前言
为了更加熟悉BeanShell,所以用几个实例来记录说明下,不同的Json格式是怎么提取相应字段和判断断言的。(会持续更新...)
一、第一种Json格式
1、Json响应数据内容如下:
{
"msg":"success",
"code":"0",
"info":{
"list":[
{
"id":13628,
"materialColor":"浅粉",
"addOrderTime":"2020-11-26 20:11:09",
"unit":"米"
},
{
"id":13629,
"materialColor":"浅粉",
"addOrderTime":"2020-11-26 20:11:09",
"unit":"米"
}
],
"pageCount":50,
"recordCount":5425
}
}
2、按要求进行提取和断言
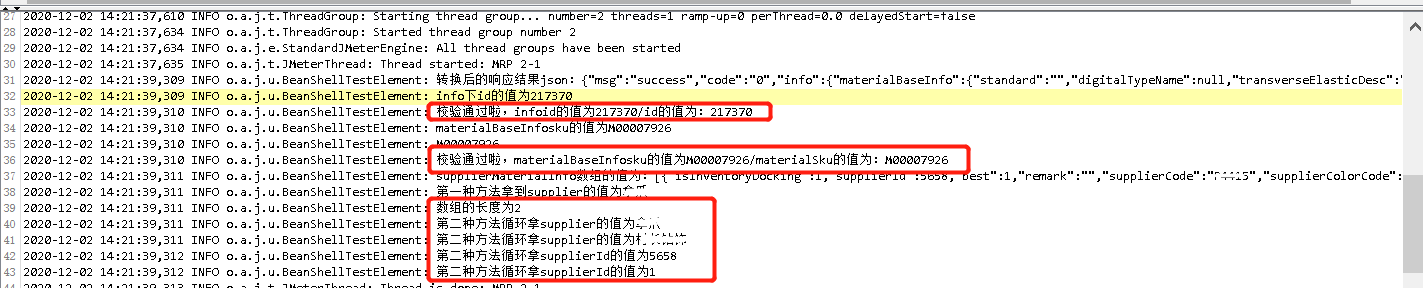
Case1:要求分别提取出msg,code,list,recordCount的值,并且断言recordCount与另一个接口返回的num是否一致,具体写法如下:
//Case1:检查返回的recordCount是否等于前一个接口提取的的num //导入json的包 import org.json.*; //获取响应结果,并转换为json String response=prev.getResponseDataAsString(); JSONObject responseJson=new JSONObject(response); log.info("转换后的响应结果json:"+ responseJson); //获取msg,code,是字符串型,所以用getString String message = responseJson.getString("msg"); String code = responseJson.getString("code"); log.info("msg的值为:"+message+"---code的值为:"+code); //获取list,因为是数组,所以要用JSONArray JSONArray list = responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getJSONArray("list"); log.info("list数组的值为:"+list); //获取recordCount:因为recordCount是数值型,所以用getInt int recordCount = responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getInt("recordCount"); log.info("recordCount的值为:"+ recordCount); //判断返回的recordCount是否等于tab的num,num是前面接口提取出的变量,在这里可以直接用${num}引用,或者用vars.get("num")也行 if(recordCount == ${num}){ Failure=false; log.info("比对结果为:"+recordCount+"="+ ${num}); } else{ Failure=true; FailureMessage="recordCount不等于tab的num,请检查"; log.info(FailureMessage); }
log.info(),是打印日志到控制台里,如下图:(在Options/Log Viewer,可以调出日志控制台)
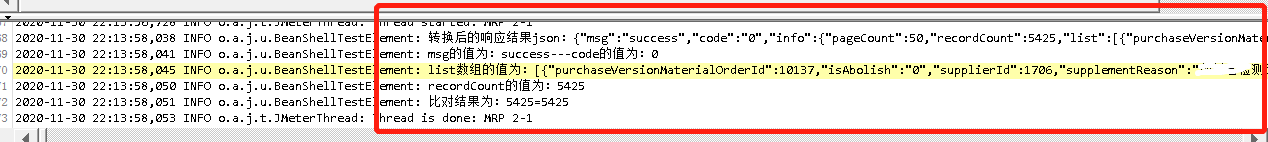
Case2:要求提取list数组里的addOrderTime,并且断言是否在另一个接口入参的时间范围内(addOrderTimeStart - addOrderTimeEnd),具体写法如下:
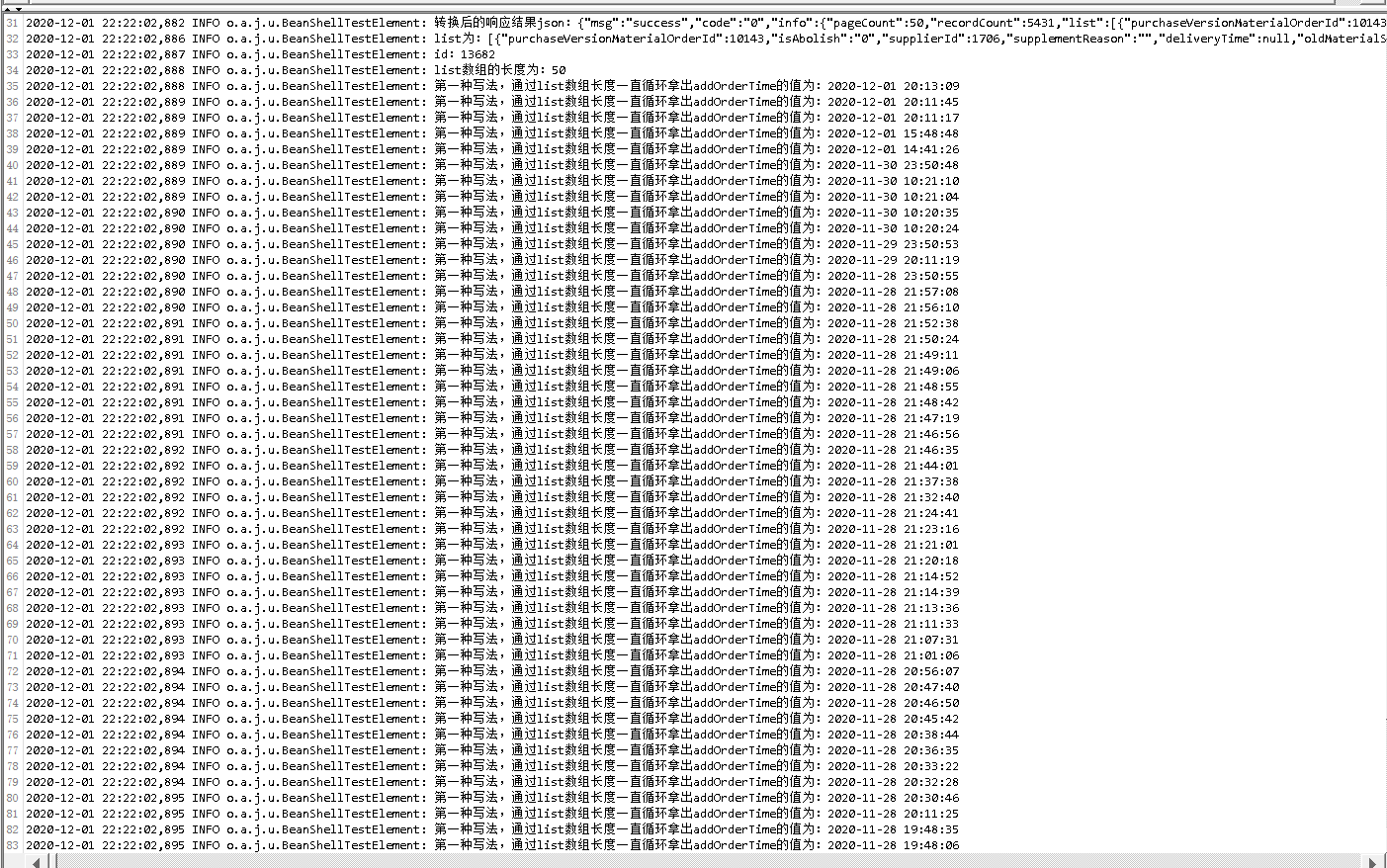
//Case2:检查返回数据的下单时间是否在检索条件内 //导入json的包 import org.json.*; //导入 时间在转换成Date类型时要用到的方法 import java.util.Date; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; //为了变量能在全局使用,所以在try{}和for{}外面先声明变量 String addOrderTime; String addOrderTime1; try { //获取响应结果,并转换为json String response=prev.getResponseDataAsString(); JSONObject responseJson=new JSONObject(response); log.info("转换后的响应结果json:"+ responseJson); //获取list里第[1]个数组对象的id值:这个与本次断言无关 JSONArray list=responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getJSONArray("list"); log.info("list为:"+ list); JSONObject jsonTemp = list.getJSONObject(1); String id = jsonTemp.get("id").toString(); log.info("id:"+id); //获取list数组的长度 int len = list.length(); String strlen = Integer.toString(len); log.info("list数组的长度为:"+strlen); //拿到list数组长度后,用for循环输出addOrderTime的值 int i ; for(i=0 ;i < len;++i) { //获取 list[ i ] 数组对象; JSONObject jsonTemp = list.getJSONObject(i); addOrderTime = jsonTemp.get("addOrderTime").toString(); log.info("第一种写法,通过list数组长度一直循环拿出addOrderTime的值为:"+addOrderTime); } //获取list里第[1]个数组对象的addOrderTime值 JSONArray list=responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getJSONArray("list"); log.info("list为:"+ list); JSONObject jsonTemp = list.getJSONObject(1); addOrderTime1 = jsonTemp.get("addOrderTime").toString(); log.info("第二种写法,直接写死数组,获取到的addOrderTime1的值为:"+addOrderTime1); } catch (Throwable ex) { log.error("Failed in Beanshell", ex); throw ex; } //获取开始时间和结束时间:这2个是在前面接口提取出来的参数变量,所以直接用${}引用即可 String beginTime = "${addOrderTimeStart}"; String endTime = "${addOrderTimeEnd}"; log.info("筛选条件的开始日期为:"+beginTime+"/"+"筛选条件的结束日期为:" +endTime); //将日期转换成Date类型,并转换成时间戳去比较大小 SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); Date date1 = format.parse(beginTime); Date date2 = format.parse(endTime); Date date3 = format.parse(addOrderTime1); log.info("转换成Date类型后输出的值分别为:"+date1+"/"+date2+"/"+date3); long beginMillisecond = date1.getTime(); long endMillisecond = date2.getTime(); long date3Millisecond = date3.getTime(); log.info("yyyy-MM-dd转换时间戳后的值:"+beginMillisecond+"/"+endMillisecond+"/"+date3Millisecond); //筛选条件的日期是年月日,而返回数据的日期是年月日时分秒,所以这里单独将addOrderTime1的值用yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss转换时间戳 SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date date4 = format.parse(addOrderTime1); long date4Millisecond = date4.getTime(); log.info("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss转换时间戳后的值:"+beginMillisecond+"/"+endMillisecond+"/"+date4Millisecond); //判断下单时间是否在检索条件范围内 if( endMillisecond > date4Millisecond && beginMillisecond < date4Millisecond){ Failure=false; log.info("校验通过啦,beginMillisecond的值为"+beginMillisecond+"/date3Millisecond的值为:"+date3Millisecond+"/endMillisecond的值为:"+endMillisecond); } else{ Failure=true; FailureMessage="不在时间范围内,请检查,beginMillisecond的值为"+beginMillisecond+"/date3Millisecond的值为:"+date3Millisecond+"/endMillisecond的值为:"+endMillisecond; log.info(FailureMessage); }
log.info(),打印日志到控制台里,如下图:

二、第二种Json格式
1、Json响应数据内容如下:
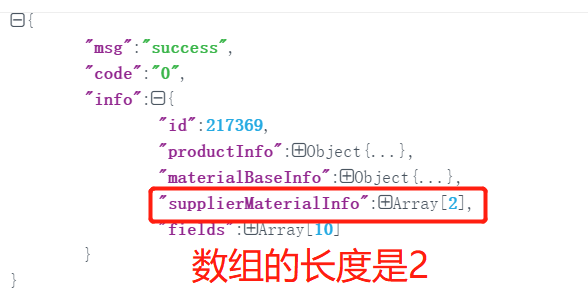
{ "msg":"success", "code":"0", "info":{ "id":217369, "materialBaseInfo":{ "id":235350, "sku":"M007925", }, "supplierMaterialInfo":[ { "id":240717, "supplierId":5658, "supplier":"XX", "supplierCode":"P445" }, { "id":240718, "supplierId":1, "supplier":"XX1", "supplierCode":"P04" } ],
2、按要求进行提取和断言
Case直接在脚本里体现了,Script如下:
import org.json.*; //获取响应结果,并转换为json String response=prev.getResponseDataAsString(); JSONObject responseJson=new JSONObject(response); log.info("转换后的响应结果json:"+ responseJson); //Case1:提取并断言返回的Info{id} int infoid = responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getInt("id"); log.info("info下id的值为"+infoid); if( infoid == ${id}){ Failure=false; log.info("校验通过啦,infoid的值为"+infoid+"/id的值为:"+ ${id}); } else{ Failure=true; FailureMessage="校验不通过呀,infoid的值为"+infoid+"/id的值为:"+ ${id}; log.info(FailureMessage); } //Case2:提取并断言返回的Info{materialBaseInfo{sku}} String materialBaseInfosku = responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getJSONObject("materialBaseInfo").getString("sku"); log.info("materialBaseInfosku的值为"+materialBaseInfosku); String materialSku = vars.get("materialSku"); log.info(materialSku); if( materialBaseInfosku.equals(materialSku)){ Failure=false; log.info("校验通过啦,materialBaseInfosku的值为"+materialBaseInfosku+"/materialSku的值为:"+ materialSku); } else{ Failure=true; FailureMessage="校验不通过呀,materialBaseInfosku的值为"+materialBaseInfosku+"/materialSku的值为:"+ materialSku; log.info(FailureMessage); } //Case3:提取返回的Info{supplierMaterialInfo[{supplierId,supplier}]} JSONArray supplierMaterialInfo = responseJson.getJSONObject("info").getJSONArray("supplierMaterialInfo"); log.info("supplierMaterialInfo数组的值为:"+supplierMaterialInfo); String supplier1 = supplierMaterialInfo.getJSONObject(0).getString("supplier"); log.info("第一种方法拿到supplier的值为"+supplier1); int len =supplierMaterialInfo.length(); log.info("数组的长度为"+len); int i; for(i=0;i<len;++i){ JSONObject jsons= supplierMaterialInfo.getJSONObject(i); supplier = jsons.getString("supplier"); log.info("第二种方法循环拿supplier的值为"+supplier); } for(i=0;i<len;++i){ JSONObject jsons= supplierMaterialInfo.getJSONObject(i); int supplierId = jsons.getInt("supplierId"); log.info("第二种方法循环拿supplierId的值为"+supplierId); }
log.info(),打印日志到控制台里,如下图: