3) { a[i] = new AirConditioner(s.nextInt()); } sum += a[i].getW(); } System.out.print(sum); s.close(); } } class TV extends Truck { public TV(int w) { super(w); } } class WashMachine extends Truck { public WashMachine(int w) { super(w); } } class AirConditioner extends Truck { public AirConditioner(int w) { super(w); } } class Truck { public int w; public Truck(int w) { super(); this.w = w; } public int getW() { return w; } public void setW(int w) { this.w = w; } }
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); int sum = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int type = s.nextInt(); int x = s.nextInt(); sum+=x; } System.out.print(sum); s.close(); } }
利用模板方法来构造相关类实现下述过程: 各种球类的玩法虽然不同,但是球类比赛的过程是类似的,都包含如下几个步骤: 1球员报道-->2比赛开始-->3比赛-->4比赛结束-->5公布比赛成绩,且其中1 2 4步相同 第3步根据球类不同,玩法不同,第5步根据得分不同,公布方式结果不同 构造类BallMatch表示球类比赛,包含方法compete表示真个比赛过程 构造各个比赛过程的函数checkin,start,play,end,annouceResult 打印信息如下: now checking in now starting now playing football now ending now annoucing result: 2-3 构造类FootballMatch和BasketBallMatch,实现具体的比赛过程。
在main函数中,读入整数i,如果为1,则构造一个足球比赛过程,如果为2则构造一个篮球比赛过程 打印比赛过程
输入格式:
比赛类型 比分
输出格式:
比赛过程信息
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 2-3输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
now checking in
now starting
now playing football
now ending
now annoucing result: 2-3import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); BallMatch bc = null; int type = s.nextInt(); if(type == 1) { bc = new FootballMatch(s.next()); } if(type == 2) { bc = new BasketBallMatch(s.next()); } bc.checkin(); bc.start(); bc.play(); bc.end(); bc.annouceResult(); s.close(); } } class BallMatch { String str; public BallMatch(String str) { super(); this.str = str; } void checkin() { System.out.println("now checking in"); } void start() { System.out.println("now starting"); } void play() {} void end() { System.out.println("now ending"); } void annouceResult() { System.out.println("now annoucing result: "+str); } } class FootballMatch extends BallMatch { public FootballMatch(String str) { super(str); } void play() { System.out.println("now playing football"); } } class BasketBallMatch extends BallMatch { public BasketBallMatch(String str) { super(str); } void play() { System.out.println("now playing basketball"); } }
设计一个教师类Teacher,要求: 属性有编号(int no)、姓名(String name)、年龄(int age)、所属学院(String seminary),为这些属性设置相应的get和set方法。 为Teacher类重写equals方法,要求:当两个教师对象的no相同时返回true。 重写Teacher类的toString方法,通过该方法可以返回“no: , name:, age: **, seminary: **”形式的字符串。
输入格式:
两个教师对象的编号,姓名,年龄,学院
输出格式:
教师的信息 两个教师是否相等
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 Linda 38 SoftwareEngineering
2 Mindy 27 ComputerScience输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no: 1, name:Linda, age: 38, seminary: SoftwareEngineering
no: 2, name:Mindy, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScience
false
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Teacher t1 = new Teacher(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next()); Teacher t2 = new Teacher(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next()); System.out.println(t1.toString()); System.out.println(t2.toString()); System.out.println(t1.equals(t2)); s.close(); } } class Teacher { public int no; public String name; public int age; public String seminary; public Teacher(int no, String name, int age, String seminary) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.seminary = seminary; } public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getSeminary() { return seminary; } public void setSeminary(String seminary) { this.seminary = seminary; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { Teacher t = (Teacher)obj; if(this.no == t.no) { return true; } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return "no: "+no+ ", name:"+name+ ", age: "+age+ ", seminary: "+seminary; } }
设计一个教师类Teacher,要求: 属性有编号(int no)、姓名(String name)、年龄(int age)、所属学院(String seminary),为这些属性设置相应的get和set方法。 为Teacher类重写equals方法,要求:当两个教师对象的no相同时返回true。 重写Teacher类的toString方法,通过该方法可以返回“no: , name:, age: **, seminary: **”形式的字符串。
输入格式:
两个教师对象的编号,姓名,年龄,学院
输出格式:
教师的信息 两个教师是否相等
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 Linda 38 SoftwareEngineering
2 Mindy 27 ComputerScience输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no: 1, name:Linda, age: 38, seminary: SoftwareEngineering
no: 2, name:Mindy, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScience
falseimport java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Teacher t1 = new Teacher(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next()); Teacher t2 = new Teacher(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next()); System.out.println(t1.toString()); System.out.println(t2.toString()); System.out.println(t1.equals(t2)); s.close(); } } class Teacher { public int no; public String name; public int age; public String seminary; public Teacher(int no, String name, int age, String seminary) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.seminary = seminary; } public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getSeminary() { return seminary; } public void setSeminary(String seminary) { this.seminary = seminary; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { Teacher t = (Teacher)obj; if(this.no == t.no) { return true; } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return "no: "+no+ ", name:"+name+ ", age: "+age+ ", seminary: "+seminary; } }
修改题目143
- 修改教师类,使得由多个Teacher对象所形成的数组可以排序(编号由低到高排序),并在main函数中使用Arrays.sort(Object[] a)方法排序
- 定义一个类TeacherManagement,包含教师数组,提供方法add(Teacher[]),使其可以添加教师,提供重载方法search,方法可以在一组给定的教师中,根据姓名或年龄返回等于指定姓名或年龄的教师的字符串信息,信息格式为:“no: , name:, age: **, seminary: **”。如果没有满足条件的教师,则返回“no such teacher”。
输入格式:
教师个数 教师信息 待查找教师的姓名 待查找教师的年龄
输出格式:
排序后的信息 按姓名查找的老师信息 按年龄查找的老师信息
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
3 Linda 38 SoftwareEngineering
1 Mindy 27 ComputerScience
4 Cindy 28 SoftwareEngineering
2 Melody 27 ComputerScience
Cindy
27输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no: 1, name: Mindy, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScience
no: 2, name: Melody, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScience
no: 3, name: Linda, age: 38, seminary: SoftwareEngineering
no: 4, name: Cindy, age: 28, seminary: SoftwareEngineering
search by name:
no: 4, name: Cindy, age: 28, seminary: SoftwareEngineering
search by age:
no: 1, name: Mindy, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScience
no: 2, name: Melody, age: 27, seminary: ComputerScienceimport java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); TeacherManagement tm = new TeacherManagement(n); Teacher[] t = new Teacher[n]; for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { t[i] = new Teacher(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next()); tm.add(t[i]); } Arrays.sort(t); for(Teacher tt : t) { System.out.println(tt.toString()); } tm.searchByName(s.next()); tm.searchByAge(s.nextInt()); s.close(); } } class Teacher implements Comparable<Teacher> { public int no; public String name; public int age; public String seminary; public Teacher(int no, String name, int age, String seminary) { this.no = no; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.seminary = seminary; } @Override public String toString() { return "no: "+no+ ", name: "+name+ ", age: "+age+ ", seminary: "+seminary; } @Override public int compareTo(Teacher o) { if(this.no > o.no) { return 1; } if(this.no < o.no) { return -1; } return 0; } // @Override // public boolean equals(Object obj) // { // return super.equals(obj); // } } class TeacherManagement { public int n = 0; Teacher[] t ; public TeacherManagement(int n) { t = new Teacher[n]; } public void add(Teacher t) { this.t[n] = t; n++; } public void searchByName(String name) { System.out.println("search by name:"); int flag = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if(t[i].name.equals(name)) { System.out.println(t[i].toString()); flag = 1; } } if(flag == 0) { System.out.println("no such teacher"); } } public void searchByAge(int age) { System.out.println("search by age:"); int flag = 0; for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if(t[i].age == age) { System.out.println(t[i].toString()); flag = 1; } } if(flag == 0) { System.out.println("no such teacher"); } } }
编写学生类,包含学号no、姓名name、成绩score,提供必要的构造函数、toString函数和equals/hashcode函数,其中,toString函数的格式为“no:xxx name:xxx score:xxx”,no参与equals和hashcode的计算 在main函数中构造一个容器存放学生对象 从命令行输入多个学生对象,存入容器中 从命令行中读入在容器上的操作,具体操作包含: add 添加一个学生(包含学号和学生姓名) delete 删除一个学生(包含学号) set 修改一个学生信息(只修改某学号学生的成绩) 完成操作后按学生的学号从小到大的顺序输出容器中的学生
输入格式:
学生个数 学生对象数据 操作数 操作内容
输出格式:
列表顺序输出集合中的学生
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
1 wong 90
2 liu 80
3 chen 70
4 fang 60
3
add 5 duan 80
delete 3
set 4 70输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no:1 name:wong score:90
no:2 name:liu score:80
no:4 name:fang score:70
no:5 name:duan score:80import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); Map<Integer,Student> map = new HashMap<Integer, Student>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int no = s.nextInt(); map.put(no, new Student(no,s.next(),s.nextInt())); } int x = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < x ; i++) { String str = s.next(); if(str.equals("add")) { int no = s.nextInt(); map.put(no, new Student(no, s.next(), s.nextInt())); } if(str.equals("delete")) { map.remove(s.nextInt()); } if(str.equals("set")) { map.get(s.nextInt()).score = s.nextInt(); } } for(Integer i : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(map.get(i).toString()); } s.close(); } } class Student { public int no; public String name; public int score; public Student(int no, String name, int score) { this.no = no; this.name = name; this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "no:"+no+" name:"+name+" score:"+score; } }
在office软件(word,excel)中,有时只需要打印整个文档中的一部分,就需要用户选择需要打印的页码范围。目前输入的页码范围格式定义为:以逗号分割,可以使用-表示连续页码。例如:1,3,5-9,20。表示需要打印的页码为1,3,5,6,7,8,9,20。
本题目要求读入一行字符串,作为需要打印的页码范围。需要注意以下几点:
- 1、页码范围输入可以不按顺序。例如:5,3,7,9-10,1-2;
- 2、连续的页码定义也可能不会按照由小到大的顺序输入。例如:1,9,5,20-15,10;
- 3、输入的页码范围可能会有重复。例如:1,9,15,5-10,12-20;
输入格式:
第一行:表示页码范围的格式化字符串
输出格式:
将需要打印的页码按照由小到大的顺序输出,以空格分割
输入样例:
1,3,5-9,20输出样例:
1 3 5 6 7 8 9 20输入样例:
12-20,1,15,9,5-10输出样例:
1 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String str = s.nextLine(); String[] s1 = str.split(","); TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<Integer>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < s1.length ; i++) { if(s1[i].contains("-")) { String[] s2 = new String[2]; s2 = s1[i].split("-"); int a = Integer.parseInt(s2[0]); int b = Integer.parseInt(s2[1]); if(a > b) { for(int j = b ; j <= a ; j++) { set.add(j); } } else { for(int j = a ; j <= b ; j++) { set.add(j); } } } else { set.add(Integer.parseInt(s1[i])); } } ArrayList l = new ArrayList(set); for(int i = 0 ; i < l.size() ; i++) { if(i == 0) { System.out.print(l.get(i)); } else { System.out.print(" "+l.get(i)); } } s.close(); } }
从键盘接收N个英文字符串(其中不同的字符串数量大于10),从头开始取5个不同的字符串放入一个集合S1,然后接着取5个不同的字符串放入另一个集合S2,按照字母顺序输出S1和S2的并集中的每个字符串(字符串区分大小写)
输入格式:
一行以空格分开的英文字符串(不同的字符串数量大于10)。
输出格式:
按照字母顺序(先比较字符串首字母,首字母相同的比较字符串第二个字母,以此类推)输出的S1和S2并集的字符串。
输入样例:
android python java javaee javase database java jsp servlet java algorithm junit输出样例:
algorithm
android
database
java
javaee
javase
jsp
python
servletimport java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String str = s.nextLine(); String[] s1 = str.split(" "); TreeSet set1 = new TreeSet<>(); TreeSet set2 = new TreeSet<>(); int i = 0; for(i = 0 ; set1.size() < 5 && i < s1.length ; i++) { set1.add(s1[i]); } for(; set2.size() < 5 && i < s1.length ; i++) { set2.add(s1[i]); } TreeSet set3 = new TreeSet<>(); set3.addAll(set1); set3.addAll(set2); List l = new ArrayList(set3); for(int j = 0 ; j < l.size() ; j++) { System.out.println(l.get(j)); } s.close(); } }
编写学生类,包含学号no、姓名name、成绩score,提供必要的构造函数、toString函数和equals/hashcode函数,其中,toString函数的格式为“no:xxx name:xxx score:xxx”,no参与equals和hashcode的计算 在main函数中构造一个Map容器存放学生对象 从命令行输入多个学生对象,存入Map中,其中key为学号,value为学生对象。 从命令行中读入在学生集合上的操作,具体操作包含: add 添加一个学生(包含学号和学生姓名) delete 删除一个学生(包含学号) set 修改一个学生信息(只修改某学号学生的成绩) 完成操作后按学生的学号从小到大的顺序输出所有学生的信息 输出时按照学生的学号顺序输出
输入格式:
学生个数 学生对象数据 操作数 操作内容
输出格式:
按照学号顺序输出集合中的学生
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
1 wong 90
2 liu 80
3 chen 70
4 fang 60
3
add 5 duan 80
delete 3
set 4 70输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no:1 name:wong score:90
no:2 name:liu score:80
no:4 name:fang score:70
no:5 name:duan score:80import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); Map<Integer, Student> map = new HashMap<Integer, Student>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { int no = s.nextInt(); map.put(no, new Student(no,s.next(),s.nextInt())); } int m = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) { String str = s.next(); if(str.equals("add")) { int no = s.nextInt(); map.put(no, new Student(no,s.next(),s.nextInt())); } if(str.equals("delete")) { map.remove(s.nextInt()); } if(str.equals("set")) { map.get(s.nextInt()).setScore(s.nextInt()); } } for(Integer i : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(map.get(i)); } s.close(); } } class Student { public int no; public String name; public int score; public Student(int no, String name, int score) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "no:"+no+" name:"+name+" score:"+score; } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; } }
编写学生类,包含学号no、姓名name、成绩score,提供必要的构造函数、toString函数和equals/hashcode函数,其中,toString函数的格式为“no:xxx name:xxx score:xxx”,no参与equals和hashcode的计算 在main函数中构造一个学生列表对象(List),用于存放多个学生对象 从命令行输入多个学生对象,存入列表中 从命令行中读入在列表对象上的操作,具体操作包含: add 添加一个学生(包含学号和学生姓名) delete 删除一个学生(包含学号) set 修改一个学生信息(只修改某学号学生的成绩) 完成操作后按列表的位置顺序输出列表中的学生
输入格式:
学生个数 学生对象数据 操作数 操作内容
输出格式:
列表顺序输出集合中的学生
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4
1 wong 90
2 liu 80
3 chen 70
4 fang 60
3
add 5 duan 80
delete 3
set 4 70输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no:1 name:wong score:90
no:2 name:liu score:80
no:4 name:fang score:70
no:5 name:duan score:80import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int n = s.nextInt(); ArrayList<Student> l = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { l.add(new Student(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt())); } int x = s.nextInt(); for(int i = 0 ; i < x ; i++) { String str = s.next(); if(str.equals("add")) { l.add(new Student(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt())); } if(str.equals("delete")) { int delno = s.nextInt(); for(int j = 0 ; j < l.size() ; j++) { if(l.get(j).no == delno) { l.remove(j); } } } if(str.equals("set")) { int setlno = s.nextInt(); for(int j = 0 ; j < l.size() ; j++) { if(l.get(j).no == setlno) { l.get(j).score = s.nextInt(); } } } } for(int i = 0 ; i < l.size() ; i++) { System.out.println(l.get(i)); } s.close(); } } class Student { public int no; public String name; public int score; public Student(int no, String name, int score) { this.no = no; this.name = name; this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "no:"+no+" name:"+name+" score:"+score; } }
镜像字符串是两个字符序列完全相反的字符串。从键盘录入两个不包含空格的字符串,判断第二个是否为第一个的镜像字符串,是则输出yes,否则输出no.
输入格式:
键盘录入的由一个空格分隔的两个字符串
输出格式:
yes(no)
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
abc cba输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
yes