unordered_map,unordered_set等相关内容总结:
unordered_map和unordered_set是在开发过程中常见的stl数据结构。其本质是hashtable。在SGI_STL中,hashtable解决冲突的办法是拉链法。下面是一些对STL中堆hashtable中有关代码阅读的一些记录。
与之相关联的几个文件
第一部分:基本数据组织说明
hashtable的重要数据组织成员及辅助理解图(一个可能的hash数据结构情况)
_Bucket[] _M_buckets
_Hash_node_base _M_before_begin
size_type _M_bucket_count // 初始桶编号为1
size_type _M_element_count

由上图可以大致总结出在SGI-STL中hashtable数据的组织。几个要点:
①.hashtable实际上是维护了一个单链标。其头节点是一个特殊的成员_M_before_begin,其没有实际的数据。按照名字来理解,是第一个数据的前一个节点。
看一下对应的相关注释:
The non-empty buckets contain the node before the first node,this design makes it possible to implement somethiing like a std::forward_list::insert_after on a container insertion and std::forward_list::erase_afer on container erase calls._M_before_begin is equivalent to std::forward_list_list::before_begin.Note that one of the non-empty buckets contains &_M_before_begin which is not a dereferenceable node so the node pointer ina bucket shall never be dereferenced ,only its next node can be.
②._M_buckets这个二级指针的作用是什么,其目的是为了通用的可以使用_M_next()函数调用拿到每个桶的头节点(对于上图就是A,D)。比如_M_buckets[1]._M_next就是桶号为1的头结点A。_M_buckets[2]._M_next就是桶号为2的数据结构的头结点D。同时对于上图示例,应当有_M_before_begin和_M_buckets[1]是相等的(见黑色实线)
第二部分:几个常见接口的调用流程及调用栈
hashtable的定义

一些方便查阅的 using和typedef
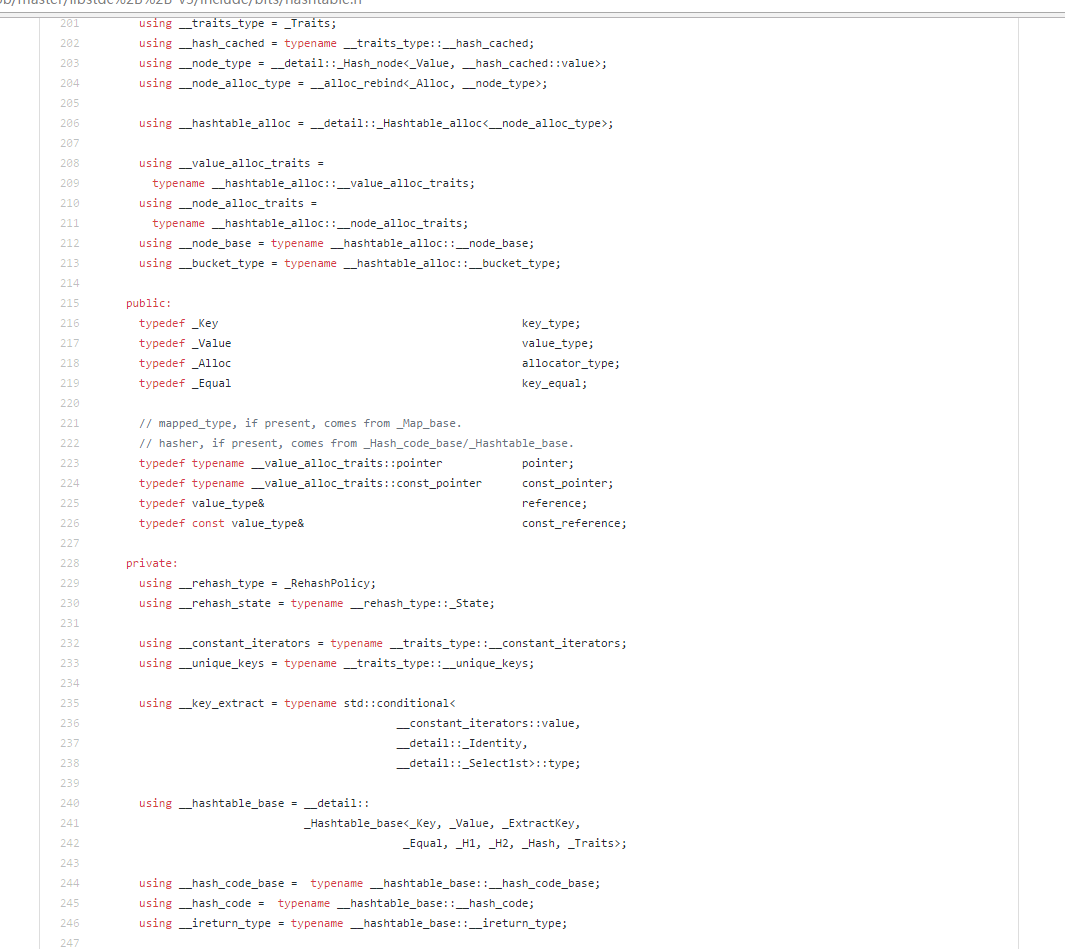

①.插入的key是如何生成的
1.对于简单类型(int等):key计算的相关代码 const key_type& __k = this->_M_extract()(__node->_M_v())
计算key值是通过_M_extrace()来计算的,其是模板参数中的_ExtraceKey,
对于unordered_map在其定义中其模板参数中_ExtraceKey是__detail::Select1st 当定义为unordered_map<int,node>,insert(std::make_pair(0,node(a)); 其就返回pair中的first,即0。
对于如果定义类似于key不是简单类型的。需要自己定义hash函数否则不能通过编译,举例https://www.zhihu.com/question/30921173
struct pairhash {public:
template <typename T, typename U>
std::size_t operator()(const std::pair<T, U> &x) const
{
return std::hash<T>()(x.first) ^ std::hash<U>()(x.second);
}};
class abc {
std::unordered_map<std::pair<int,int>, int, pairhash> rules;
};
在这种情况下。__detail::Select1st获取到的数据就是std::pair<int,int>作为key对应的值
②.hash值如何生成
__hash_code __code = this->_M_hash_code(__key); ======> return _M_h1()(__k); ======> 在key为int的时候传递的参数是std::hash<int>
其最后会调用一个宏_Cxx_hashtable_define_trivial_hash(int),其在文件functional_hash.h中,该文件内涵多种不同类型的特化hash类。该文件定义了这些简单类型是如何hash的,下面是该宏的定义,看到这种情况下,其hash值就是直接强转成size_t类型。

③.如何确定一对pair的hash桶编号 size_type __bkt = _M_bucket_index(__k,__code) ====> return ___hash_code_base::_M_bucket_index(__k,__c,_M_bucket_count); } ====> return _M_h2()(__c,__n);
其中_M_h2获取的是模板参数_H2,对于unordered_map传递进来的是__detail::_Mod_range_hashing,其内容很简单。
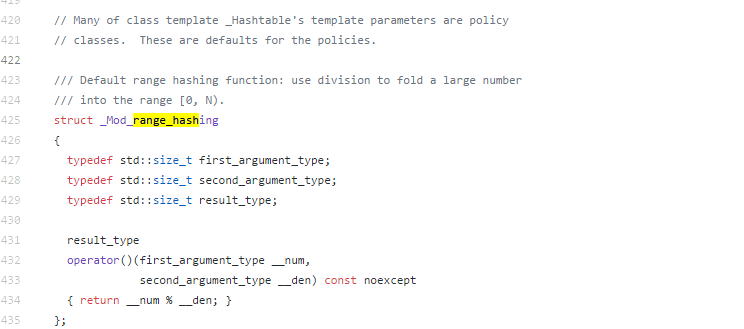
可见桶编号值为hash值mod桶数量
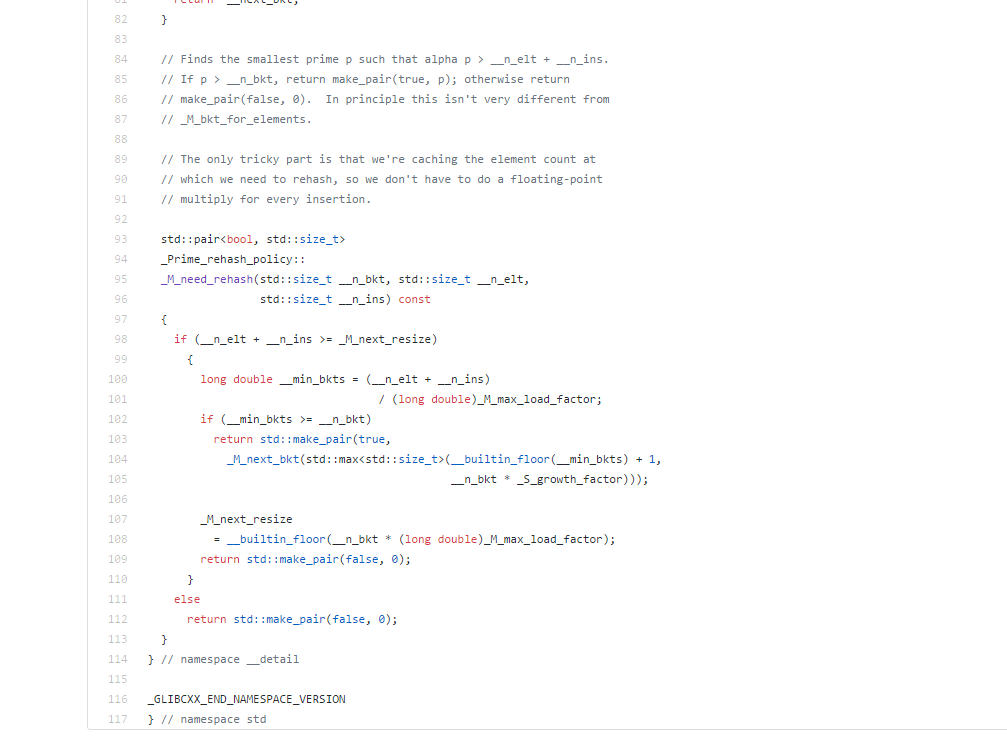
④.rehash流程:主要思路是根据当前桶的数量和元素数量,在一个大的素数表中lowerbound查找下一步合适的桶编号。
下面是一个判定是否需要rehash桶以及如果需要后算出下一个合理的桶数量。至于最终的真正_M_rehash_aux流程。主题是数据指针迁移,并且保证新的new_buckets结构像前图一样。